تعد خطط سلامة المياه (WSP) وسيلة فعَّالة لضمان أن إمدادات المياه صالحة للاستخدام الآدمي وأنها متوافقة مع المعايير الصحية وغيرها من المتطلبات التنظيمية. تعتمد الخطِّط على منهج شامل لإدارة وتقييم المخاطر لجميع الخطوات في سلسلة إمدادات المياه من أحواض تجميع مياه الأمطار إلى المستهلك.
تتكوَّن WSP في الأساس من ثلاثة عناصر رئيسية هي:
نظام تقييم لتحديد ما إذا كانت سلسلة إمدادات المياه ككل يمكنها توصيل المياه بجودة تفي بالمتطلبات الصحية. يحدِّد نظام التقييم المذكور المخاطر المحتملة في كل جزء من سلسلة الإمداد بالمياه، مستوى المجازفة لكل من المخاطر المحتملة التي تم تحديدها والإجراءات المناسبة للتحكم في هذه المخاطر من أجل ضمان أن إمدادات المياه آمنة وضمان الوفاء بالمعايير وتحقيق الأهداف وحماية صحة المستخدمين من البشر؛ انظرقضايا النظافة والصحة
يتم تحديد معنى مراقبة عمليات التشغيل بطبيعة ومرات تكرار مناسبة عند نقطة ملائمة في سلسلة الإمداد بالماء لكل من إجراءات التحكم التي يتم تحديدها وتنفيذها عن طريق تقييم النظام من أجل ضمان سرعة الكشف عن أي خروج عن الأداء المطلوب؛ و
توثيق الترتيبات الإدارية بما في ذلك تفاصيل تقييم النظام، مراقبة عمليات التشغيل ومراقبة عمليات المصادقة مع وصف الإجراءات الواجب اتخاذها في عمليات وظروف التشغيل العادية في حال عدم توافق هذه الظروف والعمليات، أو في حال احتمال عدم توافقها، مع المعايير أو القيم المستهدفة أو في حال عدم وفائها بمتطلبات مراقبة عمليات التشغيل، أو في حال احتمال وجود مخاطر تهدد صحة الإنسان. ينبغي أن تتضمن الإجراءات المذكورة تحقيقات مناسبة، إجراءات تصحيحية في صورة برامج تطوير وبرامج اتصالات وتقديم تقارير.
الأهداف
تركز الأهداف الرئيسية لخطة سلامة المياه في مجال حماية صحة الإنسان وضمان جودة ممارسات الإمداد بالمياه على الحد من تلوث مياه المصدر، خفض أو إزالة التلوث من خلال عمليات معالجة مناسبة والوقاية من حدوث التلوث في نظام شبكة التوزيع العامة والمحلية. تعد هذه الأهداف قابلة للتطبيق على جميع سلاسل الإمداد بالمياه، بغض النظر عن حجمها أو درجة تعقيدها ويتم تحقيقها من خلال:
- تطوير فهم النظام المحدَّد وقدرته على الإمداد بالمياه التي تفي بالأهداف المحدَّدة من الناحية الصحية؛
- تحديد المصادر المحتملة للتلوث وكيفية السيطرة عليها؛
- التحقق من تنفيذ إجراءات التحكم من أجل السيطرة على المخاطر؛
- استخدام نظام لمراقبة إجراءات التحكم داخل نظام المياه؛
- استخدام إجراءات تصحيحية في الوقت المناسب لضمان التزويد بالمياه الصالحة للشرب باستمرار؛ والتحقق من جودة مياه الشرب للتأكد من تنفيذ WSP بشكل صحيح والتأكد من الوصول إلى الأداء المطلوب من أجل الوفاء بالأهداف أو المعايير الوطنية والإقليمية والمحلية لجودة المياه
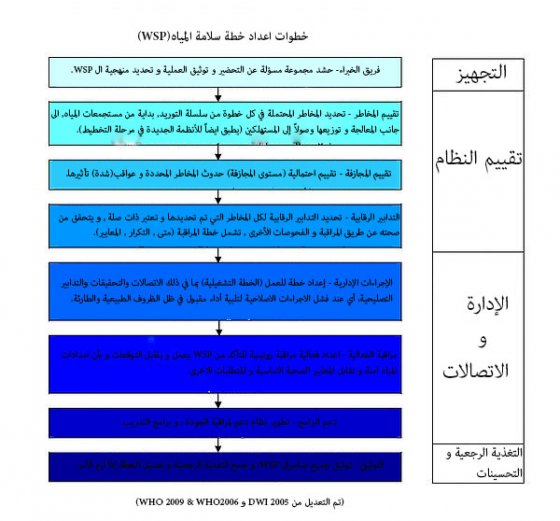
الخطوات الرئيسية لتطوير WSP
ومن الأدوات المماثلة إلى حد ما فيما يتعلق بالصرف الصحي مخططات الصرف الصحي في المدن.
تعد خطط سلامة المياه قابلة للتطبيق على جميع أنظمة الإمداد بالمياه، بغض النظر عن حجمها أو درجة تعقيدها. وهذا يعني أن WSPقابلة للتطبيق على أنظمة الإمداد بالماء على نطاق كبير أو صغير سواء في المناطق الحضرية أو الريفية. يتطلب تنفيذ منهج WSPدعم مالي وتقني على حدٍ سواء من الإدارة العليا للوحدة. من المهم أن يتمتع فريق WSPبالقدرة والخبرة اللازمة لفهم عمليات استخراج المياه ومعالجتها وتوزيعها والتعامل مع المخاطر التي يمكن أن تؤثر على سلامة المياه في نظام الإمداد (BATRAM et. al. 2009).
Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Third Edition
This volume of the Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality explains requirements to ensure drinking-water safety, including minimum procedures and specific guideline values, and how those requirements are intended to be used. The volume also describes the approaches used in deriving the guidelines, including guideline values. It includes fact sheets on significant microbial and chemical hazards.
WHO (2008): Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Third Edition. Third Edition incorporating the First and Second Addenda. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 23.04.2012]A Brief Guide to Water Safety Plans
This document precisely describes the concept and key stages of WSP. It also describes the brief guidance on the preparation and content of WSPs for each element of the water supply chain.
DWI (2005): A Brief Guide to Water Safety Plans. London: Drinking Water Inspectorate (DWI) URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-step Risk Management for Drinking-water Suppliers
In 2004, the WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality recommended that water suppliers develop and implement "Water Safety Plans" (WSPs) in order to systematically assess and manage risks. Since this time, governments and regulators, water suppliers and practitioners have increasingly embraced this approach, but they have also requested further guidance. This much-anticipated workbook answers this call by describing how to develop and implement a WSP in clear and practical terms. Stepwise advice is provided through 11 learning modules, each representing a key step in the WSP development and implementation process.
BARTRAM, J. CORRALES, L. DAVISON, A. DEERE, D. DRURY, D. GORDON, B. HOWARD, G. RINEHOLD, A. STEVENS, M. (2009): Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-step Risk Management for Drinking-water Suppliers. Geneva/London: World Health Organization (WHO); International Water Association (IWA) URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]كتيب الادارة المتكاملة للموارد المائية فى احواض الانهار والبحيرات وطبقات المياة الجوفية العابرة للحدود
التقدم في مجال مياه الشرب و الاصحاح.جينف.سويسرا
يلقي هذا التقرير الضوء علي ما تم إنجازه بشأن المياه والإصحاح والمجالات التي نحتاج فيها إلي تسريع المجهود.
منظمة الصحة العالمية , اليونيسيف (2014): التقدم في مجال مياه الشرب و الاصحاح.جينف.سويسرا. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Language: Arabic
ﺩﻻﺌل ﺠﻭﺩﺓ ﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺭﺏ.جينيف.سويسرا
دليل تطهير مياه الشرب في حالات الطوارئ.ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﺐ ﺍﻹﻗﻠﻴﻤﻲ ﻟﺸﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻮﺳﻂ
هو دليل يوضح تطهير مياه الشرب في حالات الطوارئ يتناول الأساليب والطرق.
منظمة الصحة العالمية (2004): دليل تطهير مياه الشرب في حالات الطوارئ.ﺍﻟﻤﻜﺘﺐ ﺍﻹﻗﻠﻴﻤﻲ ﻟﺸﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻮﺳﻂ. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.
يهدف هذا الدليل إلى تقديم الإرشاد العملي، لتسهيل تطوير خطة سلامة المياه، مع التركيز على إمدادات المياه المنظمة التي تديرها منشأة مياه أو ما شابه.
منظمة الصحة العالمية,الإتحاد الدولي للمياه (2009): ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Language: Arabic
Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-step Risk Management for Drinking-water Suppliers
In 2004, the WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality recommended that water suppliers develop and implement "Water Safety Plans" (WSPs) in order to systematically assess and manage risks. Since this time, governments and regulators, water suppliers and practitioners have increasingly embraced this approach, but they have also requested further guidance. This much-anticipated workbook answers this call by describing how to develop and implement a WSP in clear and practical terms. Stepwise advice is provided through 11 learning modules, each representing a key step in the WSP development and implementation process.
BARTRAM, J. CORRALES, L. DAVISON, A. DEERE, D. DRURY, D. GORDON, B. HOWARD, G. RINEHOLD, A. STEVENS, M. (2009): Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-step Risk Management for Drinking-water Suppliers. Geneva/London: World Health Organization (WHO); International Water Association (IWA) URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Water Safety Plans: Managing Drinking-Water Quality from Catchment to Consumer
This document describes the Water Safety Plan approach with relevant case studies.
DAVISON, A. HOWARD, G. STEVENS, M. CALLAN, P. FEWTRELL, L. DEERE, D. BARTRAM, J. (2005): Water Safety Plans: Managing Drinking-Water Quality from Catchment to Consumer. Geneva: World Health Organization URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]A Brief Guide to Water Safety Plans
This document precisely describes the concept and key stages of WSP. It also describes the brief guidance on the preparation and content of WSPs for each element of the water supply chain.
DWI (2005): A Brief Guide to Water Safety Plans. London: Drinking Water Inspectorate (DWI) URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Water Safety Plans (WSP) for Urban Piped Water Supplies in Developing Countries
The book is designed to guide the user through the process of developing Water Safety Plans (WSP). It provides a simple step-by-step approach to developing WSPs for operators and managers of piped water supplies. At each stage, the principles of the stage are outlined as well as methods and tools required to achieve these principles. Each section ends with a summary of key competencies achieved from each stage.
GODFREY, S. HOWARD, G. (2004): Water Safety Plans (WSP) for Urban Piped Water Supplies in Developing Countries. UK: WEDC, Loughborough University URL [Accessed: 23.07.2010]Water Safety Plans (WSP) Book2 Supporting Water Safety Management for Urban Piped Water Supplies in Developing Countries
This book is a collection of contributions from specialists in key areas, which have been identified, to aid the successful implementation of the Water Safety Plans. The book is divided into two sections: section one addresses the prerequisites required prior to establishing a WSP and section two focuses on the supporting programmes required to ensure effective risk management is achieved.
GODFREY, S. HOWARD, G. (2005): Water Safety Plans (WSP) Book2 Supporting Water Safety Management for Urban Piped Water Supplies in Developing Countries. UK: WEDC, Loughborough University URL [Accessed: 23.07.2010]Water Safety in Buildings
Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Fourth Edition
This volume of the Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality explains requirements to ensure drinking-water safety, including minimum procedures and specific guideline values, and how those requirements are intended to be used. The volume also describes the approaches used in deriving the guidelines, including guideline values. It includes fact sheets on significant microbial and chemical hazards.
WHO (EDITOR) (2011): Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality, Fourth Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 11.07.2018]Chemical Safety of Drinking Water Assessing Priorities for Risk Management
Identifying and prioritizing chemical risks presents a challenge, especially in developing countries, because information on the presence of chemicals in water supplies is often lacking. This document provides guidance to help readers to meet that challenge. It shows how information on aspects such as geology and industrial and agricultural development, which is often readily available, can be used to identify potential chemical contaminants (and potential sources of chemicals), from catchment to consumer, and thus prioritize risks. This is a supporting document to the Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality (WHO 2008 and WHO 2011), and it is aimed at policy-makers, regulators, managers and public health practitioners at national and local level.
WHO (2007): Chemical Safety of Drinking Water Assessing Priorities for Risk Management. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) URL [Accessed: 12.10.2011]خطة سلامة المياه. الشركة القابضة لمياه الشرب و شركة مياه الشرب بالاسكندرية. مصر
هي مناهج اﻟﻬﺩﻑ منها ﻫﻭ ﺗﻭﻓﻳﺭ ﺍﻟﻣﻳﺎﻩ ﺍﻻﻣﻧﺔ ﺑﺎﺳﺗﻣﺭﺍﺭوﺍﻟﺣﺩ ﻣﻥ ﺍﻟﻣﺧﺎﻁﺭ ﺍﻟﻛﺑﺭﻯ ﺍﻟﺗﻰ ﻻ ﺗﺧﺿﻊ ﻟﻠﺿﺑﻁ ﻓﻰ ﺍﻟﻭﻗﺕ ﺍﻟﺣﺎلي
ﻭﻓﺎء ﻋﻭﺽ ﻣﺣﻣﺩ (2015): خطة سلامة المياه. الشركة القابضة لمياه الشرب و شركة مياه الشرب بالاسكندرية. مصر. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Language: Arabic
إدارة الموارد المائية رهان التنمية المستدامة في ظل تحديات الألفية الثالثة.الجزائر.
يهدف هذا البحث إلى تقديم مسح وتحليل أهم التطورات الحديثة في موضوع المياه باعتباره التحدي الراهن في ظل النظام العالمي الجديد لإدارة الموارد المائية
بن عـنتر عبد الرحمان ,اونيس عبد المجيد (2014): إدارة الموارد المائية رهان التنمية المستدامة في ظل تحديات الألفية الثالثة.الجزائر.. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Language: Arabic
ﻧﻈﺎم ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ اﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ وﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ اﻟﻨﻘﺎط اﻟﺤﺮﺟﺔ (اﻟﻬﺎﺳﺐ) . المملكة العربية السعودية
هو ﻧﻈﺎم وﻗﺎﺋﻲ ﻳﻌﻨﻰ ﺑﺴﻼﻣﺔ اﻟﻐﺬاء ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼل ﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ اﻷﺧﻄﺎر اﻟﺘﻲ ﺗﻬﺪد ﺳﻼﻣﺘﻪ , وﻣﻦ ﺛﻢ تحديد النقاط الحرجة
الهيئة العامة للغذاء و الدواء (2006): ﻧﻈﺎم ﺗﺤﻠﻴﻞ اﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ وﺗﺤﺪﻳﺪ اﻟﻨﻘﺎط اﻟﺤﺮﺟﺔ (اﻟﻬﺎﺳﺐ) . المملكة العربية السعودية. URL [Accessed: 14.08.2017]Language: Arabic
الادارة المتكاملة للموارد المائية
ﺇﻥ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻤﺴﺘﻨﺩ ﻴﺤﻭﻱ ﺴﺒﻌﺔ ﻓﺼﻭل. ﻴﺘﻌﻠﻕ ﻓﺼل ﺍﻟﺘﻘﺩﻴﻡ ﺒﺎﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﻌﺫﺒﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻡ ﺒﺎﻟﺘﺭﻜﻴﺯ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺇﻗﻠـﻴﻡ ﺸﻤﺎل ﺃﻓﺭﻴﻘﻴﺎ ﻭﺍﻟﺴﻭﺩﺍﻥ. ﻭ ﻴﺴﺎﻋﺩ ﻫﺫﺍ ﺍﻟﻔﺼل ﻜﺜﻴﺭﺍﹰ ﻟﻠﺘﺭﻜﻴﺯ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺘﻭﺯﻴﻊ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺍﺭﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﺌﻴﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺴـﻭﺩﺍﻥ ﻭﺍﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﻟﻴﺔ، ﻭﺍﻻﺤﺘﻴﺎﺝ ﻟﻺﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻜﺎﻤﻠﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﻭﺍﺭﺩ ﺍﻟﻤﺎﺌﻴﺔ ﻭﻤﻥ ﺜﻡ ﺍﻟﻤﻨﺎﻁﻕ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺜﻴﺔ ﻟﺘﺩﺭﻴﺏ ﺍﻟﻁﻼﺏ.
ﻋﺼﺎﻡ ﻤﺤﻤﺩ ﻋﺒﺩ الماجد ﺠﺎﻤﻌﺔ ﺍﻟﺴﻭﺩﺍﻥ ﻟﻠﻌﻠﻭﻡ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻜﻨﻭﻟﻭﺠﻴﺎ. الخرطوم. السودان. الادارة المتكاملة للموارد المائية. ﻤﺭﻜﺯ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺙ ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻤﻲ ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻼﻗﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺨﺎﺭﺠﻴﺔ URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]مياه الشرب. ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻬﻭﺭﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺭﺒﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺴﻭﺭﻴﺔ
تحدد ﻫﺬﻩ المواصفة ﺍﻟﻘﻴﺎﺳﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺴﻮﺭﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﻭﻁ ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻮﺍﺟﺐ ﺗﻮﺍﻓﺮﻫﺎ في المياه الصالحة ﻟﻠـﺸﺮﺏ ﻭﺍﻟﺼﻨﺎﻋﺎﺕ الغذائية بما فيها المياه المعبئة وتشمل الجوانب الحيوية المجرية.
ﻭﺯﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﺼﻨﺎﻋﺔ (2007): مياه الشرب. ﺍﻟﺠﻤﻬﻭﺭﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﺭﺒﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﺴﻭﺭﻴﺔ. URL [Accessed: 25.08.2017]Language: Arabic
Experiences from pilot projects to implement water safety plans in Bangladesh
This report describes the process of implementation of Water Safety Plans in Bangladesh since 2004. It also consolidates the experience of the development of ‘model’ WSPs for key rural water supply technologies and of implementing WSPs in communities by NGOs and the Department of Public Health Engineering (DPHE).
ARSENIC POLICY SUPPORT UNIT (2006): Experiences from pilot projects to implement water safety plans in Bangladesh. Dhaka: Policy Support Unit (APSU) URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Water Safety Plan for Rain Water Harvesting System in Rural Water Supply System
The case study from Bangladesh on application of WSP for Rain Water Harvesting Systems.
DPHE-ITN (2006): Water Safety Plan for Rain Water Harvesting System in Rural Water Supply System. URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Water Safety Plan and Selected Case Studies
Presentation on Water Safety Plans, describing different examples of WSP from the Philippines.
PERALTA, G. (n.y): Water Safety Plan and Selected Case Studies. Powerpoint Presentation. Manlia: WHO URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Water Safety Plans for Utilities in Developing Countries – A case study from Kampala, Uganda
This is a case study on implementation of WSP at Kampala, Uganda.
GODFREY, S. NIWAGABA, C. HOWARD, G. TIBATEMWA, S. (n.y): Water Safety Plans for Utilities in Developing Countries – A case study from Kampala, Uganda. URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Lessons from Water Safety Plans for small-scale water supply systems as developed by schools in Romania
This publication analyses the question whether water safety approaches can be implemented with the involvement of schools, and whether the approach can be used in order to mobilize the community for minimizing water related health risks. It describes the results and experiences from a case study in Romania, draws conclusions from this and discusses future perspectives of WSP.
SAMWEL, M. JORRITSMA, F. RADU, O. (2006): Lessons from Water Safety Plans for small-scale water supply systems as developed by schools in Romania. Utrecht, Annemasse Cedex, Munich: Women in Europe for a Common Future (WECF) URL [Accessed: 06.05.2019]Water safety plans: methodologies for risk assessment and risk management in drinking-water systems
This paper reviews and describes the implementation of WSP implemented at Water Supply System in Portugal.
VIEIRA, J.M.P. (2005): Water safety plans: methodologies for risk assessment and risk management in drinking-water systems. المُدخلات: The Fourth Inter-Celtic Colloquium on Hydrology and Management of Water Resources: URL [Accessed: 25.07.2010]Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-step Risk Management for Drinking-water Suppliers
In 2004, the WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality recommended that water suppliers develop and implement "Water Safety Plans" (WSPs) in order to systematically assess and manage risks. Since this time, governments and regulators, water suppliers and practitioners have increasingly embraced this approach, but they have also requested further guidance. This much-anticipated workbook answers this call by describing how to develop and implement a WSP in clear and practical terms. Stepwise advice is provided through 11 learning modules, each representing a key step in the WSP development and implementation process.
BARTRAM, J. CORRALES, L. DAVISON, A. DEERE, D. DRURY, D. GORDON, B. HOWARD, G. RINEHOLD, A. STEVENS, M. (2009): Water Safety Plan Manual: Step-by-step Risk Management for Drinking-water Suppliers. Geneva/London: World Health Organization (WHO); International Water Association (IWA) URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]Developing Water Safety Plans involving schools. Introducing “Water Safety Plans” for small-scale water supply systems. Manual for teacher and pupils
The WSP manual is based on the WHO instrument to assess the risks for small scale water supply systems and contains information concerning water safety plans, background information, educational information and suggestions for teachers. With this manual teachers and pupils can develop water safety plans for small scale water supply systems together.
MOELLER, D. SAMWEL, M. (2008): Developing Water Safety Plans involving schools. Introducing “Water Safety Plans” for small-scale water supply systems. Manual for teacher and pupils. Utrecht/Munich/Annemasse: Women in Europe for a Common Future URL [Accessed: 06.01.2011]Water Safety Plans - Training package. Facilitator handbook
This handbook is one third of a water safety plan (WSP) training package. It accompanies the WSP training workbook and WSP training PowerPoint presentations. The handbook is designed to be used by professional and non-professional trainers, who should have prior knowledge and understanding of WSPs, and who are facilitating WSP training based on the 2009 WSP manual of the International Water Association (IWA) and the World Health Organization (WHO). The training is targeted at all professionals involved in the management of drinking-water safety
WHO IWA (2012): Water Safety Plans - Training package. Facilitator handbook. WHO URL [Accessed: 08.04.2013]Water Safety Plans - Training package. Participant workbook
This workbook is designed to be used by participants attending a water safety plan (WSP) training workshop that has been organized around the materials developed by the International Water Association (IWA) and World Health Organization (WHO). The learning material included in this workbook relates explicitly to the theory sessions that will be presented and the designed exercises. It therefore cannot be used as a standalone document to train people on all WSP aspects.
WHO IWA (2012): Water Safety Plans - Training package. Participant workbook. WHO URL [Accessed: 08.04.2013]Water Safety Plans – Resources to support implementation
This flyer was developed by WHO and IWA during World Water Day 2010, highlighting the need of WSP for improvement of drinking water quality.
WHO ; IWA (2010): Water Safety Plans – Resources to support implementation. Geneva and London: World Health Organisation (WHO) and International Water Association (IWA) URL [Accessed: 18.06.2019]WSPortal: Health through Water
This WSPortal developed by WHO provides key stages and components of WSP with relevant case studies and tools.
Water Safety Portal
This WSPortal developed by WHO and IWA aims to contribute to improving and maintaining the safety of drinking water supplies through the effective implementation of WSPs. It contains collection of case studies, references and tools, which provide practical guidance and evidence-based material of relevance that can be applied appropriately for a range of circumstances.
Water safety plan quality assurance tool
The WSP Quality Assurance Tool, jointly developed by WHO and the International Water Association (IWA), with support from AusAID, DWI (UK), MHLW (Japan) and NSF International. It facilitates an objective assessment of efforts in water safety planning, the approach recommended by the WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality to ensure consistent supplies of safe drinking-water. It systematically highlights the areas in a WSP where progress is made and where opportunities for improvement present themselves.


