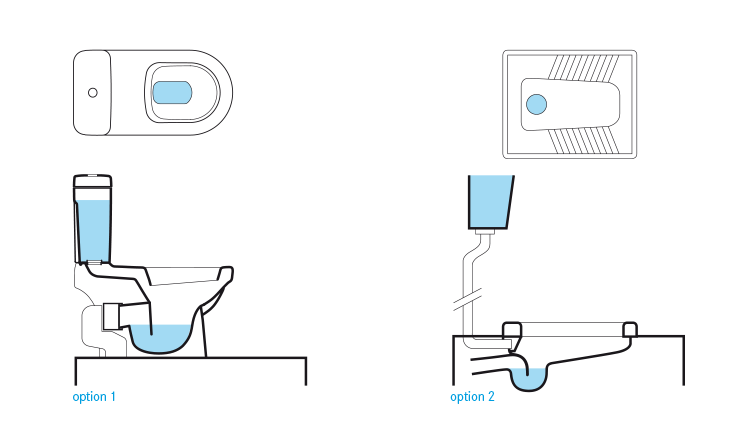
يُصنع مِرحاض الدفْق بالسيفون Cistern Flush Toilet عادةً من الخزف، وهو واجهة مُستخدم تُصنع بكميات كبيرة بواسطة المصانع، ويتكوّن مِرحاض الدفْق من: خزان للمياه (سيفون، أو صندوق طرد) إذ يوفر مياه الشطف لتنظيف المِرحاض، وفتحة سفلية تُودع بها فضلات الجسم.
يتميز مِرحاض الدفْق بالسيفون بدمجه للحاجز المائي Water Seal (أو كوع الرائحة) ؛ لمنع الروائح من الارتداد مرة أخرى من خلال أنابيب السباكة. أما المياه المُخزَّنة في السيفون Cistern الموجود أعلى فتحة المِرحاض فيتم إطلاقها عن طريق سحب أو دفع المقبض. وهذا يسمح للماء بالجريان إلى فتحة المِرحاض والاختلاط بفضلات الجسم وحملها للتخلص منها.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
البراز، البول، مياه تنظيف المرحاض، (مياه تنظيف الشرج)، (مواد التطهير الجافة) |
المياه السوداء |
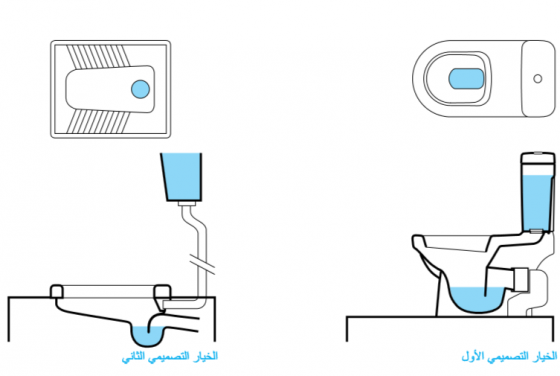
لا يجب التفكير في مِرحاض الدفْق إلا إذا توفرت محليًّا كل الوصلات واللوازم والملحقات والأدوات الخاصة. ويجب أن يتصل مِرحاض الدفْق بمصدر دائم للمياه من أجل الدفْق، كما يجب أن يتصل أيضًا بإحدى تقنيات الجمع والتخزين/المُعالجة أو النقل وذلك لاستقبال المياه السوداء. ويناسب مِرحاض الدفْق الاستخدامات الخاصة والعامة على حد سواء.
تُستخدم المراحيض الحديثة من 6 إلى 9 لترات من المياه للدفْق بينما صُمِمَت النماذج القديمة لاستخدام كميات أكبر من مياه الدفْق تصل إلى 20 لترًا. تتوفر حاليًا أنواع مختلفة من مراحيض الدفْق التي تستخدم كميات أقل من 3 لترات من المياه للدفْق. وفي بعض الحالات نجد أن كمية المياه المُستخدمة للدفْق لا تكفي لإفراغ فتحة المِرحاض، وبالتالي علَى المُستخدم أن يسحب السيفون مرتين أو أكثر لتنظيف فتحة المِرحاض جيدًا، مما يناقض الغرض الأساسي وهو ترشيد استهلاك المياه.
يتطلب تركيب مِرحاض الدفْق سبّاكًا ذو خبرة، وعليه التأكد من أن كل الصمامات متصلة بشكل صحيح، ومحكمة الإغلاق كما ينبغي، وبالتالي سيُضمن الحد من التسرب.
مِرحاض آمن ومريح في الاستخدام بشرط الحفاظ على نظافته.
على الرغم من أن مياه الدفْق تشطف فتحة المِرحاض باستمرار إلا أنه ينبغى أن يتم غسل المِرحاض للتنظيف، وأن يحدث ذلك بانتظام للحفاظ على النظافة الصحية، ولمنع تراكم الأوساخ. كما تُعتبر الصيانة مطلوبة لاستبدال أو إصلاح بعض الأجزاء الميكانيكية أو الوصلات، ويجب أن تُجمع المُنتجات التي تُستخدم للنظافة أثناء الطمث في صندوق منفصل.
الصرف الصحي الموقعي والمركزي - للمدن والتجمعات السكانية الصغيرة
بناء الحمامات وطرق تحسينها وصيانتها
Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation systems in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes . (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 4 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC)Assembling and Installing a New Toilet
Describes how to install a toilet with full color photos and step-by-step instructions.
MAKI, B. (2005): Assembling and Installing a New Toilet. Hammerzone.com URL [Accessed: 25.08.2014]The Flush Toilet is Ecologically Mindless
Critical article by environmental activist and Stockholm Water Price Laureate Sunita Narain, on why it is mindless to waste so much clean water to flush away excreta.
NARAIN, S. (2002): The Flush Toilet is Ecologically Mindless. المُدخلات: Down to Earth: Volume 19 URL [Accessed: 12.05.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFCompendium of Technologies
Toilets: Installation and Repair
Describes each part of the toilet in detail and provides links to other tools, such as how to install a toilet, how to fix a leaking toilet and other toilet essentials.
VANDERVORT, D. (2007): Toilets: Installation and Repair. HomeTips.com URL [Accessed: 25.08.2014]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFSick Water? The central role of wastewater management in sustainable development
This book not only identifies the threats to human and ecological health that water pollution has and highlights the consequences of inaction, but also presents opportunities, where appropriate policy and management responses over the short and longer term can trigger employment, support livelihoods, boost public and ecosystem health and contribute to more intelligent water management.
CORCORAN, E. ; NELLEMANN, C. ; BAKER, E. ; BOS, R. ; OSBORN, D. ; SAVELLI, H. (2010): Sick Water? The central role of wastewater management in sustainable development. A Rapid Response Assessment. United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), UN-HABITAT, GRID-Arendal URL [Accessed: 05.05.2010] PDFSanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation systems in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Lecture Notes . (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 4 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC)Closing the loop – Ecological Sanitation for food security
This document was compiled during an international, interdisciplinary workshop in Mexico. This manuscript increases the understanding of how to develop more sustainable sanitation systems, particularly in urban/peri-urban contexts, while contributing to food production and improved nutrition.
ESREY, S.A. ANDERSSON, I. HILLERS, A. SAWYER, R. (2001): Closing the loop – Ecological Sanitation for food security. Stockholm: Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency URL [Accessed: 24.11.2010]The Flush Toilet is Ecologically Mindless
Critical article by environmental activist and Stockholm Water Price Laureate Sunita Narain, on why it is mindless to waste so much clean water to flush away excreta.
NARAIN, S. (2002): The Flush Toilet is Ecologically Mindless. المُدخلات: Down to Earth: Volume 19 URL [Accessed: 12.05.2019]Ecological Sanitation A Way to Solve Global Sanitation Problems
The paper presents an introduction to ecological sanitation (ecosan) principles and concepts including re-use aspects (available nutrients and occurring risks), and case studies of ecosan concepts in both industrialised and developing countries.
LANGERGRABER, G. MUELLEGGER, E. (2004): Ecological Sanitation A Way to Solve Global Sanitation Problems. Vienna: University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences URL [Accessed: 14.03.2011]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFA Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for Small Island Developing States (SIDS) in the Pacific Region
This directory is part of UNEP collaboration with SIDS on the implementation of the Waste Management chapter of the Barbados Programme of Action. It focuses primarily on proven sound environmental technologies for solid, liquid and hazardous waste management plus those currently successfully being used in SIDS within the Pacific Region.
UNEP (2002): A Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for Small Island Developing States (SIDS) in the Pacific Region. The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) URL [Accessed: 28.03.2012]Construction of Ecological Sanitation Latrine
This document sets out the principles for adopting an ecological sanitation approach, as well as providing guidance on the construction ecological sanitation latrines and their operation. It is intended to support sanitation field practitioners and WaterAid in Nepal ’s partners in the delivery of appropriate services and technologies to fit the needs of different users. .It is also equally hoped that this document will be of value to other organisations and sector stakeholders involved in sanitation promotion and ecological sanitation.
WATER AID (2011): Construction of Ecological Sanitation Latrine. Kathmandu: Water Aid URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation
The purpose of this guide is to assist local contracting authorities and their partners in identifying those sanitation technologies best suited to the different contexts that exist within their town. The first part of the guide contains a planning process and a set of criteria to be completed; these assist you in characterizing each area of intervention so that you are then in a position to identify the most appropriate technical solutions. The second part of the guide consists of technical factsheets which give a practical overview of the technical and economic characteristics, the operating principle and the pros and cons of the 29 sanitation technology options most commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa.
MONVOIS, J. GABERT, J. FRENOUX, C. GUILLAUME, M. (2010): How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 4 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]How to Manage Public Toilets and Showers
The purpose of this decision-making aid is to provide practical advice and recommendations for managing toilet blocks situated in public places. It is primarily aimed at local decision-makers in developing countries and at their partners (project planners and managers).
TOUBKISS, J. (2010): How to Manage Public Toilets and Showers. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 5 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Mix or NoMix - A Closer Look at Urine Source Separation
Beside the headarticle about 'Novaquatis', an inter- and transdisciplinary Eawag project, investigated urine source separation and treatment as an option for modern wastewater management, there are more article about urine sepeartion and its development.
EAWAG (2007): Mix or NoMix - A Closer Look at Urine Source Separation. (= Eawag News , 63 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) URL [Accessed: 06.02.2012]Novaquatis final report. NoMix – A new approach to urban water management
From 2000 to 2006, the cross-cutting project Novaquatis explored the potential of urine source separation – also known as NoMix technology. Novaquatis comprises nine work packages, largely organized around the various stages of a nutrient cycle (e.g. user acceptation, sanitary technologies, storage and transport, urine treatment and fertiliser production, micropollutants in urine, urine-based fertilisers). The final report contains the results of all working packages as well as a practical guide for interested NoMix user.
LARSEN, T. A. LIENERT, J. (2007): Novaquatis final report. NoMix – A new approach to urban water management. Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute for Environmental Science (EAWAG) URL [Accessed: 12.05.2019]Available Sanitation Technologies for Rural and Peri-Urban Africa
The presentation allows for a good overview on existing types of pit latrines in Africa, but also on other types of sanitation technologies such as the conventional flush toilet, the pour flush toilet, and the urine diversion dehydration toilet (UDDT).
MORGAN, P. (2007): Available Sanitation Technologies for Rural and Peri-Urban Africa. Stockholm : Ecological Sanitation Research (EcoSanRes), Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) URL [Accessed: 20.06.2013]http://www.hammerzone.com/
This page describes how to install a toilet with full colour photos and step-by-step instructions.
http://www.hometips.com/
This page describes each part of the toilet in detail and provides links to other tools, such as how to install a toilet, how to fix a leaking toilet and other toilet essentials.
A Better Toilet For A Cleaner World
The sanitation technology paradigm is under review, as past approaches are not sufficient or affordable to close the sanitation coverage gap. In 2011, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) launched the bold Reinvent the Toilet Challenge (RTTC) program to promote the development of radically new innovations to address the sanitation challenge on a large-scale. The RTTC is premised on the fact that ground-breaking improvements are required in toilet design and fecal sludge management to close the urban sanitation gap. The RTTC is focused on reinventing the flush toilet, a break-through public health invention that has not changed substantially since the first flush toilet patent was issued in 1775.

