تعمل محطات النقل (التحويل) أو الخزَّانات الحاوية تحت الأرض Transfer Station (Underground Holding Tank) كنقاط وسيطة لتصريف حمأة مياه المجاري، وذلك عندما يصعب نقلها إلى مرفق المُعالجة (شبه) المركزي. ويتطلب الأمر شاحنة شفط لتفريغ محطات النقل عند امتلائها.
يقوم مشغلو معدات تفريغ الحمأة التي تعمل يدويًّا أو المعدات الصغيرة ذات المُحركات بتصريف الحمأة إلى محطة النقل المحلية، بدلًا من التخلص منها بشكل غير قانوني، أو الانتقال من أجل تصريفها إلى موقع بعيد للمُعالجة أو التخلص. وعندما تمتلئ محطة النقل، تقوم شاحنة الشفط بتفريغ محتوياتها، وتُؤخذ الحمأة إلى مرفق مُعالجة مناسب. قد تَفرض البلديات أو الهيئات المعنية بالصرف الصحي الحصول على تصاريح للتصريف في محطة النقل؛ وذلك لتعويض تكاليف تشغيل وصيانة المرفق.
في المناطق الحضرية، يجب أن يتم تحديد أماكن محطات النقل بعناية، وإلا فقد تُصبح الروائح مصدرًا للإزعاج، وخاصةً إذا لم يتم صيانتها بشكلٍ جيد.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
الحمأة |
الحمأة |
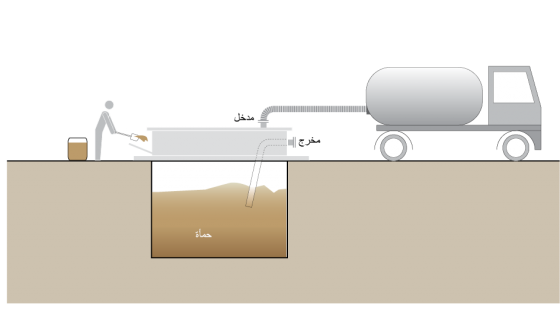
تكون محطات النقل مُناسِبة للمناطق الحضرية عالية الكثافة السكانية، حيث لا تُوجد نقطة تصريف بديلة لحمأة مياه المجاري. وقد يُساعد إنشاء عدة محطات للنقل على الحد من التخلص غير القانوني من الحمأة، وقد يُعزز ذلك أيضًا من سوق عمل تفريغ الحمأة.
تكون محطات النقل كافية خصوصًا في الأماكن التي يحدث بها تفريغ الحمأة على نطاقٍ صغير. كما أن في المدن الكبيرة يُمكنها أن تُقلل من التكاليف التي تتكبدها الشركات المُشغّلة للشاحنات عن طريق تقليل مسافات النقل، والحد من إهدار الوقت بسبب ازدحام المرور. ويُمكن لمقدمي خدمة التفريغ المحليين أن يقوموا بتصريف الحمأة في محطات النقل خلال النهار، بينما تقوم الشاحنات الكبيرة بتفريغ الخزَّانات والذهاب إلى محطة المُعالجة ليلًا عندما تكون حركة المرور خفيفة.
ينبغي أن تتواجد محطات النقل بحيث يمكن الوصول إليها بسهولة، وتكون مُناسِبة وسهلة الاستخدام. وعلى حسب عمليات الصيانة، فقد تُشكّل الروائح مشكلة للسكان المجاورين؛ ومع ذلك فإن الفوائد المُكتسبة من محطات النقل -مقارنةً بالتخلص غير القانوني من الحمأة في الهواء الطلق- قد تُعوِّض إلى حد كبير أيَّ مضايقات.
تتكون محطة النقل من: مكان لوقوف شاحنات الشفط أو عَرَبَات الجر الخاصة بالحمأة، ونقطة توصيل لخراطيم التصريف، وخزَّان. ويجب أن تكون نقطة التصريف منخفضة بما يكفي للحد من الانسكابات عند قيام العمال بتفريغ عَرَبَات الحمأة يدويًّا. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، ينبغي أن تحتوي محطة النقل على فتحة تهوية، وشبكة حجز المخلفات لإزالة القمامة، ومرفق لغسل الشاحنات. ويجب أن يتم إنشاء الخزَّان الحاوي بشكلٍ جيد، لمنع التسرب و/أو رشح المياه السطحية إليه.
وهناك اختلاف بين محطة النقل )التحويل( ومحطة تصريف شبكة المجاري )محطة الرفع(Sewer Discharge Station (SDS)، حيث تتشابه محطة الرفع مع محطة النقل، ولكنها ترتبط مباشرةً بشبكة صرف صحي تقليدية بقوة الجاذبية؛ حيث يتم ضخ الحمأة المفرَّغة في محطة الرفع في شبكة الصرف الصحي الرئيسية، إما مباشرةً أو على فترات زمنية مُحدَّدة؛ وذلك لتحسين أداء شبكة الصرف الصحي ومحطة مُعالجة مياه الصرف و/أو تقليل أحمال الذروة Peak Loads.
يمكن تجهيز محطات النقل بأجهزة رقمية لتسجيل البيانات لمتابعة الكميات وأنواع المُدخلات ومصادرها، وكذلك لجمع بيانات الأشخاص الذين يُصَرِّفون في المحطة، وبهذه الطريقة، يتمكن مسؤول التشغيل من جمع معلومات مُفصَّلة، والقيام بالتخطيط والاستعداد السليم للأحمال المختلفة.
يجب أن يتم تحديد نظام إصدار التصاريح أو فرض رسوم الدخول للمحطات بعناية، بحيث لا يتم استبعاد الأشخاص الراغبين في الخدمة بسبب ارتفاع التكاليف، مع الوضع في الاعتبار توليد دخلٍ كافٍ لتشغيل وصيانة محطات النقل على نحوٍ مستدام.
تمتلك محطات النقل القدرة على تحسين صحة المجتمع بشكلّ كبير، وذلك عن طريق تزويد المجتمع بحل محلي غير باهظ التكلفة للتخلص من حمأة مياه المجاري. وبتوفير محطات النقل، لم يعُد مقدمو خدمات التفريغ المستقلون -أو على نطاق صغير- مُجبرين على تصريف الحمأة بطريقة غير قانونية، وأصبح مالكو المنازل أكثر استعدادًا لتفريغ الحُفر الخاصة بهم. وعندما يتم تفريغ الحُفر بشكلٍ مُنتظم، ويتم الحد من التخلص غير القانوني للحمأة؛ يُمكن أن تتحسن الصحة العامة للمجتمع بشكلٍ ملحوظ. ويجب اختيار الموقع بعناية لتحقيق أقصى قدرًا من الكفاءة، وللحد من الروائح والمشاكل لسكان المناطق القريبة.
يجب تنظيف شبكات حجز المخلفات من وقت لآخر لضمان التدفق المستمر ومنع ارتداد المياه. ويجب أيضًا إزالة الحصى والرمال والحمأة المتراكمة بشكل دوري من الخزَّان. ويجب أن يكون هناك نظام جيد لتفريغ محطة النقل؛ حيث إن طفح الخزَّان الممتلئ بالكامل ليس بأحسن حالًا من طفح الحُفرة. وينبغي تنظيف منصة ومنطقة التحميل بانتظام لتقليل الروائح الكريهة، والذباب، وناقلات الأمراض الأخرى قبل أن تُشكّل إزعاجًا.
الدليل التصميمى لمحطات معالجة مياة الصرف الصحى بالمملكة .
Language: Arabic
الكود المصري لتصميم وتنفيذ خطوط المواسير لشبكات مياة الشرب والصرف الصحي
Accra Sewerage Improvement Project (ASIP)
This report describes the Accra Sewerage Improvement Project (ASIP) that will provide two new major sewage treatment plants at Densu Delta and Legon to cover the 2020 horizon. The project will comprise the six compontents: (A) Treatment Plants and Pumping Stations, (B) Sewerage Networks and Sanitation Facilities, (C) Environmental Measures, (D) Institutional Strengthening, (E) Engineering Services, and (F) Project Management.
AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT FUND (2005): Accra Sewerage Improvement Project (ASIP). (= Appraisal Report ). Abidjan: Infrastructure Department Central and West Regions URL [Accessed: 30.07.2014]Faecal Sludge in Accra, Ghana: Problems of Urban Provision
Urban on-site sanitation services present challenges for emptying, transporting, disposing and treating faecal waste. Transfer stations can be used by household-level emptiers to safely dispose of faecal sludge, but they rarely exist. Accra's use of transfer stations has provided an opportunity to research their functioning, as part of broader faecal sludge management arrangements. The paper discusses the benefits offered by use of transfer stations, as well as reasons currently limiting their operation. The paper concludes that correct use of transfer stations can provide improvements for existing faecal sludge management and reduce indiscriminate dumping.
BOOT, N. L. ; SCOTT, R. E. (2009): Faecal Sludge in Accra, Ghana: Problems of Urban Provision. المُدخلات: Water Science Technology: Volume 60 , 623-631.Business Analysis of Fecal Sludge Management: Emptying and Transportation Services in Africa and Asia
This study maps the urban sanitation situation and assesses business and operating models for fecal sludge management in 30 cities across 10 countries in Africa and Asia, specifically focussing on the extraction and transportation market segments.
CHOWDHRY, S. KONE, D. (2012): Business Analysis of Fecal Sludge Management: Emptying and Transportation Services in Africa and Asia. Seattle: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation URL [Accessed: 22.07.2014]Faecal Sludge Management
This is the first book to compile the current state of knowledge on faecal sludge management. It addresses the organization of the entire faecal sludge management service chain, from the collection and transport of sludge, to the current state of knowledge of treatment options, and the final end use or disposal of treated sludge. It presents an integrated approach that brings together technology, management, and planning, based on Sandec’s 20 years of experience in the field. It also discusses important factors to consider when evaluating and upscaling new treatment technology options. The book is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, engineers, and practitioners in the field who have some basic knowledge of environmental and/or wastewater engineering.
STRANDE, L. ; RONTELTAP, M. ; BRDJANOVIC, D. (2014): Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation. London: IWA Publishing URL [Accessed: 16.07.2014]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFGuide to Septage Treatment and Disposal
The purpose of this guide is to present practical information on the handling, treatment, and disposal of septage in a concise, recommendations-oriented format for easy use by administrators of waste management programs, septage haulers, and managers or operators of septage handling facilities. The guide is not intended to provide detailed engineering design information.
U.S. EPA (1994): Guide to Septage Treatment and Disposal. (= EPA/625/R-94/002 ). Washingtion D.C.: United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development URL [Accessed: 30.05.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFFaecal Sludge Management
This is the first book to compile the current state of knowledge on faecal sludge management. It addresses the organization of the entire faecal sludge management service chain, from the collection and transport of sludge, to the current state of knowledge of treatment options, and the final end use or disposal of treated sludge. It presents an integrated approach that brings together technology, management, and planning, based on Sandec’s 20 years of experience in the field. It also discusses important factors to consider when evaluating and upscaling new treatment technology options. The book is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, engineers, and practitioners in the field who have some basic knowledge of environmental and/or wastewater engineering.
STRANDE, L. ; RONTELTAP, M. ; BRDJANOVIC, D. (2014): Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation. London: IWA Publishing URL [Accessed: 16.07.2014]Liquid Industrial Waste Holding Tanks
This is a technical paper about liquid waste holding tanks and their construction.
GRANHOLM, J.M. CHESTER, S.E. (2007): Liquid Industrial Waste Holding Tanks. Lansing: Michigan Department Of Environmental Qualityhttp://michigan.gov/documents/deq/deq-ess-p2tas-liwholdingtank_207979_7.pdf URL [Accessed: 24.01.2011]Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes
This module pays special attention to the haulage, treatment and reuse or disposal of faecal sludge. It covers both technical and non-technical (socio-cultural, economic, political etc.) aspects and provides practical information on design, financing and planning of faecal sludge treatment plants.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]Towards an Improved Faecal Sludge Management (FSM)
More than two billion urban dwellers in developing countries use on-site sanitation facilities such as pit latrines, septic tanks and aqua privies for excreta and wastewater disposal. Since on-site sanitation installations will serve the growing urban populations in developing countries for decades to come, increasing faecal sludge quantities will have to be managed. Proper faecal sludge management (FSM) is the important link missing in integrated urban sanitation upgrading efforts.
KONE, D. STRAUSS, M. SAYWELL, D. (2007): Towards an Improved Faecal Sludge Management (FSM). Duebendorf: EAWAG/SANDEC URL [Accessed: 15.12.2010]Smart Sanitation Solutions
Smart Sanitation Solutions presents examples of low-cost household and community-based sanitation solutions that have proven effective and affordable. A wide range of innovative technologies for toilets, collection, transportation, treatment and use of sanitation products that have already helped thousands of poor families to improve their lives is illustrated.
NWP (2006): Smart Sanitation Solutions. Examples of innovative, low-cost technologies for toilets, collection, transportation, treatment and use of sanitation products. (= Smart water solutions ). Amsterdam: Netherlands Water Partnership (NWP) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. LUETHI, C. MOREL, A. ZURBRUEGG, C. SCHERTENLEIB, R. (2008): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) and Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) URL [Accessed: 15.02.2010] PDFA Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation
The publication presents appropriate technologies for sanitation and highlights socio-economic aspects of planning and implementing. Emphasis is given to household-level sanitation improvements for urban areas, as well as rural areas and small communities. Background information on sanitation, in-depth technical information on the design, construction, operation and maintenance and project planning and development processes involved in projects and programmes complement the book.
WHO (1992): A Guide to the Development of On-site Sanitation. Geneva: World Health Organisation (WHO) URL [Accessed: 14.04.2010]Accra Sewerage Improvement Project (ASIP)
This report describes the Accra Sewerage Improvement Project (ASIP) that will provide two new major sewage treatment plants at Densu Delta and Legon to cover the 2020 horizon. The project will comprise the six compontents: (A) Treatment Plants and Pumping Stations, (B) Sewerage Networks and Sanitation Facilities, (C) Environmental Measures, (D) Institutional Strengthening, (E) Engineering Services, and (F) Project Management.
AFRICAN DEVELOPMENT FUND (2005): Accra Sewerage Improvement Project (ASIP). (= Appraisal Report ). Abidjan: Infrastructure Department Central and West Regions URL [Accessed: 30.07.2014]Faecal Sludge Management in Accra, Ghana: Strengthening Links in the Chain
This case study is about a research in Accra (Ghana), which has identified important constraints to achieving an efficient and fully functioning faecal sludge management (FSM) chain, with consequences for both people and the environment. Opportunities to improve the institutional and operating environment are identified, particularly affecting engagement between the public and private sector and civil society.
BOOT, N. SCOTT, R. (2008): Faecal Sludge Management in Accra, Ghana: Strengthening Links in the Chain. Loughborough: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) URL [Accessed: 24.01.2011]Business Analysis of Fecal Sludge Management: Emptying and Transportation Services in Africa and Asia
This study maps the urban sanitation situation and assesses business and operating models for fecal sludge management in 30 cities across 10 countries in Africa and Asia, specifically focussing on the extraction and transportation market segments.
CHOWDHRY, S. KONE, D. (2012): Business Analysis of Fecal Sludge Management: Emptying and Transportation Services in Africa and Asia. Seattle: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation URL [Accessed: 22.07.2014]Guide to Septage Treatment and Disposal
The purpose of this guide is to present practical information on the handling, treatment, and disposal of septage in a concise, recommendations-oriented format for easy use by administrators of waste management programs, septage haulers, and managers or operators of septage handling facilities. The guide is not intended to provide detailed engineering design information.
U.S. EPA (1994): Guide to Septage Treatment and Disposal. (= EPA/625/R-94/002 ). Washingtion D.C.: United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development URL [Accessed: 30.05.2019]Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation
A presentation about faecal sludge management in developing countries.
EAWAG ; SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (Eawag), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (Sandec) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]
