المضخّات اليدوية هي أجهزة رفعٍ للماء يمكن تشغيلها يدويًا لسحب المياه من مصادر المياه السطحية ومصادر المياه الجوفية والخزانات والمستودعات المائية، أو لضخ المياه في شبكات التوزيع. فهي سهلة التركيب نسبيًا وبسيطة في تشغيلها وقادرة على رفع كميات كافية من الماء لمُجتمع صغير من أعماق تصل إلى 80 مترًا. وتستخدم على نطاق واسع في الأماكن التي يصعب الوصول فيها إلى مصادر الطاقة، أو في الأماكن التي تكون الموارد المالية المتاحة فيها للاستثمار محدودة، أو الأماكن التي لا يوجد فيها احتياجٌ مُفرطٌ للماء المنزلي. هناك الكثير من نماذج الضخ المتوفرة وبتكلفة منخفضة وتناسب معظم الظروف المحلية. ومع ذلك فإن تشغيل وصيانة تلك المضخات يتطلب مشاركة المجتمع المحلي، وخاصة إذا تم استخدام المضخة بشكل كبير.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
المياة العذبة , مياة الشرب |
المياة العذبة , مياة الشرب |
تستخدم أجهزة رفع المياه لسحب المياه من مصادر المياه السطحية ( البحيرات و الأنهار أو الخزانات )، ومصادر المياه الجوفية ( الآبار المحفورة باليد أو الآبار المحفورة آلياً ) خزانات المياه الجوفية، أو لضخ المياه في شبكات التوزيع أو انظمة الري
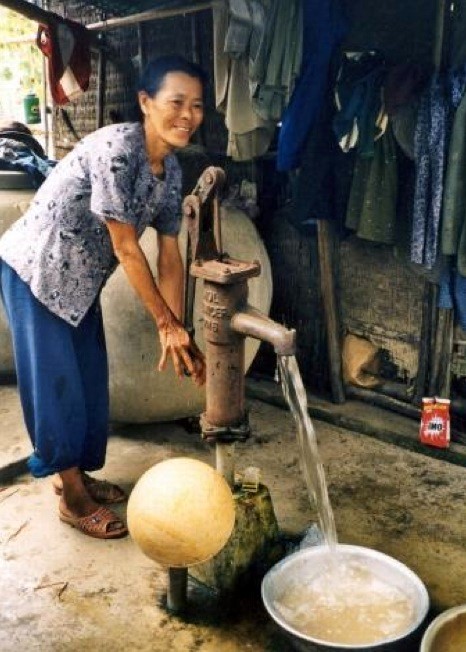
المضخَّات التى تعمل باليد (والتي تُسمَّى أيضًا مضخات يدوية أو مضخات تعمل بالطاقة البشرية) هي من أجهزة رفع المياه التي تقوم بشكل رئيسي بإمداد المياه للمجتمع والتي يمكن تشغيلها يدويًا. تشمل المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية أيضًا مضخاتٍ تعمل بالقدم (HOLDEN & SWANEPOEL 2004)، وانظمة الحبل والدلو مع أو من دون آلة رفعٍ أو شادوف (OLLEY 2008).

مضخة رقم 6 – مضخة شفط الآبارالضحلة. المصدر: بيومان (2011)
المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية قادرة على رفع كميات صغيرة نسبيًا من المياه من أعماق تصل إلى 100 متر، وتستخدم على نطاق واسع في الأماكن التي يكون فيها الوصول إلى مصادر الطاقة محدودٌ، أو في الأماكن التي تكون الموارد المالية المتاحة فيها للاستثمارعليها قيود، أو الأماكن التي لا يوجد فيها احتياج للماء المنزلي بشكل مفرط. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فهي سهلة التركيب نسبيًا وبسيطة إلى حد ما في التشغيل، مما يجعلها واحدة من أكثر تقنيات رفع المياه المستخدمة والواعدة فى الأماكن الريفية في الدول النامية (OLLEY 2008).
المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية لديها القدرة على تحسين المجتمع انظام الإدارة المحلية للمياه ، وبالتالي تحسين سُبُل العيش إلى حدٍّ كبيرٍ. من حيث توفير المياه الصالحة للشرب؛ المضخات اليدوية تعتبرالأسرع والأسهل والأكثر أمانًا بالمقارنة بأجهزة الرفع بالحبل والدلو. من ناحية الري؛ المضخات التي تعمل باليد (أو بالقدم) يُمكنها زيادة المحاصيل الزراعية بنسبة كبيرة كونها غير مُعتمدة على تأجير مضخات ديزل مكلفة وثقيلة، ويمكن للمزارعين الري بحرية واستقللية عندما يصبح الوقت أنسب ما يكون لري المحاصيل. وبذلك يتم تمكين السيدات، والأطفال وصغار المزارعين بشكل متساوٍ ( انظر أيضا قضايا المساواة بين الجنسين ).

مضخة في مدغشقر تعمل بالحبل المصدر: BAUMANN( 2011)
أمَّا على الجانب السلبي، فإنَّ أنظمة المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية فشلت في كثير من الأحيان بسبب عدم وجود مشاركة من المجتمع المحلي وبسبب عدم توافر الصيانة الكافية، وبسبب تركيب المضخات التي كانت لا تصلح للاستخدام الكثيف والمتكرر. الاعتراف الصريح بهذه الحقيقة يؤدي إلى أنظمة ضخ بسيطة ومنخفضة التكلفة (VLOM: المضخات التي يمكن تشغيلها وصيانتها داخل القرية)؛ والتي يمكن تشغيلها وصيانتها من قبل المجتمع المحلي دون مساعدة خارجية، وإلى التوعية بأهمية المشاركة المجتمعية في التخطيط لمشروعات تركيب المضخات منذ البداية وعدم الاسستغناء عن إدارة الصيانة (SKINNER & SHAW n.y.).
إنشاء نظام المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية لإمداد المياه يتطلب تحليلًا شاملاً؛ فعند اختيار نظام الضخ ، ينبغي الأخذ في الاعتبار مجموعةً واسعةً من الخيارات من أجل اختيار الحل الأمثل على المدى الطويل. إستشر OLLEY 2008: المضخات اليدوية لرفع المياه التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية ( PP.1-2 ) للحصول على قائمة كاملة من المعايير والأسئلة الأساسية التي يجب الإجابة عليها قبل اختيار المضخات.
حتى اليوم، يوجد المئات من المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية والتي تم بناؤها على أساس عدة مبادئ ميكانيكية. المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية تبنى على واحدة أو أكثر من هذه المبادئ. (BAUMANN 2000):
الرفع المباشر: يتم رفع المياه فيزيائياً في وعاء. مثلًا استخدام نظام الحبل مع الدلو أو النازح أو نظام العجلة الفارسية الميكانيكي لرفع المياه.
الإزاحة: الماء غير قابل للانضغاط وبالتالي يمكن دفعه أو إزاحته (التقنية الترددية).مثلًا المضخات الكبَّاسة، مضخات ذات الحبل ، والمضخات التدريجية (المتتالية) ذات التجويف، والمضخات الهيدروليكية ذات الحاجز الهوائي.
إيجاد سرعة ضغط : يمكن دفع المياه بسرعة عالية. العزم الناتج يمكن أن يستخدم إمّا لخلق ضغط أو للتدفق (التقنية الدورانية/ الترددية؟). مثال: مضخات ذات عامود دوران حلزوني، مضخات ذات المروحة، مضخات الطرد المركزي، مضخات التحكم في السرعة، والمضخات النفاثة.
وغالبًا تُصنف المضخات التي تعمل باليد إلى مضخات الآبار الضحلة والتي يبلغ عمقها 7 أمتار ومضخات الآبار العميقة التي يزيد عمقها عن 7 أمتار.
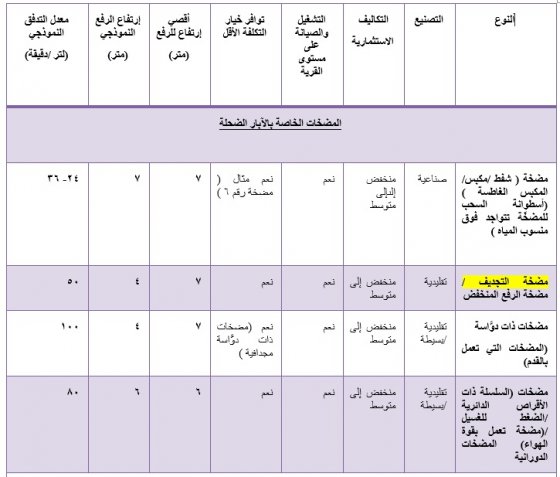
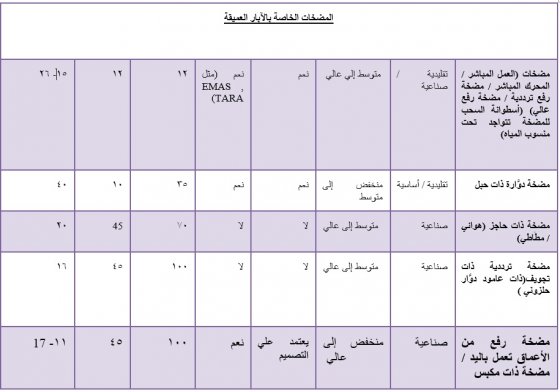
أنظمة ضخ المياة تعمل بالطاقة البشرية لإمداد المجتمع بالماء .(مقتبس بتصرّف من OLLEY (2008))
اعتمادًا على هذه الأنواع من المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية، فإنَّه يوجد العديد من نماذج المضخات المختلفة، ونماذج أخرى متفرعة ومتنوعة ومتاحة، كل منها لديه خصائص مُختلفة ( مثل التكاليف ومتطلبات الصيانة والتشغيل والجوانب الصحية، وما إلى ذلك) وبالتالي تتناسب مع مُختلف الظروف المحلية المُختلفة. للحصول على وصف مفصّل لنماذج المضخّة انظر مونتجور وآخرون(2010). للأغراض الزراعية؛ يوجد العديد من الأشكال الأخرى لأجهزة رفع المياه ( انظر ايضًا: اولاي 2008: أجهزة رفع المياه بالطاقة البشرية والحيوانية للري).
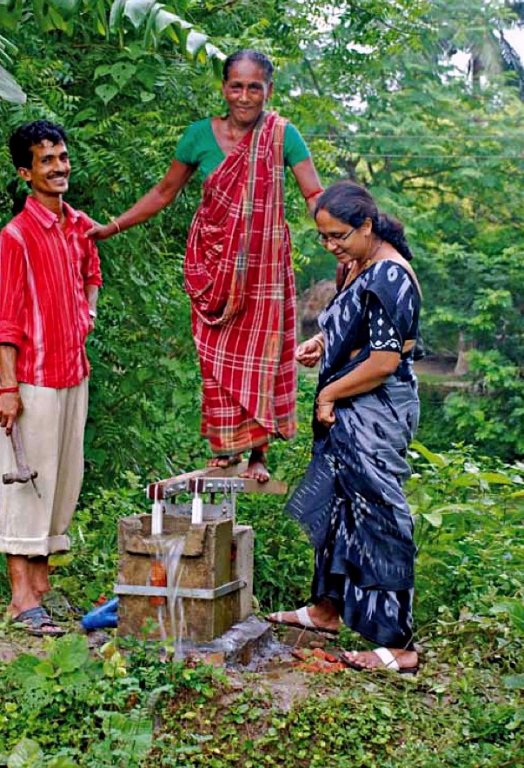

مضخة الدوَّاسة ( المجدافية) (التي تعمل بالقدم)،تعديلٌ على مضخة الدوَّاسة المصدر W3W (2011)
رأس المال للمضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية يرتبط بشكل أساسيّ بشراء وتركيب المضخة وبناء نظام التغطية والتصريف والسياج المحيط بها(HOLDEN & SWANEPOEL 2004). تختلف تكاليف المضخة بشدّة وفقًا لنوع المضخة المختارة من حيث النوع والمواد. بالنسبة لمعظم أنواع المضخات فإنَّ الخيارات ذات التكلفة المنخفضة متوفرة ويمكن الإستفادة من المواد المحلية والجهود المتوفرة . أنظرBAUMANN (2011): المضخات اليدوية منخفضة التكلفة للحصول على وصف مفصَّل لنماذج محدّدة لمضخات منخفضة التكلفة.
تظهر بيانات عدد من أصحاب المصلحة في إفريقيا أنّ العديد من المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية هي في الواقع مُعطَّلة على الرغم من أنها كانت تعتبر قوية وصيانتها بسيطة. وهذا يمثل أزمةَ ضياع الاستثمار في البنية التحتية. الحقيقة المزعجة هى أن البنية التحتية التى تم تركيبها لإمداد المياه فى المناطق الريفية كان من الصعب استمرارها فى العمل بعكس ما كان متوقعًا وبناءً عليه باءت بالفشل بسبب ضعف عملية الصيانة وذلك قبل مرور عمرالتصميم الافتراضي لها. (شبكة إمداد المياه فى المناطق الريفية 2010)
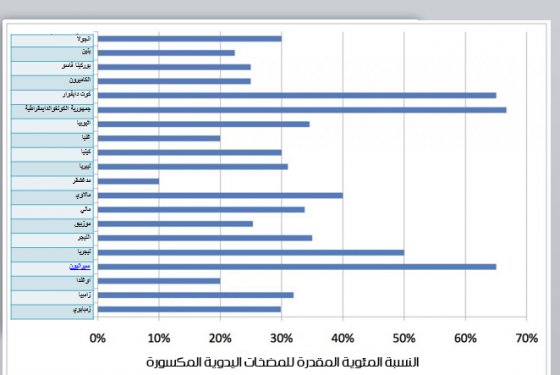
النسبة المئوية التقديرية للمضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية المعطلة (المحطمة) في البلدان الإفريقية. المصدر RWSN (2011)
بناء نقاط جديدة لامدادات المياه بدلاً من صيانة تلك الموجودة حاليًا هو أمر يصعب اعتباره جيداً. إن شبكة إمدادات المياه فى المناطق الريفية تُحارِب من أجل إنشاء أنظمة دعم مؤسساتيّة وآلياتٍ مادية واقعية وطويلة المدى (انظر أيضًا تمويل و بناء النظام المؤسسي )، والتي يمكن أن تؤدي إلى تشغيلٍ وصيانةٍ بقدرٍ كافٍ ولفترة طويلة وبالتالي توفير إمداد للمياه فى المناطق الريفية بشكل مستدام. (RWSN 2010)
ويمكن القول، أنَّه من حيث تحسين نظم إمدادات المياه، فإنَّ الدعم المالي الخارجي ينبغي أن يركز أكثرعلى بناء القدرات بدلًا من توفير المواد والأدوات (المجَّانية). مع الأخذ في الاعتبار أن الأشياء التى تشتريها بنفسك ستقوم برعايتها بشكل أفضل والفكرة هي جعل الناس يدفعون لانشاء أنظمة إمدادات المياه (انظرأيضًا تسعير المياه و بدلًا من التبرع لهم. ومع ذلك، قد يكون الدعم خياراً ضمن السياق إذا تم تنظيم وتنسيق ومراقبة المشروع بصورة جيدة (انظرأيضًا المساهمات الحكومية ). وحيث أن العائلات الفردية في كثير من الأحيان لا تكون قادرة على تحمّل تكاليف بئر ومضخةٍ خاصة بها؛ فإنه من المطلوب توفير شكلٍ من الإدارة المالية:مثل تقاسم التكاليف بين مجموعة من العائلات أو استخدام مدخرات المجتمع المحلي حيث يمكن لكليهما أن يوفّرنظام إمداد مياه مناسباً ويحقِّقَ ترابطاً مجتمعياً جيداً. بدلًا من ذلك، فإنَّ التمويل الصغير قد يكون أيضًا خياراً آخر.
وبشكلٍ مساوٍ؛ فإنّ مشاركة المستخدم أثناء عملية التنفيذ (انظر أيضًا خطة العمل المجتمعية و التشغيل والصيانة أمرٌ مهمٌّ لتمكين المضخات اليدوية من العمل لمدّة طويلة . لتحقيق هذا الهدف فإنه من الممكن اختيار شخص للعناية بهذه المهمة (بشكل مدفوع الأجر) حيث يقوم بتنفيذ المهام الجسدية اللازمة مثل تنظيف المنطقة، وتشحيم الأجزاء المتحركة، وإحكام ربط البراغي والصواميل، ورصد معدل الإنتاج وطلب المساعدة في حالة حدوث مشاكل كبيرة وأيضًا تدريب المستخدمين على كيفية استخدام المضخة بشكل صحيح وأيضا يكون من واجباته الإرشاد العام بالقضايا المتعلقة بالرعاية الصحية (ELSON et al. n.y.).
أما بالنسبة للصيانة المادّية فأنواع المضخات المختلفة تتطلب مستوىً مختلفاً من الاهتمام والانتباه ومهام مختلفةٍ للصيانة (ELSON et al. n.y.). معلوماتٌ مفصلةٌ عن صيانة أنظمة المضخات الأكثر شيوعا موجودةٌ في (BRIKKE & BREDERO 2003..
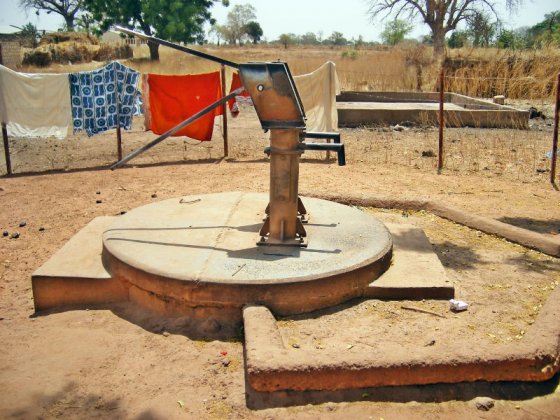

مضخة أعماق ذات مكبس تشمل غطاء ومصرف في ولالان،مقاطعة باديبو، جامبيا المصدر: WATER CHARITY (n.y.)
استخدام مضخة للآبار المحفورة باليد يجلب تحسنًا ملحوظًا في ما يتعلّق invalid link إغلاق فتحة المضخة نفسها بغطاء خراساني مُحكم وتغطية المضخة نفسها يمنع التلوث القادم من السطح بشكل فعّال (أنظر حماية مصدر المياه ومع ذلك، فإنَّ بعض أنواع المضخات (مثل مضخات الحبل) قد تحتاج إلى عنايةٍ خاصة فيما يتعلق بالنظافة حيث أنَّ الحبل يتلامس حتماً بالبيئة الخارجية
تُناسب المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية بشكل كبير المجتمعاتِ الريفية الصغيرة التي تعاني من قلة مصادرالطاقة والموارد المالية وذات الاحتياجات المائية المنخفضة نوعًا ما. العديد من أنواع المضخات المختلفة التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية تم تصنيعها وتطويرها لتتناسب مع العديد من الظروف المحلية. ومع ذلك، فإن جميع المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية، لاسيِّما ذات التكلفة المنخفضة، تتطلب صيانة متكررة بشكل كبير. المجتمع الذي يقوم على نظام المضخة التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية يجب أن يكون قادرًا على إيجاد طريقةٍ لتنظيم عملية التشغيل والصيانة. كما أنّ القبول الثقافي أيضاً قد يكون عائقًا لإقامة نظام يعمل بالمضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية لتوفيرالمياه مثال: ( نظام المضخات التي تعمل بالقدم غير مُتقبَّل ثقافيًا في كل مكان ) (SMET & WIJK 2002).
وأخيرًا فإنَّ المضخات التي تعمل بالطاقة البشرية هي تقنية واعدة جدًا لرفع المياه وقادرةعلى تحسين نظام توفير المياه بصورة كبيرة وبالتالي تحسين معيشة المجتمع المحلي.
Water Lifting
This comprehensive manual presents different pumps and water lifting techniques and elaborates on technology choice and the role of the institutional framework.
BAUMANN, E. (2000): Water Lifting. (= Series of Manuals on Drinking Water Supply , 7 ). St. Gallen: Swiss Centre for Development Cooperation in Technology and Management (SKAT) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFLow-cost Hand Pumps
This guidance note points out the strengths and limitations of a number of low cost pumps. It provides an overview of the application, technical details, materials used, installation and maintenance, manufacturing requirements and costs of several low cost pumps, including information on the numbers installed and locations.
BAUMANN, E. (2011): Low-cost Hand Pumps. St. Gallen: Rural Water Supply Network (RWSN) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFLinking Technology Choice with Operation and Maintenance in the context of community water supply and sanitation. A reference Document for Planners and Project Staff
This document is addressed to planners and staff of water supply and sanitation projects on household and community level. The reader is guided through the main steps of informed choices regarding the main proven technologies for water supply, purification and water treatment at household and community level. Each technology is described in a small factsheet, regarding its functioning, actors and their roles, the main operation and maintenance (O&M) requirements and problems, which can occur.
BRIKKE, F. BREDERO, M. (2003): Linking Technology Choice with Operation and Maintenance in the context of community water supply and sanitation. A reference Document for Planners and Project Staff. Geneva: World Health Organization and IRC Water and Sanitation Centre URL [Accessed: 03.06.2018] PDFIntroductory Guide to Appropriate Solution for Water and Sanitation
WASH Technology Information Packages – for UNICEF WASH Programme and Supply Personnel
The Technology Information Packages (TIPs) provide technology selection guidelines for UNICEF WASH programme officers and partner organisations. They describe various different technologies and suggest how a programme using these technologies could be implemented.
MONTANEGRO, A. BAUMANN, E. SUTTON, S. ERPF, K. (2010): WASH Technology Information Packages – for UNICEF WASH Programme and Supply Personnel. Copenhagen: UNICEF URL [Accessed: 02.04.2012] PDFSmall Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Pumping - Chapter 9
This book provides a general introduction to a wide range of technologies. Among the topics covered are: planning and management of small water supplies, community water supplies in Central and Eastern European countries, water quality and quantity, integrated water resources management, artificial recharge, rainwater harvesting, spring water tapping, groundwater withdrawal, water lifting, surface water intake, water treatment, aeration, coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation, multi-stage filtration, desalination technology, disinfection, household level water treatment, technologies for arsenic and iron removal from ground water, and emergency and disaster water supply. Chapter 9: Pumping
SMET, J. ; WIJK, C. van (2002): Small Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Pumping - Chapter 9. The Hague: International Water and Sanitation Centre (IRC) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFTreadle pumps in India
Deep-well hand piston pump including apron and drain in Wallalan, Upper Badibu District, Gambia
ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.
يهدف هذا الدليل إلى تقديم الإرشاد العملي، لتسهيل تطوير خطة سلامة المياه، مع التركيز على إمدادات المياه المنظمة التي تديرها منشأة مياه أو ما شابه.
منظمة الصحة العالمية,الإتحاد الدولي للمياه (2009): ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Language: Arabic
ﺩﻻﺌل ﺠﻭﺩﺓ ﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺭﺏ.جينيف.سويسرا
إستريجيات الإدارة السليمة لمياه الشرب الصالحة للإستخدام الآدامي
Language: Arabic
ﺗﻨﻤﻴﺔ ﻣﻮﺭﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺠﻮﻓﻴﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺨﺰﺍﻧﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺠﻮﻓﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺜﺎﻧﻮﻳﺔ، ﺇﺳﺘﺮﺍﺗﻴﺠﻴﺔ ﺍﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﻹﻣﺪﺍﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﻟﻠﻘﺮﻯ ﻭﺍﻟﺒﻠﺪﺍﺕ ﺍﻟﺼﻐﻴﺮﺓ.ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻧﺎﻣﺞ المصاحب ﻟﻠﺸﺮﺍﻛﺔ العالمية ﻟﻠﻤﻴﺎﻩ.واشنطن.الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية
Language: Arabic
الري الموضعي .دليل للفلاح .المملكة المغربية، المملكة الإسبانية، منظمة الأمم المتحدة للأغذية والزراعة
Language: Arabic
Community Water Supply. The Handpump Option
This document presents conclusions of five years of work devoted to the assessment of available technology and management options for the wide-scale implementation of community water supply systems.
ARLOSOROFF, S. TSCHANNERL, G. GREY, D. JOURNEY, W. KARP, A. LANGENEFFER, O. ROCHE, R. (1987): Community Water Supply. The Handpump Option. Washington D.C.: THE WORLD BANK URL [Accessed: 02.04.2012]Water Lifting
This comprehensive manual presents different pumps and water lifting techniques and elaborates on technology choice and the role of the institutional framework.
BAUMANN, E. (2000): Water Lifting. (= Series of Manuals on Drinking Water Supply , 7 ). St. Gallen: Swiss Centre for Development Cooperation in Technology and Management (SKAT) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFLow-cost Hand Pumps
This guidance note points out the strengths and limitations of a number of low cost pumps. It provides an overview of the application, technical details, materials used, installation and maintenance, manufacturing requirements and costs of several low cost pumps, including information on the numbers installed and locations.
BAUMANN, E. (2011): Low-cost Hand Pumps. St. Gallen: Rural Water Supply Network (RWSN) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFTechnology Options – Handpumps, Mechanised Pumps and Surface Water
A wide range of different hand pump models is presented. For each model, pictures, schemes and detailed descriptions including information on materials, manufacturing, maintenance and technical performance is provided.
BAUMANN, E. ERPF, K. (2005): Technology Options – Handpumps, Mechanised Pumps and Surface Water. St. Gallen: Rural Water Supply Network (RWSN) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFLinking Technology Choice with Operation and Maintenance in the context of community water supply and sanitation. A reference Document for Planners and Project Staff
This document is addressed to planners and staff of water supply and sanitation projects on household and community level. The reader is guided through the main steps of informed choices regarding the main proven technologies for water supply, purification and water treatment at household and community level. Each technology is described in a small factsheet, regarding its functioning, actors and their roles, the main operation and maintenance (O&M) requirements and problems, which can occur.
BRIKKE, F. BREDERO, M. (2003): Linking Technology Choice with Operation and Maintenance in the context of community water supply and sanitation. A reference Document for Planners and Project Staff. Geneva: World Health Organization and IRC Water and Sanitation Centre URL [Accessed: 03.06.2018] PDFZambia - National Guidelines for Sustainable Operation and Maintenance of Hand Pumps in Rural Areas
The Ministry of Local Government and Housing, in consultation and collaboration with key stakeholders, has formulated National Guidelines to improve the utilisation of water resources on a sustainable basis through effective O&M. These guidelines are based on the experiences of implementation of rural water supply projects in Zambia.
MLGH (2007): Zambia - National Guidelines for Sustainable Operation and Maintenance of Hand Pumps in Rural Areas. Zambia: Ministry of Local Government and Housing (MLGH) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFWASH Technology Information Packages – for UNICEF WASH Programme and Supply Personnel
The Technology Information Packages (TIPs) provide technology selection guidelines for UNICEF WASH programme officers and partner organisations. They describe various different technologies and suggest how a programme using these technologies could be implemented.
MONTANEGRO, A. BAUMANN, E. SUTTON, S. ERPF, K. (2010): WASH Technology Information Packages – for UNICEF WASH Programme and Supply Personnel. Copenhagen: UNICEF URL [Accessed: 02.04.2012] PDFSmart Water Solutions. Examples of Innovative, Low-cost Technologies for Wells, Pumps, Storage, Irrigation and Water Treatment
This booklet on water technologies gives examples of innovations such as the use of sunlight to purify water, effective low-cost water filters, low-cost drip irrigation and locally produced hand pumps that are five times cheaper than imported pumps.
NWP (2006): Smart Water Solutions. Examples of Innovative, Low-cost Technologies for Wells, Pumps, Storage, Irrigation and Water Treatment. The Hague: Netherlands Water Partnership (NWP) URL [Accessed: 02.04.2012] PDFSmall Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Technologies for Arsenic Removal - Chapter 23
This book provides a general introduction to a wide range of technologies. Among the topics covered are: planning and management of small water supplies, community water supplies in Central and Eastern European countries, water quality and quantity, integrated water resources management, artificial recharge, rainwater harvesting, spring water tapping, groundwater withdrawal, water lifting, surface water intake, water treatment, aeration, coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation, multi-stage filtration, desalination technology, disinfection, household level water treatment, technologies for arsenic and iron removal from ground water, and emergency and disaster water supply. Chapter 23: Technologies for Arsenic Removal
SMET, J. ; WIJK, C. van (2002): Small Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Technologies for Arsenic Removal - Chapter 23. The Hague: International Water and Sanitation Centre (IRC) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFSmall Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Pumping - Chapter 9
This book provides a general introduction to a wide range of technologies. Among the topics covered are: planning and management of small water supplies, community water supplies in Central and Eastern European countries, water quality and quantity, integrated water resources management, artificial recharge, rainwater harvesting, spring water tapping, groundwater withdrawal, water lifting, surface water intake, water treatment, aeration, coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation, multi-stage filtration, desalination technology, disinfection, household level water treatment, technologies for arsenic and iron removal from ground water, and emergency and disaster water supply. Chapter 9: Pumping
SMET, J. ; WIJK, C. van (2002): Small Community Water Supplies: Technology, People and Partnership: Pumping - Chapter 9. The Hague: International Water and Sanitation Centre (IRC) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFTools for Assessing the O&M Status of Water Supply and Sanitation in Developing Countries
Problems with the operation and maintenance of water supply and sanitation have long been recognised as key constraints to the sustainability of these services. In order to address these problems in both urban and rural areas of developing countries, this document proposes a framework for management and tools for assessing the status of operation and maintenance (O&M) through measurement and evaluation of performance.
WHO (2000): Tools for Assessing the O&M Status of Water Supply and Sanitation in Developing Countries. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 02.04.2012] PDFSocial adoption of groundwater pumping technology and the development of groundwater cultures. Governance at the point of abstraction
This thematic paper examines the historic and ongoing development of water lifting technologies and the governance problems and solutions that have arisen from controlled or uncontrolled groundwater abstraction. It also examines legislation to improved pump efficiency and the economics and life cycle costing of borehole pumps.
FAO GEF IAH IHP World Bank (2012): Social adoption of groundwater pumping technology and the development of groundwater cultures. Governance at the point of abstraction. FAO URL [Accessed: 08.04.2013] PDFSurvey on social economic and agronomic impact of the installation of the Swiss Concrete Pedal Pump in Tanzania. Report
To measure the impact of the pedal pump on the farmers’ life in Tanzania, a survey has been carried out in Magoma, a village of Korogwe District, where the pumps have been implanted by the Swiss-based NGO W3W.
FALCOZ, C. SEUROT, E. (2009): Survey on social economic and agronomic impact of the installation of the Swiss Concrete Pedal Pump in Tanzania. Report. Morogoro: : ENSAIA, Engineering Schoof of Agronomy, Nancy PDFImpact of Treadle Pump Irrigation Technology on Smallholder Poverty and Food Security in Malawi. A Case Study of Blantyre and Mchinji Districts
This case study analyses the impact of the treadle pump on smallholder poverty and food security in Malawi.
MANGISONI, J.H. (2006): Impact of Treadle Pump Irrigation Technology on Smallholder Poverty and Food Security in Malawi. A Case Study of Blantyre and Mchinji Districts. Lilongwe: University of Malawi URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFInterAide Support to Operation and Maintenance of Rural Water Supplies in Malawi in 2008
InterAide started a new O&M project in 2008 in three different districts located in the central region of Malawi. This report provides a description of the project, including the financial and human resource inputs.
SAINT MELOIR, B. de (2009): InterAide Support to Operation and Maintenance of Rural Water Supplies in Malawi in 2008. St. Gallen: Rural Water Supply Network (RWSN) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFLow-cost Pump Alternatives for Rural Communities in Honduras
This report presents advantages and limitations of two types of low-cost pumps - the EMAS Flexi and the Rope Pump - used in several rural communities in Honduras, considering the users’ perspectives
WSP (2004): Low-cost Pump Alternatives for Rural Communities in Honduras. Meeting Demand for Access to Safe Drinking Water. Lima: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP). URL [Accessed: 02.04.2012] PDFThe Rope Pump Concept
This document contains a general guide for local Rope Pump manufacture. It addresses readers interested in this appropriate technology for water lifting that consider introducing the Rope Pump locally. Only generic features of the Rope Pump Concept are explained and hints for successful pump production are given.
ERPF, K. (2005): The Rope Pump Concept. St. Gallen: Rural Water Supply Network (RWSN) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFSealing a borehole with a sanitary seal
This poster is part of the series of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene posters designed by the Water, Engineering and Development Center of Loughborough University.
SKINNER, B.H. CHATTERTON, K. SHAW, R. (2013): Sealing a borehole with a sanitary seal . Poster. (= WEDC Posters , 5 ). London: Water, Engineering and Development Center (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 28.08.2013] PDFDrainage from Water Points
This poster is part of the series of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene posters designed by the Water, Engineering and Development Center of Loughborough University.
SKINNER, B.H. CHATTERTON, K. SHAW, R. (2013): Drainage from Water Points. Poster. (= WEDC Posters , 7 ). London: Water, Engineering and Development Center (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 28.08.2013] PDFA Water Handbook
The Water Handbook is the result of wide collaboration within UNICEF. It provides a broad overview of state-of-the-art programming for water management, protection and supply.
UNICEF (1999): A Water Handbook. (= Water, Environment and Sanitation Technical Guidelines , 2 ). New York: United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) URL [Accessed: 08.03.2019] PDFHandpump Technologies
The Rural Water Supply Network is a global knowledge network for rural water supply technologies and approaches. The website provides many excellent publications on various topics on rural development, particularly on hand pumping technologies. This section presents an overview of the different manual pumps for drinking water.
Water lifting devices
The Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO) compiled a very comprehensive publication on water-lifting devices. Its purpose is to provide a basis for comparing and choosing between all present options for lifting irrigation water on small and medium sized land-holdings.
Summary of EMAS technologies
EMAS is a Mobile School for Water and Sanitation based in Bolivia, and run by Wolfgang Eloy Buchner. Many videos are provided showing in detail how EMAS pumps can be constructed.
Constructing a Water Well Hand Pump
Agua: yaku presents a simple and inexpensive method for constructing a hand pump.
Rope Pump Part 2
In this video, the principle of the rope pump is explained illustratively. Also, it elaborates on the reason why organisations make villagers pay for pumps instead of donating them.
IDEI, India, Low-cost treadle pumps for irrigation - Ashden Award winner
Low-cost treadle pumps for irrigation can improve the livelihood of communities significantly. This video introduces a project, which promotes the installation and use of treadle pumps in Uttar Pradesh, India.