بِرَك تثبيت المُخلّفات السائلة (الأكسدة) Waste Stabilization Ponds هي مُسطّحات مائية كبيرة من صُنع الإنسان. يُمكن استخدام البِرَكبشكل مُنفرد، أو تكون مُتصلة على هيئة سلسلة لتحسين عملية المُعالجة. هُناك ثلاثة أنواع من البِرَك: (1) البِرَك اللاهوائية Anaerobic، (2) بِرَك الأكسدة الاختيارية (الهوائية - اللاهوائية) Facultative (3) البِرَك الهوائية (الإنضاج Maturation)، ولكُل منها خصائص مُختلفة مُتعلّقة بالتصميم والمُعالجة.
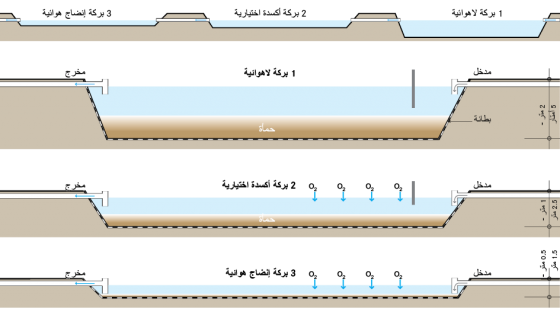
لمُعالجة أكثر فعالية، فإنَّ بِرَك تثبيت المُخلّفات السائلة (الأكسدة) يجب أن تكون مُتّصلة في سلسلة من ثلاث بِرَك أوأكثر، حيث تتدفق المياه من البركة اللاهوائية إلى بركة المُعالجة الاختيارية، وفي النهاية إلى البركة الهوائية. البركة اللاهوائية هي مرحلة المُعالجة الابتدائية والتي تُقلل الحِمل العضوي في مياة الصرف، والعُمق بكامله لهذه البركة العميقة -إلى حد ما- يكون لا هوائيًّا؛ وتحدث إزالة المواد الصلبة والاحتياج الحيوي للأكسجين BOD بواسطة الترسيب ومن خلال عملية الهضم اللاهوائي داخل الحمأة؛ البكتيريا اللاهوائية تُحوِّل الكربون العضوي إلى غاز الميثان، ومن خلال هذه العملية يتم إزالة ما يصل إلى 60% من الاحتياج الحيوي للأكسجين BOD.
في سلسلة بِرَك تثبيت المُخلّفات السائلة (الأكسدة) المُتتابعة، فإنَّ التدفقات السائلة الخارجة من البِركة اللاهوائية تنتقل إلى بركة المُعالجة الاختيارية (الهوائية - اللاهوائية)، حيث يتم إزالة المزيد من الاحتياج الحيوي للأكسجين BOD. تستقبل الطبقة العليا من البِركة الأكسجين من: الانتشار الطبيعي للهواء، واختلاط الرياح مع المياه، وناتج التمثيل الضوئي للطحالب. والطبقة السفلية تكون محرومة من الأكسحين وبالتالي تصبح لاأكسجينية أو لاهوائية. وتتراكم المواد الصلبة القابلة للترسيب في القاع؛ حيث يتم هضمها. والكائنات الحية الهوائية واللاهوائية تعمل معًا لتحقيق انخفاض في نسب الاحتياج الحيوي للأكسجين BOD قد يصل إلى 75%.
البرك اللاهوائية وبرك المُعالجة الاختيارية مُصمّمة لإزالة الاحتياج الحيوي للأكسجين BOD، في حين أنَّ البِرَك الهوائية مُصمَّمة لإزالة مُسببات الأمراض. والبركة الهوائية عادةً ما يُشار إليها ببركة الإنضاج، أو البركة النهائية لأنَّها عادةً ما تكون الخطوة النهائية في سلسلة من برك المُعالجة وتحقق المُستوى النهائي من المُعالجة، وهي ليست عميقة؛ لتضمن اختراق ضوء الشمس لكامل العُمق من أجل حدوث عملية التمثيل الضوئي. والتمثيل الضَوئي للطحالب يُطلق الأُكسجين إلى الماء وأيضًا في نفس الوقت يستهلك ثاني أُكسيد الكربون الناتج عن عملية تنفس البكتريا. ولأنَّ التمثيل الضوئي يعتمد على ضوء الشمس، فإنَّ مُستويات الأُكسجين الذائب تكون أعلى أثناء النهار وتقل في الليل. و يزيد الأُكسجين الذائب أيضًا بواسطة اختلاط الرياح الطبيعي مع المياه
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
المياة السوداء , المياة البنية , المياة الرمادية , الحمأة |
التدفقات السائلة الخارجة , الحمأة |
بِرَك تثبيت المخلفات تقع ضمن الطرق الأكثر شيوعًا وفعَاليةً في مُعالجة مياه الصرف حول العالم. وهي مُناسبة خصيصًا للمُجتمعات الريفية وشبه الحضرية، التي لديها مساحات أرض كبيرة غير مُستخدمة، وتكون على مسافة بعيدة من المنازل والأماكن العامة. إلا أنها غير مناسبة للأماكن شديدة الكثافة السكانية أو المناطق الحضرية.
البِرَك اللاهوائية يتم إنشاؤها لعمق يتراوح من 2 إلى 5 أمتار، ولها مُدة احتجاز قصيرة نسبيًّا تتراوح ما بين يوم واحد إلى سبعة أيَّام. وبِرَك المُعالجة الاختيارية يجب أن تَكون مبنية لأعماق تتراوح بين 1 إلى 2.5 متر ولها مُدَّة احتجاز ما بين 5 إلى 30 يومًا. البِرَك الهوائية عادةً ما تتراوح ما بين 0.5 إلى 1.5 متر في العمق، وإذا استخدمت مدمجةً مع بِرَك الطحالب و/أو تربية الأسماك ، فهذا النوع من البِرَك يكون فعَّالًا في إزالة معظم النتيروجين والفوسفور من التدفقات السائلة الخارجة. من الناحية المثالية، فإنَّ العديد من البِرَك الهوائية يُمكن إنشاؤها على التوالي لِتُقدّمَ مُستوًى عالٍ من إزالة مُسببات الأمراض.
المُعالجة الأولية تُعتبر أمرًا ضروريًّا لمنع تكوُّن الخبث الطافي)الزَبَد( فوق البرك، ولمنع دخول المزيد من المواد الصلبة والقمامة إلى البِرَك. ويجب تبطين البِرَك؛ لمنع رشح وتسرب المياه الموجودة في البِركة إلى المياه الجوفية عبر طبقات الأرض. ويُمكن عمل البطانة الخاصة بالبِركة من الطين، أو الأسفلت، أو التربة المدكوكة، أو أي مادة غير مُنفذة للسوائل. لحماية البِركة من الجريان السطحي والانجراف؛ فإنَّه يجب بناء حاجز واقٍ حول البِركة باستخدام المواد الناتجة عن عمليات الحفر. كما يجب بناء الحاجز لضمان إبقاء الناس والحيوانات بعيدًا عن المنطقة، ولحماية البِرَك من إلقاء القمامة والمُلوثات فيها.
على الرغم من أن التدفقات السائلة الخارجة من البِرَك الهوائية تحتوي عامة على نسبة قليلة من ُمسببات الأمراض، فإنَّه لا ينبغي بأي حال من الأحوال أن تُستخدم هذه البِرَك للاستجمام )الاستخدامات الترفيهية( أو كمصدر ماء مباشر للاستهلاك أو الاستخدام المنزلي.
يجب إزالة الخبث )الزَبَد( الذي يتراكم على سطح البِركة بانتظام. كما يجب أيضًا إزالة النباتات المائية )ذات الأوراق الكبيرة( الموجودة في البِركة، حيث إنها من الممكن أن تقدم للبعوض بيئةً مُناسبة للتكاثر، كما أنها تمنع الضوء من اختراق الماء.
المياه ،الصرف الصحي النظافة الصحية وظروف الإقامة في السجون
ارشادات فى تصميم وتشغيل وصيانة محطات معالجة المياة العادمة
المعالجة البيولوجية لمياه الصرف الصحى المبادئ وأعمال النمذجة والتصميم
Language: Arabic
التلوث : المخاطر والحلول
برك تثبيت المخلفات السائلة
Notes in the Design and Operation of Waste Stabilization Ponds in Warm Climates of Developing Countries
Anaerobic, facultative and maturation ponds as wells as aerated lagoon systems are presented as an appropriate solution in developing countries where sewerage systems are present. The technical content was reviewed by Prof. Duncan Mara (University of Leeds, England). Detailed design, operation and maintenance guidance is given. Hence, this paper can be useful as a technical manual.
ARTHUR, J.P. (1983): Notes in the Design and Operation of Waste Stabilization Ponds in Warm Climates of Developing Countries . (= World Bank Technical Paper , 7 ). Washington: The World Bank URL [Accessed: 08.05.2018] PDFGuidance Manual on Water Supply and Sanitation Programmes
This manual has been prepared as a tool to help improve DFID's (Department for International Developments, United Kingdom) support for water supply and sanitation projects and programmes in developing countries. Its particular focus is on how DFID assistance can best meet the needs of the urban and rural poor for water supply and sanitation services.
DFID (1998): Guidance Manual on Water Supply and Sanitation Programmes. London: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) for the Department for International Development (DFID) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2018]Corinna, Main - Corinna Sewer District
Advanced Integrated Wastewater Pond Systems
Waste Stabilization Pond Systems are summarized and Advanced Integrated Wastewater Pond Systems (AIWPS) are investigated. Detailed study about each treatment units and reaction mechanisms are studied. Fecal coliform bacteria removal mechanisms, the effect of parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, organic loading, solar radiation on removal efficiency is investigated. Some of AIWPS applications are given, emphasizing removal efficiencies in every unit. Based on operational simplicity, low cost and high removal efficiencies (99% BOD5, suspended solids and coliform bacteria removal), AIWPS is highly recommended for up to 1000 mg/L BOD5 concentration. Because of its high coliform bacteria removal efficiency, the effluent of AIWPS may be used for irrigation purposes.
ERTAS, T. PONCE, V.M. (2005): Advanced Integrated Wastewater Pond Systems. San Diego: San Diego State University (SDSU) URL [Accessed: 07.02.2012]Waste Stabilization Ponds and Constructed Wetlands Design Manual
Design Manual for Waste Stabilization Ponds in Mediterranean Countries
Waste Stabilization Ponds: A Design Manual for Eastern Africa.
Greywater Management in Low and Middle-Income Countries, Review of Different Treatment Systems for Households or Neighbourhoods
This report compiles international experience in greywater management on household and neighbourhood level in low and middle-income countries. The documented systems, which vary significantly in terms of complexity, performance and costs, range from simple systems for single-house applications (e.g. local infiltration or garden irrigation) to rather complex treatment trains for neighbourhoods (e.g. series of vertical and horizontal-flow planted soil filters).
MOREL, A. DIENER, S. (2006): Greywater Management in Low and Middle-Income Countries, Review of Different Treatment Systems for Households or Neighbourhoods. (= SANDEC Report No. 14/06 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 27.05.2019]Pond Treatment Technology
Waste Stabilisation Ponds
Waste Stabilisation Ponds is the third volume in the series Biological Wastewater Treatment. The major variants of pond systems are fully covered, namely: facultative ponds, anaerobic ponds, aerated lagoons, maturation ponds. The book presents in a clear and informative way the main concepts, working principles, expected removal efficiencies, design criteria, design examples, construction aspects, operational guidelines and sludge managment for pond systems.
SPERLING, M. von (2007): Waste Stabilisation Ponds. (= Biological Wastewater Treatment Series , 3 ). London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 01.11.2013] PDFBiological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 1
Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions gives a state-of-the-art presentation of the science and technology of biological wastewater treatment, particularly domestic sewage. The book covers the main treatment processes used worldwide with wastewater treatment in warm climate regions given a particular emphasis where simple, affordable and sustainable solutions are required. The 55 chapters are divided into 7 parts over two volumes: Volume One: (1) Introduction to wastewater characteristics, treatment and disposal; (2) Basic principles of wastewater treatment; (3) Stabilisation ponds; (4) Anaerobic reactors; Volume Two (also available in the SSWM library): (5) Activated sludge; (6) Aerobic biofilm reactors; (7) Sludge treatment and disposal.
SPERLING, M. von LEMOS CHERNICHARO, C.A. de (2005): Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 1. London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture
The report suggests that emerging trends in low-cost, decentralised naturally-based infrastructure and urban wastewater management which promote the recovery and reuse of wastewater resources are increasingly relevant. Technologies for these sanitation options are presented. The concept of managing urban wastewater flows at a decentralised or "intermediate" level, based on micro watersheds, is explored. Effluent treatment standards that are currently accepted in order to protect public health and safety are reviewed.
ROSE, D.G. (1999): Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture. (= Cities Feeding People (CFP) Report Series. , 27 ). Ottawa: International Development Research Center Canada (IDRC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2018]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFIndex of dept/chem-eng/Biotech-Environ/FUNDAMENT
Waste Stabilisation Ponds
This document provides information and instructions on waste stabilisation ponds. Various case studies are mentioned, e.g. the wastewater-fed fishponds in Calcutta in India.
VARON, M. P. MARA, D. D. (2004): Waste Stabilisation Ponds. Delft: International Water and Sanitation Centre URL [Accessed: 17.05.2012]Training Material on Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment
This training manual emphasizes basics of biogas technology as well as design principles and technical considerations. A sample design exercise and some technical drawings and sketches are also given.
WAFLER, M. (2008): Training Material on Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment. (= Ecosan Expert Training Course ). Aarau: Seecon GmbH URLWastewater stabilization ponds: Principles of planning and practice.
The book has been divided in two parts. Part A provides a comprehensive summary concerning the various aspects of constructing, operating and maintaining pond systems. It also considers aspects such as management and safety. Part B is intended for persons making the preliminary designs on which cost estimates and, hence, choices can be made. In particular, the appendix and annex provide a working example and a simple methodology to help the designer in preparing adequately detailed designs.
WHO (1987): Wastewater stabilization ponds: Principles of planning and practice.. (= WHO EMRO Technical Publication , 10 ). Alexandria: World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern MediterraneanPhilippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid
This Sanitation Sourcebook distils some of the core concepts of sanitation in a user-friendly format so that the book can serve as a practical reference to sanitation professionals and investment decision-makers, particularly the local governments. The annexe contains a practical collection of factsheets on selected sanitation system options.
WSP (2007): Philippines Sanitation Source Book and Decision Aid. pdf presentation. Washington: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP). URL [Accessed: 01.06.2019]Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume II. Wastewater Use in Agriculture
Volume II of the Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and greywater provides information on the assessment and management of risks associated with microbial hazards and toxic chemicals. It explains requirements to promote the safe use of wastewater in agriculture, including minimum procedures and specific health-based targets, and how those requirements are intended to be used. It also describes the approaches used in deriving the guidelines, including health-based targets, and includes a substantive revision of approaches to ensuring microbial safety.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume II. Wastewater Use in Agriculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 05.06.2019] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFFacultative Lagoons
Short factsheet on the design, operation, maintenance and costs of facultative ponds in the United States.
EPA (2002): Facultative Lagoons. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet ). United States Environment Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 12.04.2010]Solids Separation and Pond Systems for the Treatment of Faecal Sludges in the Tropics
The report sets out to provide guidelines for the preliminary design of faecal sludge treatment schemes comprising solids-liquid separation and stabilisation ponds. The document is based on the results of collaborative field research conducted by the Ghana Water Research Institute and SANDEC on full and pilot-scale faecal sludge (FS) treatment plants located in Accra, Ghana.
HEINSS, U. LARMIE, S.A. STRAUSS, M. (1998): Solids Separation and Pond Systems for the Treatment of Faecal Sludges in the Tropics . Lessons Learnt and Recommendations for Preliminary Design . (= SANDEC Report , 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 12.04.2010]SOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Co-treatment of Faecal Sludge and Wastewater in Tropical Climates
This article provides operational and design guidance for the co-treatment of faecal sludge in waste stabilisation ponds and in activated sludge sewage treatment plants. Problems which may arise when highly concentrated faecal sludge is not properly included in the design of the co-treatment system are also discussed.
HEINSS, U. STRAUSS, M. (1999): SOS - Management of Sludges from On-Site Sanitation. Co-treatment of Faecal Sludge and Wastewater in Tropical Climates. Duebendorf and Accra: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG) URL [Accessed: 21.04.2010]Epuration des eaux usées par Lagunage a Microphytes et a Macrophytes en Afrique de l'Ouest et du Centre- Etat des lieux, performances épuratoires et critères de dimensionnement
Stabilization ponds are a very promising sustainable centralized wastewater treatment option for West Africa due to the favourable climate. Pilot studies could demonstrate their performance in the local context; however none of the full-scale applications works. Besides the poor economic situation and little political support, it is also the lack of training and research that contributes to this situation. This work presents the establishment of an international research collaboration network and main technical recommendations based on an exhaustive assessment on the state-of-the-art of stabilization ponds in the West-African context.
KONE, D. (2002): Epuration des eaux usées par Lagunage a Microphytes et a Macrophytes en Afrique de l'Ouest et du Centre- Etat des lieux, performances épuratoires et critères de dimensionnement. (= Doctoral Thesis ). Lausanne: Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL).Language: French
Design Manual for Waste Stabilization Ponds in India
How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation
The purpose of this guide is to assist local contracting authorities and their partners in identifying those sanitation technologies best suited to the different contexts that exist within their town. The first part of the guide contains a planning process and a set of criteria to be completed; these assist you in characterizing each area of intervention so that you are then in a position to identify the most appropriate technical solutions. The second part of the guide consists of technical factsheets which give a practical overview of the technical and economic characteristics, the operating principle and the pros and cons of the 29 sanitation technology options most commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa.
MONVOIS, J. GABERT, J. FRENOUX, C. GUILLAUME, M. (2010): How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 4 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture
The report suggests that emerging trends in low-cost, decentralised naturally-based infrastructure and urban wastewater management which promote the recovery and reuse of wastewater resources are increasingly relevant. Technologies for these sanitation options are presented. The concept of managing urban wastewater flows at a decentralised or "intermediate" level, based on micro watersheds, is explored. Effluent treatment standards that are currently accepted in order to protect public health and safety are reviewed.
ROSE, D.G. (1999): Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse- options for urban agriculture. (= Cities Feeding People (CFP) Report Series. , 27 ). Ottawa: International Development Research Center Canada (IDRC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2018]Part Three: Stabilization Ponds
Almost 200 pages on the treatment process and design parameters of waste stabilisation ponds. Very exhaustive.
SPERLING, M. von (2005): Part Three: Stabilization Ponds. المُدخلات: SPERLING, M. von ; LEMOS CHERNICHARO, C.A. de ; (2005): Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 1. London: 495-646. URL [Accessed: 16.02.2011]Basic Principles of Wastewater Treatment
Basic Principles of Wastewater Treatment is the second volume in the series Biological Wastewater Treatment, and focusses on the unit operations and processes associated with biological wastewater treatment. The major topics covered are: microbiology and ecology of wastewater treatment, reaction kinetics and reactor hydraulics, conversion of organic and inorganic matter, sedimentation, aeration.
SPERLING, M. von (2007): Basic Principles of Wastewater Treatment. (= Biological Wastewater Treatment Series , 2 ). London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Waste Stabilisation Ponds
This document provides information and instructions on waste stabilisation ponds. Various case studies are mentioned, e.g. the wastewater-fed fishponds in Calcutta in India.
VARON, M. P. MARA, D. D. (2004): Waste Stabilisation Ponds. Delft: International Water and Sanitation Centre URL [Accessed: 17.05.2012]Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 1
Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions gives a state-of-the-art presentation of the science and technology of biological wastewater treatment, particularly domestic sewage. The book covers the main treatment processes used worldwide with wastewater treatment in warm climate regions given a particular emphasis where simple, affordable and sustainable solutions are required. The 55 chapters are divided into 7 parts over two volumes: Volume One: (1) Introduction to wastewater characteristics, treatment and disposal; (2) Basic principles of wastewater treatment; (3) Stabilisation ponds; (4) Anaerobic reactors; Volume Two (also available in the SSWM library): (5) Activated sludge; (6) Aerobic biofilm reactors; (7) Sludge treatment and disposal.
SPERLING, M. von LEMOS CHERNICHARO, C.A. de (2005): Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 1. London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management"
Technical information on environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment.
UNEP ; MURDOCH UNIVERSITY (2004): Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management". The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP/GPA), Coordination OfficeWastewater stabilization ponds: Principles of planning and practice.
The book has been divided in two parts. Part A provides a comprehensive summary concerning the various aspects of constructing, operating and maintaining pond systems. It also considers aspects such as management and safety. Part B is intended for persons making the preliminary designs on which cost estimates and, hence, choices can be made. In particular, the appendix and annex provide a working example and a simple methodology to help the designer in preparing adequately detailed designs.
WHO (1987): Wastewater stabilization ponds: Principles of planning and practice.. (= WHO EMRO Technical Publication , 10 ). Alexandria: World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern MediterraneanBox 1: Sanitation and Wastewater Reuse in Ghana
Case study from Ghana. Studies have been carried out to improve sewerage, effluent disposal and sanitation through offsite and on-site sanitation facilities. The Accra Sewerage Improvement Project will provide two new sewage treatment plants, based on waste stabilization ponds, with outfalls discharging into the sea and into watercourses. Transfer of sanitation and sewerage functions from central government agencies to the assemblies is considered in the National Environmental Sanitation Policy, which is however not automatically combined with a corresponding transfer of capacities and operational funds.
BAHRI, A. (2009): Box 1: Sanitation and Wastewater Reuse in Ghana. المُدخلات: BAHRI, A. ; (2009): Managing the other side of the Water Cycle - Making Wastewater an Asset. Stockholm: 23-24. URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]Lagunas de Estabilizacion para Descarga de Liquidos de Camiones Atmosfericos
This publication deals with the feasibility of waste stabilisation ponds for the simultaneous treatment of collected sludge (by vacuum trucks) and wastewater from the domestic sewer system. The principal objective of the study was to asses if existing treatment ponds could be used in the future as thickening ponds for the sludge.
INGALLINELLA, A.M. FERNANDEZ, R. SANGUINETTI, G. HERGERT, L. QUEVDO, H. STRAUSS, M. MONTANGERO, A. (2001): Lagunas de Estabilizacion para Descarga de Liquidos de Camiones Atmosfericos. Duebendorf and Acra: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG) and Water Research Institute (CSIR) Ghana URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]Language: Spanish
Ecological Sanitation and Reuse of Wastewater. Ecosan. A Thinkpiece on ecological sanitation
This paper shows that there are comprehensive experiences and available technologies that meet new and sustainable sanitation requirements. Ecological sanitation constitutes a diversity of options for both rich and poor countries, from household level up to wastewater systems for mega-cities and needs to become recognised by decision-makers at all levels.
JENSSEN, P.D. HEEB, J. HUBA-MANG, E. GNANAKAN, K. WARNER, W. REFSGAARD, K. STENSTROEM, T.A. GUTERSTRAM, B. ALSEN, K.W. (2004): Ecological Sanitation and Reuse of Wastewater. Ecosan. A Thinkpiece on ecological sanitation. Norway: The Agricultural University of Norway URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]The impact of urbanization on sanitary conveyances and sewage treatment facilities in the city of Lusaka, Zambia
This publication presents a study to determine the effective operation of wastewater collection systems and sewage treatment plants (waste stabilization ponds) of Lusaka. It highlights the impact of urbanization on sanitary infrastructure and the urban environment. Some of the key issues to achieve ecological sanitation in developing countries are discussed.
KAAWANGA, O.C. (2003): The impact of urbanization on sanitary conveyances and sewage treatment facilities in the city of Lusaka, Zambia. المُدخلات: Proceeding of the 2nd international symposium on ecological sanitation: Volume 1 , 927-933. URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]Sewage Fed Aquaculture Systems of Kolkata. A Century-old Innovation of Farmers
Case Study on the fishponds in sewage-fed lagoons in Kolkata.
NANDEESHA, M.C. (2002): Sewage Fed Aquaculture Systems of Kolkata. A Century-old Innovation of Farmers. المُدخلات: Aquaculture Asia: Volume 7 , 28-32. URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]Opportunities in Fecal Sludge Management for Cities in Developing Countries: Experiences from the Philippines
In July 2012, a team from RTI International deployed to the Philippines to evaluate four FSM programs with the goal of reporting on best practices and lessons learned. The four cases—Dumaguete City, San Fernando City, Maynilad Water for the west zone of metro Manila, and Manila Water from the east zone of metro Manila—were chosen to highlight their different approaches to implementing FSM.
ROBBINS, D. STRANDE, L. DOCZI, J. (2012): Opportunities in Fecal Sludge Management for Cities in Developing Countries: Experiences from the Philippines. North Carolina: RTI International URL [Accessed: 10.06.2019]Water for Urban Agriculture
Evaluation des performances épuratoires de trois systèmes d’épuration biologique des eaux usées domestique à Ouagadougou- Burkina Faso
Comparative assessment of three waste stabilization ponds (from very small to very large scale) in Ouagadougou.
SPUHLER, D. KENFACK, S. TOGOLA, L. KLUTSE, A. TANDIA C.T. (2006): Evaluation des performances épuratoires de trois systèmes d’épuration biologique des eaux usées domestique à Ouagadougou- Burkina Faso . Ouagadougou: Réseau CREPA (Centre Régional Pour l'Eau Potable et l'Assainissement à faible coût) URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]Language: French
Treating Faecal Sludge in Ponds
Field research conducted by SANDEC and its partners at the Water Research Institute in Ghana, and information gathered from the scarce literature on faecal sludge treatment is presented in this publication. Issues dealt with in this document are the differences in design principles for the treatment of faecal sludge in waste stabilization in opposition to the treatment of wastewater; handling of faecal sludge solids; the role of anaerobic ponds in faecal sludge treatment; and ammonia (NH3-N) toxicity.
STRAUSS, M. LARMIE, S.A. HEINSS, U. MONTANGERO, A. (1999): Treating Faecal Sludge in Ponds. Duebendorf and Accra: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG) and Water Research Institute (CSIR) Ghana URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]Notes in the Design and Operation of Waste Stabilization Ponds in Warm Climates of Developing Countries
Anaerobic, facultative and maturation ponds as wells as aerated lagoon systems are presented as an appropriate solution in developing countries where sewerage systems are present. The technical content was reviewed by Prof. Duncan Mara (University of Leeds, England). Detailed design, operation and maintenance guidance is given. Hence, this paper can be useful as a technical manual.
ARTHUR, J.P. (1983): Notes in the Design and Operation of Waste Stabilization Ponds in Warm Climates of Developing Countries . (= World Bank Technical Paper , 7 ). Washington: The World Bank URL [Accessed: 08.05.2018] PDFGuidance Manual on Water Supply and Sanitation Programmes
This manual has been prepared as a tool to help improve DFID's (Department for International Developments, United Kingdom) support for water supply and sanitation projects and programmes in developing countries. Its particular focus is on how DFID assistance can best meet the needs of the urban and rural poor for water supply and sanitation services.
DFID (1998): Guidance Manual on Water Supply and Sanitation Programmes. London: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) for the Department for International Development (DFID) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2018]Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes
This module pays special attention to the haulage, treatment and reuse or disposal of faecal sludge. It covers both technical and non-technical (socio-cultural, economic, political etc.) aspects and provides practical information on design, financing and planning of faecal sludge treatment plants.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]Waste Stabilization Ponds and Constructed Wetlands Design Manual
Design Manual for Waste Stabilization Ponds in India
Ponds. Lecture notes
How to Design Wastewater Systems for Local Conditions in Developing Countries
This manual provides guidance in the design of wastewater systems in developing country settings. It promotes a context-specific approach to technology selection by guiding the user to select the most suitable technologies for their area. It provides tools and field guides for source characterization and site evaluation, as well as technology identification and selection. This manual is primarily addressed to private and public sector service providers, regulators and engineers/development specialists in charge of implementing wastewater systems.
ROBBINS, D.M. LIGON, G.C. (2014): How to Design Wastewater Systems for Local Conditions in Developing Countries. London: International Water Association (IWA) URL [Accessed: 20.01.2015]Waste Stabilization Ponds and Constructed Wetlands Manual.
Design manual for designers, builders and operators on the design and operation of artificially constructed wetlands and waste stabilization ponds. The supporting information includes a standard systems approach which can be adopted universally; the theoretical background on the biological, chemical and physical processes of each method, the current state of the technology and technical knowledge on how to design, operate and maintain them; and theoretical knowledge on how best the models may be used to describe the systems.
UNEP (n.y): Waste Stabilization Ponds and Constructed Wetlands Manual. . United Nations Environmental Programme International Environmental Technology Center (UNEP-IETC) and the Danish International Development Agency (Danida) URL [Accessed: 19.04.2010]FS Management – Review of Practices, Problems and Initiatives
A study on management and institutional aspects regarding the challenges and possible improvements in managing faecal sludge.
STRAUSS, M. MONTANGERO, A. (2002): FS Management – Review of Practices, Problems and Initiatives. London and Duebendorf: DFID Project R8056, Capacity Building for Effective Decentralised Wastewater Management, Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]http://www.unep.or.jp/Ietc/Publications/Water_Sanitation/ponds_and_wetlands/index.asp
Manual and supporting information by the UN environmental programme, providing information for designers, builders and operators on artificially constructed wetlands and waste stabilization ponds. The supporting information includes a standard systems approach which can be adopted universally; the theoretical background on the biological, chemical and physical processes of each method, the current state of the technology and technical knowledge on how to design, operate and maintain them; and theoretical knowledge on how best the models may be used to describe the systems.
Clinton Water District. Case Study of the Facultative Lagoon System
The Clinton Water District provides a secondary level of wastewater treatment by using a facultative lagoon system. Clinton’s lagoon system was constructed in 1987. The two lagoons are operated in series and cover approximately 26 acres.


