المُرشِّح بالتنقيط Trickling Filter (أو المُرشِّح بالتقطير، أو المُرشِّح الزلطي) هو مُفاعل حيوي بمُرشِّح ثابت، يعمل -غالبًا- تحت الظروف الهوائية. يتم تقطيرُ أو رشُ مياه الصرف -التي تم ترسيبها سابقًا- فوق المُرشِّح. وبينما يتخلل الماء مسام المُرشِّح، فإن المواد العضوية يتم تحللها بواسطة الغشاء الحيوي Biofilm المُغطّي لمادة المُرشِّح.
يتم ملءُ المُرشِّح بمواد ذات مساحة سطحٍ نوعيةٍ Specific Surface Area كبيرة، مثل الصخور، أو الحصى، أو قطع مفرومة من القوارير المصنوعة من البولي فينيل كلوريد PVC، أو وَسَط ترشيحي من البلاستيك مُصنَّع خصيصًا لذلك. يوفّر السطح النوعي الكبير مساحة كبيرة لتكوين الغشاء الحيوي. وتؤكسِد الكائنات -التي تنمو في طبقة الغشاء الحيوي الرقيقة على سطح الوسط- الحِمل العضوي في مياه الصرف الصحي إلى ثاني أكسيد الكربون والماء، بينما تعمل في الوقت ذاته على توليد كتلة حيوية جديدة.
يتم تقطير مياه الصرف الواردة -التي تمت مُعالجتها أوليًّا- على المُرشِّح، وذلك باستخدام -على سبيل المثال- رشاشٍ دوَّار بهذه الطريقة، يَمُر وَسَط الترشيح بدورات من حَقن الجرعات والتعرض للهواء. ومع ذلك، يتم استنفاذ الأكسجين بواسطة الكُتلة الحيوية، والطبقات الداخلية قد تكون لاأكسجينية أو لاهوائية.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
التدفقات السائلة الخارجة ,المياة السوداء , المياة البنية , المياة الرمادية |
التدفقات السائلة الخارجة ,الحمأة |
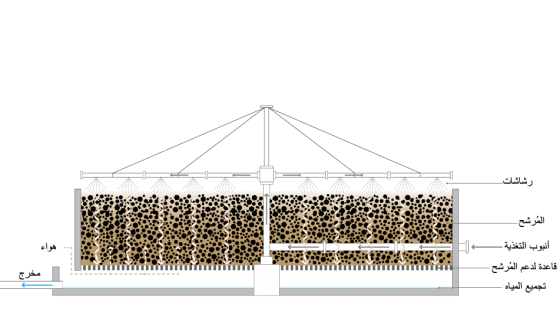
يمكن استخدام هذه التقنية فقط بعد الترويق )الترسيب( الابتدائي، حيث إن الحِمل العالي من المواد الصلبة سوف يؤدي إلى انسداد المُرشِّح. يمكن تصميم نظام حيوي مُنخفض الطاقة )يعمل بالجاذبية(، ولكن بشكل عام إن الإمدادات المُستمرة من الطاقة ومياه الصرف مطلوبة.
بالمُقارنة مع التقنيات الأخرى )على سبيل المثال بِركة تثبيت المخلفات السائلة (الأكسدة فإن المُرشِّحات بالتنقيط تُعتبر صغيرة الحجم، وعلى الرغم من ذلك، فهي أكثر ملاءمةً في المناطق شبه الحضرية أو الريفية الكبيرة.
يُمكن إنشاء المُرشِّحات بالتنقيط في كل البيئات تقريبًا، لكن يلزمها تعديلات خاصة في المناخات الباردة.
يكون عمق المُرشِّح -عادةً- من 1 إلى 2.5 متر، ولكن المُرشِّحات المملوءة بالمواد البلاستيكية الخفيفة يُمكن أن تصل إلى عُمق 12 مترًا. مواد الترشيح المثالية تكون مُنخفضة التكاليف ومتينة ولديها مساحة سطح كبيرة (نسبةً إلى الحجم) وخفيفة وتسمح للهواء بالسريان عبر المُرشِّح. تُعتبر الصخور المجروشة أو الحصى -إن كانت متوفرة- هي الخيار الأقل تكلفةً. وينبغي أن تكون جسيمات مواد الترشيح مُوحّدة الحجم، ويجب أن تتراوح أقطار النسبة الأكبر منها )95%( ما بين 7 إلى 10 سنتيمتر. يمكن استخدام الصخور ذات مساحة السطح النوعية ما بين 45 إلى 60 م2/م3 كمواد تعبئة للمُرشِّح، كما تستخدم المواد البلاستيكية ذات مساحة سطحٍ نوعيةٍ ما بين 90 إلى 150 م2/م3 لنفس الغرض. المسام الكبيرة لمادة المُرشِّح )كما في المواد البلاستيكية( هي أقل عُرضة للانسدادات، وتُوّفر سريانًا جيدًا للهواء. كما أن المُعالجة الابتدائية -أيضًا- ضرورية لمنع الانسدادات، وضمان المُعالجة الفعَّالة.
التدفق الكافي للهواء مُهم لضمان أداء المُعالجة الجيد، ولمنع انبعاث الروائح. ولا بد أن تضمن قاعدة التصريف للمُرشِّح توفير ممرات للهواء عندما يصل الملء لحده الأقصى. تدعم القاعدة المسامية السفلية جسم المُرشِّح، وتسمح بتجميع التدفقات السائلة الخارجة والحمأة الزائدة. ويصمم المُرشِّح الزلطي عادة مع نمطٍ لإعادة تدوير المياه المُعالجة الناتجة لتحسين ترطيب وتنظيف مواد المُرشِّح.
مع مرور الوقت، ستنمو الكتلة الحيوية وتُصبح سميكة، والطبقة المُلاصقة )لمادة المُرشِّح( ستُحرَم من الأكسجين، ثم تدخل في حالة التأكسد التلقائي )الاستهلاك الباطِنيّ للأكسجين( Endogenous State، والتي سوف تفقد فيها قُدرتها على البقاء مرتبطة وملتصقة بمادة المُرشِّح وستنفصل عنها. كما تؤدي أيضًا ظروف التحميل العالية إلى انفصال الكتلة الحيوية عن مادة المُرشِّح. ويجب ترويق التدفقات السائلة الخارجة في حَوْض ترسيب؛ وذلك لإزالة أي كتلة حيوية قد تمت إزاحتها من المُرشِّح. مُعدّل الحمل الهيدروليكي والمُغذيات )أي مقدار مياه الصرف التي يُمكن ضخها إلى المُرشِّح( يتم تحديدهما اعتمادًا على خصائص مياه الصرف، ونوع الوسط الترشيحي، ودرجة الحرارة المُحيطة، ومُتطلبات التصريف.
تتطلب مشاكل الرائحة والذباب أن يتم بناء المُرشِّح بعيدًا عن المنازل ومناطق الأعمال. ولا بد من اتّخاذ التدابير وإجراء القياسات المناسبة للمُعالجة الأولية والابتدائية، وتصريف التدفقات السائلة الخارجة، ومُعالجة المواد الصلبة، حيث إن كل منها لا تزال تُمثّل مخاطر صحية.
تتطلب أعمال التشغيل والصيانة مُشغِّلين ذوي خبرة؛ لمتابعة المُرشِّح، وإصلاح المضخة في حالة حدوث أي مشاكل. ويجب إزالة الحمأة التي تتراكم على المُرشِّح بشكل دوري؛ لمنع الانسدادات، ولبقاء الغشاء الحيوي رقيق وهوائي. يُمكن أن تُستخدم معدلات الأحمال الهيدروليكية العالية )جرعات التدفق( لغسل المُرشِّح. وينبغي أن تُحدَّد معدلات الجرعات والغسيل المثلى عن طريق التشغيل في الموقع.
يجب أن تبقى مادة المُرشِّح رطبة؛ حيث تحدث مشكلة جفاف المُرشِّح في الليل عندما ينخفض معدل تدفق المياه، أوعندما ينقطع التيار الكهربائي.
المعالجة البيولوجية لمياه الصرف الصحى المبادئ وأعمال النمذجة والتصميم
Language: Arabic
ارشادات فى تصميم وتشغيل وصيانة محطات معالجة المياة العادمة
التلوث : المخاطر والحلول
Introduction to Greywater Management. FactSheet
This factsheet provides information and experiences on simple greywater treatments including sorption, infiltration, vertical soil filters and also trickling filters.
ECOSANRES (2008): Introduction to Greywater Management. FactSheet. (= EcoSanRes Factsheet , 8 ). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute EcoSanRes Programme URL [Accessed: 22.04.2010]Ecosan Curriculum 2.3
Sustainable Wastewater Management in Urban Areas
A document about sustainable wastewater management in urban areas.
JENSSEN, P.D. GREATOREX, J.M. WARNER, W. S. (2004): Sustainable Wastewater Management in Urban Areas. (= Kapitel 4. Kurs WH33, Konzeptionen dezentralisierter Abwasserreinigung und Stoffstrommanagement ). Hannover: University of HannoverTrickling Filters - Filter Classification
Decentralised Wastewater Treatment Methods for Developing Countries
Different operation and maintenance options are presented with respect to sustainable plant operation, the use of local resources, knowledge, and manpower.
NATURGERECHTE TECHNOLOGIEN, BAU- UND WIRTSCHAFTSBERATUNG (TBW) GmbH (2001): Decentralised Wastewater Treatment Methods for Developing Countries. GTZ and GATEIntroduction to Greywater Management
The report gives a comprehensive description of the main components in successful greywater management. Examples as well as recommendations are given for designing and dimensioning treatment systems.
RIDDERSTOLPE, P. (2004): Introduction to Greywater Management. (= EcoSanRes Publication Series, Report 2004-4 ). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute, EcoSanRes Programme URL [Accessed: 19.05.2010]DEWATS
Exhaustive report on technological, operational and economic aspects of decentralised waste water treatment systems. Spreadsheet examples support the reader in designing and planning waste water treatment systems components.
SASSE, L. BORDA (1998): DEWATS. Decentralised Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries. Bremen: Bremen Overseas Research and Development Association (BORDA) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Health (Pathogen) Considerations Regarding the Use of Human Waste in Aquaculture
This study reviews the potential health risks and current epidemiological evidence for actual risks from pathogen transmission through wastewater aquaculture.
STRAUSS, M. (n.y): Health (Pathogen) Considerations Regarding the Use of Human Waste in Aquaculture. (pdf presentation). Switzerland: Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries at the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and TechnologyWastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. LUETHI, C. MOREL, A. ZURBRUEGG, C. SCHERTENLEIB, R. (2008): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) and Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) URL [Accessed: 15.02.2010] PDFTrickling Filter - The History of Fixed Film Wastewater Treatment Systems
Trickling Filters
Short Factsheet on the applicability and design criteria of trickling filters including a lot of information on operation and maintenance (form the United States Environment Protection Agency (EPA).
U.S. EPA (2000): Trickling Filters. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet, EPA 832-F , 14 ). United States Environment Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Trickling Filters Nitrification
Short factsheet on nitrification in trickling filters (form the United States Environment Protection Agency (EPA).
U.S.EPA (2000): Trickling Filters Nitrification. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet, EPA 832-F , 15 ). United States Environment Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 17.05.2012]Chapter 4. Wastewater Technologies
Comprehensive overview (in form of factsheets) on the different components of wastewater treatment systems (collection, transfer, onsite treatment, centralised and decentralised treatment, reuse, sludge management and disposal) adapted to the Caribbean Region. Industrial wastewater treatment is also discussed.
UNEP (2004): Chapter 4. Wastewater Technologies. المُدخلات: UNEP (2004): A Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for SIDS in the Caribbean Region. Nairobi: 63-125.Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management"
Technical information on environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment.
UNEP ; MURDOCH UNIVERSITY (2004): Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management". The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP/GPA), Coordination OfficeGuidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management
Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making
These guidance notes are designed to provide state governments and urban local bodies with additional information on available technologies on sanitation. The notes also aid in making an informed choice and explain the suitability of approaches.
WSP (2008): Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making. pdf presentation. New Delhi: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Introduction to Greywater Management
The report gives a comprehensive description of the main components in successful greywater management. Examples as well as recommendations are given for designing and dimensioning treatment systems.
RIDDERSTOLPE, P. (2004): Introduction to Greywater Management. (= EcoSanRes Publication Series, Report 2004-4 ). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute, EcoSanRes Programme URL [Accessed: 19.05.2010]Trickling Filters Nitrification
Short factsheet on nitrification in trickling filters (form the United States Environment Protection Agency (EPA).
U.S.EPA (2000): Trickling Filters Nitrification. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet, EPA 832-F , 15 ). United States Environment Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 17.05.2012]The Attached Growth Process – An old technology takes on new forms
The Pipeline Newsletter was formerly edited by the National Small Flows Clearinghouse (NSFC) and is now edited by the National Environmental Service Center based at the West Virginia University (USA). Popular with small community officials, citizens, maintenance and inspection personnel, and community educators, each quarterly issue of Pipeline focuses on a single wastewater topic and presents it in an easy-to-read format. This issues deals with attached-growth processes, including trickling filters, rotating biological contactors, sand filters, peat filters, textile filters and subsurface flow wetland.
NSFC (2004): The Attached Growth Process – An old technology takes on new forms. (= Pipeline , 1 / 15 ). Morgantown: National Small Flows Clearinghouse URL [Accessed: 22.04.2010]Decentralised Wastewater Treatment Methods for Developing Countries
Different operation and maintenance options are presented with respect to sustainable plant operation, the use of local resources, knowledge, and manpower.
NATURGERECHTE TECHNOLOGIEN, BAU- UND WIRTSCHAFTSBERATUNG (TBW) GmbH (2001): Decentralised Wastewater Treatment Methods for Developing Countries. GTZ and GATEWastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFChapter 4. Wastewater Technologies
Comprehensive overview (in form of factsheets) on the different components of wastewater treatment systems (collection, transfer, onsite treatment, centralised and decentralised treatment, reuse, sludge management and disposal) adapted to the Caribbean Region. Industrial wastewater treatment is also discussed.
UNEP (2004): Chapter 4. Wastewater Technologies. المُدخلات: UNEP (2004): A Directory of Environmentally Sound Technologies for the Integrated Management of Solid, Liquid and Hazardous Waste for SIDS in the Caribbean Region. Nairobi: 63-125.Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management"
Technical information on environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment.
UNEP ; MURDOCH UNIVERSITY (2004): Environmentally sound technologies in wastewater treatment for the implementation of the UNEP/GPA "Guidelines on Municipal Wastewater Management". The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP/GPA), Coordination OfficeTechnology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making
These guidance notes are designed to provide state governments and urban local bodies with additional information on available technologies on sanitation. The notes also aid in making an informed choice and explain the suitability of approaches.
WSP (2008): Technology Options for Urban Sanitation in India. A Guide to Decision-Making. pdf presentation. New Delhi: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Biological Filters: Trickling and RBC Design
The application of biological filters (fixed film processes) for the removal of ammonia from brackish or salt wastewaters from fish farms is discussed. The biological removal of ammonia in fixed-film processes is explained and design examples for ammonia removal in either trickling filters or rotating biological contactors are discussed.
HOCHHEIMER, J.N. WHETON, F.W. (1998): Biological Filters: Trickling and RBC Design. المُدخلات: LIBEY, G.S. ; TIMMONS, M.B. (1998): Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Recirculating Aquaculture Roanoke. Virginia: 291–318. URL [Accessed: 18.03.2010]Ecosan Greywater Demonstration Project. Case study from Kuching, Malaysia
The city of Kuching is currently lacking a wastewater treatment plant, and the local subsurface conditions make a conventional centralised wastewater system expensive to implement. Most buildings are equipped with two separate wastewater outlets, one outlet for blackwater and one for greywater. The proposed system treats greywater from nine households, and consists of a baffled septic tank, followed by a dosing chamber from where the greywater flows into four vertical down-flow, single-pass aerobic biofilters before reaching a subsurface horizontal-flow planted filter. Finally, the treated greywater is discharged into a stormwater drain.
MOREL A. DIENER S. (2006): Ecosan Greywater Demonstration Project. Case study from Kuching, Malaysia. المُدخلات: MOREL, A. ; DIENER, S. ; (2006): Greywater Management in Low and Middle-Income Countries, Review of Different Treatment Systems for Households or Neighbourhoods. Duebendorf: 76-79.Trickling Filter Design
Short PowerPoint Presentation on the design of trickling filters available on the Tropak Hompage hosted by the Turkish Dokuz Eylul University in Izmir.
LESIKAR, B. (2000): Trickling Filter Design. Izmir: Dokuz Eylul University URL [Accessed: 24.02.2010]Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 1
Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions gives a state-of-the-art presentation of the science and technology of biological wastewater treatment, particularly domestic sewage. The book covers the main treatment processes used worldwide with wastewater treatment in warm climate regions given a particular emphasis where simple, affordable and sustainable solutions are required. The 55 chapters are divided into 7 parts over two volumes: Volume One: (1) Introduction to wastewater characteristics, treatment and disposal; (2) Basic principles of wastewater treatment; (3) Stabilisation ponds; (4) Anaerobic reactors; Volume Two (also available in the SSWM library): (5) Activated sludge; (6) Aerobic biofilm reactors; (7) Sludge treatment and disposal.
SPERLING, M. von LEMOS CHERNICHARO, C.A. de (2005): Biological Wastewater Treatment in Warm Climate Regions Volume 1. London: International Water Association (IWA) Publishing URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Trickling Filters
Short Factsheet on the applicability and design criteria of trickling filters including a lot of information on operation and maintenance (form the United States Environment Protection Agency (EPA).
U.S. EPA (2000): Trickling Filters. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet, EPA 832-F , 14 ). United States Environment Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 03.06.2019]Trickling Filters Nitrification
Short factsheet on nitrification in trickling filters (form the United States Environment Protection Agency (EPA).
U.S.EPA (2000): Trickling Filters Nitrification. (= Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet, EPA 832-F , 15 ). United States Environment Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 17.05.2012]Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual
Rather old design manual for onsite wastewater treatment options. However, valuable information on established systems such as septic tanks, sand filters, aerobic treatment units (suspended growth and fixed film), disinfection, nutrient removal as well as wastewater segregation and recycling are given. Additional information is given on disposal methods and appurtenances.
U.S.EPA (1980): Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual. (= EPA 625/1-80 , 12 ). United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water Office of Research and Developmenthttp://en.wikipedia.org/
Wikipedia entry on trickling filters.

