يشير التفريغ والنقل بالمجهود البشري Human-Powered Emptying and Transport إلى الطرق اليدوية المختلفة التي تمكن الأشخاص من تفريغ و/أو نقل الحمأة وفضلات الجسم الصلبة المتولدة بالموقع داخل مرافق الصرف الصحي.
وتتم عملية التفريغ اليدوي للحُفر، والحُجرات، والخزَّانات بإحدى هاتين الطريقتين:
1) استخدام الدِلاء والجواريف، أو
2) استخدام المضخات (الطلمبات أو الطرمبات) اليدوية المُتنقلة والمصممة لتفريغ الحمأة ومنها على سبيل المثال: مضخات السحب Gulpers، أو المضخات الهزازة Rammers، أو مضخات نزح الحمأة يدويًّا MDHP، أو مضخات تفريغ الحُفر يدويًّا MAPET.
بعض تقنيات الصرف الصحي لا يمكن تفريغها إلا باستخدام الطرق اليدوية، على سبيل المثال: حُفرة ألترنا وحُجرات التجفيف ، حيث يجب استخدام الجاروف للتفريغ؛ نظرًا لأن محتوى هاتين التقنيتين يكون صلبًا، ولا يمكن إزالته باستخدام شفاط أو مضخة. أما في حالة تفريغ الحمأة الرطبة أو اللزجة فينبغي استخدام المضخة اليدوية أو شاحنة الشفط، ولا ينبغي تفريغها باستخدام الدِلاء نظرًا لارتفاع مخاطر انهيار الحُفر، والأبخرة السامة، والتعرض للحمأة غير المُعقمة.
وتُعتبر مضخات الحمأة اليدوية من الاختراعات الحديثة نسبيًّا، كما أنها بدت من الوسائل الواعدة كونها حل فعَّال منخفض التكلفة لتفريغ الحمأة، وذلك لعدة أسباب سواء سهولة الوصول، أو السلامة، أو التكلفة الاقتصادية، أو عندما يتعثر استخدام تقنيات تفريغ أخرى
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
الحمأة ,السماد العضوي , البراز المجفف , دبال الحفرة |
الحمأة ,السماد العضوي , البراز المجفف , دبال الحفرة |
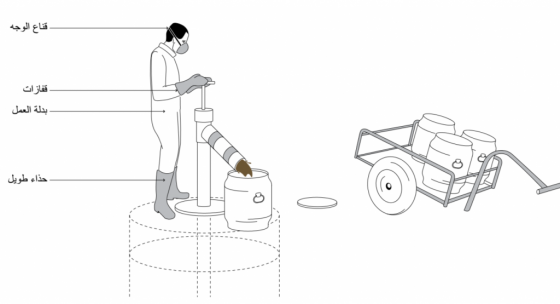
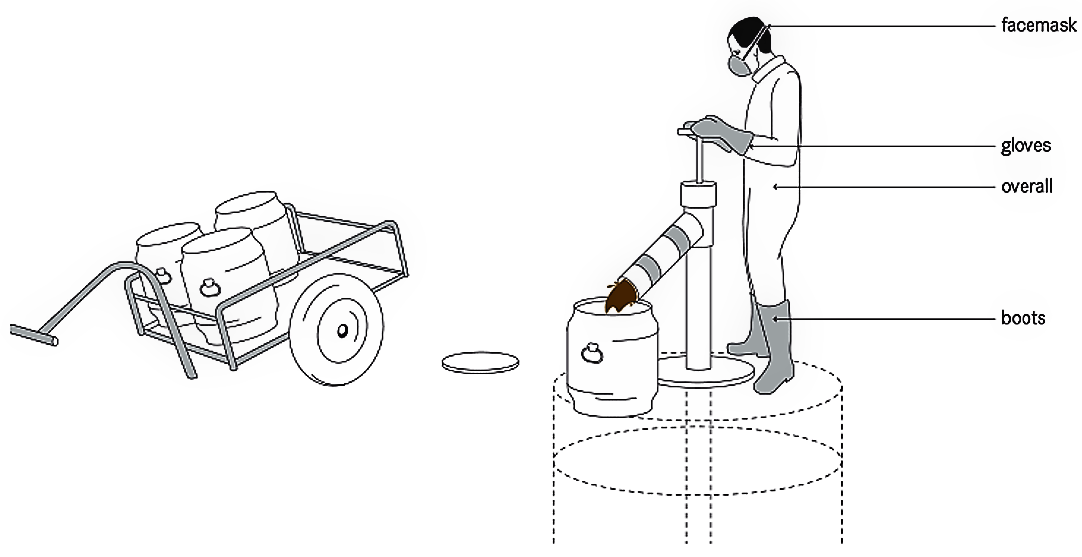
Human-powered emptying of pits, vaults and tanks can be done in one of two ways:
- using buckets and shovels, or
- using a portable, manually operated pump specially designed for sludge (e.g., the Gulper, the Rammer, the MDHP or the MAPET).
Some sanitation technologies can only be emptied manually, for example, the fossa alternaor dehydration vaults. These technologies must be emptied with a shovel because the material is solid and cannot be removed with a vacuum or a pump (e.g. the fossa alterna, aroborloo, composting toilets or UDDTs).
When sludge is viscous or watery it should be emptied with a hand pump, a MAPET or a vacuum truck, and not with buckets because of the high risk of collapsing pits, toxic fumes, and exposure to unsanitised sludge.
Manual sludge pumps are relatively new inventions and have shown promise as being low-cost, effective solutions for sludge emptying where, because of access, safety or economics, other emptying techniques are not possible.
صُممت مضخات الحمأة اليدوية )مثل مضخات السحب Gulpers( للعمل بنفس مفهوم مضخات المياه اليدوية، حيث يتم إنزال طرف الأنبوب داخل الحُفرة أو الخزَّان بينما يبقى الشخص القائم بالتشغيل على السطح؛ وعندما يقوم القائم بالتشغيل بدفع وسحب مقبض المضخة، يتم ضخ الحمأة إلى الأعلى ثم تصريفها عبر فتحة التصريف. ويمكن جمع الحمأة داخل براميل، أو أكياس، أو عربات وإزالتها من الموقع مع عدم وقوع ضرر على القائم بالتشغيل إلا في أضيق الحدود. هذا ويمكن صنع المضخات اليدوية محليًّا باستخدام قضبان مُصنعة من الفولاذ، وصمامات، وأغلفة من بلاستيك البولي ڨينيل كلوريد PVC.
تتكون تقنية تفريغ الحُفر يدويًّا Manual Pit Emptying Technology: MAPET من مضخة تعمل يدويًّا متصلة بخزَّان شفط مُحمَّل على عربة تُدفع باليد. ويقوم الخرطوم المتصل بالخزَّان بسحب الحمأة من داخل الحُفرة. فبمجرد تدوير عجلة المضخة اليدوية، يُفرَّغ خزَّان الشفط من الهواء محدثًا فارق في الضغط؛ يعمل على سحب الحمأة إلى أعلى باتجاه الخزَّان. وبالاعتماد على درجة تجانس الحمأة، يمكن لتقنية تفريغ الحُفر يدويًّا MAPET أن تَضُخ الحمأة إلى ارتفاعات قد تصل إلى ثلاثة أمتار.
بناءً على العوامل الثقافية والدعم السياسي، فإنه يُمكن النظر إلى العمال الذين يقومون بالتفريغ اليدوي على أنهم يقومون بتوفير خدمة مهمة للمجتمع. وينبغي على البرامج التي تُديرها الحكومة، أن تسعى لإضفاء الشرعية على عمل هؤلاء العمال، وخلق بيئة مواتية Enabling Environment من خلال توفير التصاريح والتراخيص، بالإضافة إلى المساعدة على تشريع ممارسة تفريغ المراحيض يدويًّا.
يُعتبر حماية العمال بشكل ملائم هو الجانب الأكثر أهمية في التفريغ اليدوي، وذلك باستخدام: القفازات، والأحذية الطويلة Boots، وبدلات العمل Overalls، وأقنعة الوجه. كذلك ينبغي -بشكل دوريّ- عَمل الفحوصات الطبية وإعطاء التطعيمات اللازمة لكل المُتعاملين مع الحمأة.
تُعتبَر إضافة الكيماويات أو النفط، خلال عملية تفريغ الحُفر لتجنب الروائح من الممارسات الشائعة؛ إلا إنه لا يُنصَح بهذه الممارسة؛ لأنها تُسبب صعوبات في وحدات المُعالجة بعد ذلك، بالإضافة إلى المخاطر على صحة العمال.
إذا تطلب تفريغ الحُفر يدويًّا هدم البلاطة الأرضية Slab؛ فإن استخدام مضخة الحمأة اليدوية في هذه الحالة يُصبح أوفر في التكلفة. ومع ذلك فإن المضخة اليدوية لا يمكنها تفريغ الحُفرة بشكلٍ كامل، وبالتالي ينبغي تفريغ الحُفرة بشكل ممتكرر )مرة فياالعام(
تحتاج مضخات الحمأة التي تُدَار يدويًّا إلى عمليات الصيانة االيومية ( التنظيف، والإصلاح، والتطهير)وعلى العمالالذين يقومون بتفريغ المراحيض يدويًّا أن يقوموا بتنظيف وصيانة أدواتهم وملابسهم الواقية؛ لمنع أي تلامس مع الحمأة.
المياه ،الصرف الصحي النظافة الصحية وظروف الإقامة في السجون
بناء الحمامات وطرق تحسينها وصيانتها
Guidance Manual on Water Supply and Sanitation Programmes
This manual has been prepared as a tool to help improve DFID's (Department for International Developments, United Kingdom) support for water supply and sanitation projects and programmes in developing countries. Its particular focus is on how DFID assistance can best meet the needs of the urban and rural poor for water supply and sanitation services.
DFID (1998): Guidance Manual on Water Supply and Sanitation Programmes. London: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) for the Department for International Development (DFID) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2018]Bringing pit emptying out of the darkness
This paper is one of a series that look sanitation partnerships in poor urban communities, that questions when and why partnership may be appropriate or inappropriate to the delivery of on-site sanitation services. It is a comparison of two manual emptying projects.
EALES, K. (2005): Bringing pit emptying out of the darkness. A comparison of approaches in Durban, South Africa, and Kibera, Kenya. United Kingdom: Building Partnerships for Development in Water and Sanitation URL [Accessed: 21.10.2013]Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes
This module pays special attention to the haulage, treatment and reuse or disposal of faecal sludge. It covers both technical and non-technical (socio-cultural, economic, political etc.) aspects and provides practical information on design, financing and planning of faecal sludge treatment plants.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]The Gulper – a manual latrine/drain pit pump
This short document describes the functioning of the gulper technology to empty pit latrines or septic tanks.
IaW (2007): The Gulper – a manual latrine/drain pit pump. Phnom Penh/Casteren: Ideas at Work (IaW) URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]MAPET. A neighbourhood based pit emptying service with locally manufactured hand pump equipment in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
This document is the final report of the MAPET project in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Project objectives were to contribute to the improvement of environmental sanitation in unplanned areas by facilitating an effective and hygienic pit emptying services, and to improve the informal traditional pit emptying method by making it more efficient and hygienic.
MULLER, M.S. RIJNSBURGER J. (1992): MAPET. A neighbourhood based pit emptying service with locally manufactured hand pump equipment in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Gouda: WASTE advisers on urban environment and development URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]Manual Desludging Hand Pump (MDHP)
This paper introduces manual desludging hand pump. The design, its use and maintenance is illustrated with many images.
OXFAM (n.y): Manual Desludging Hand Pump (MDHP). Various places: Oxfam International URL [Accessed: 09.12.2010]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFAdventures in search of the ideal portable pit-emptying machine
This article explores the ideal portable pit-emptying machine for South Africa owing to site access constraints. The Water Research Commission of South Africa funded experimental development of a number of technologies designed to fill the gap between large vacuum tankers and manual emptying. This paper describes these attempts.
STILL, D. O RIORDAN, M. MC BRIDE, A. LOUTON, B. (2013): Adventures in search of the ideal portable pit-emptying machine. Rugby: Practical Action Publishing URL [Accessed: 07.08.2013]Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes
This module pays special attention to the haulage, treatment and reuse or disposal of faecal sludge. It covers both technical and non-technical (socio-cultural, economic, political etc.) aspects and provides practical information on design, financing and planning of faecal sludge treatment plants.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]MAPET. A neighbourhood based pit emptying service with locally manufactured hand pump equipment in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania
This document is the final report of the MAPET project in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Project objectives were to contribute to the improvement of environmental sanitation in unplanned areas by facilitating an effective and hygienic pit emptying services, and to improve the informal traditional pit emptying method by making it more efficient and hygienic.
MULLER, M.S. RIJNSBURGER J. (1992): MAPET. A neighbourhood based pit emptying service with locally manufactured hand pump equipment in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Gouda: WASTE advisers on urban environment and development URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation
The purpose of this guide is to assist local contracting authorities and their partners in identifying those sanitation technologies best suited to the different contexts that exist within their town. The first part of the guide contains a planning process and a set of criteria to be completed; these assist you in characterizing each area of intervention so that you are then in a position to identify the most appropriate technical solutions. The second part of the guide consists of technical factsheets which give a practical overview of the technical and economic characteristics, the operating principle and the pros and cons of the 29 sanitation technology options most commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa.
MONVOIS, J. GABERT, J. FRENOUX, C. GUILLAUME, M. (2010): How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 4 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Manual Desludging Hand Pump (MDHP)
This paper introduces manual desludging hand pump. The design, its use and maintenance is illustrated with many images.
OXFAM (n.y): Manual Desludging Hand Pump (MDHP). Various places: Oxfam International URL [Accessed: 09.12.2010]Microbial Exposure and Health Assessments in Sanitation Technologies and Systems
This book focuses on the health factors related to pathogenic organisms. The attempt is to assess and review evidences in relation to health impact and to discuss the findings based on epidemiological evidence, risk assessment and behavioural aspects and practices.
STENSTROEM, A. SEIDU, R. EKANE, M. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2011): Microbial Exposure and Health Assessments in Sanitation Technologies and Systems. (= EcoSanRes Series , 1 ). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute (SEI) URL [Accessed: 28.11.2011]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. LUETHI, C. MOREL, A. ZURBRUEGG, C. SCHERTENLEIB, R. (2008): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) and Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council (WSSCC) URL [Accessed: 15.02.2010] PDFEmptying Pit Latrines
This technical brief describes several possibilities of emptying pit latrines and helps to find the most suitable method.
PICKFORD, J. SHAW, R. (1997): Emptying Pit Latrines. (= Technical Briefs, No. 54 ). Loughborough: Water and Environmental health at London and Loughborough (WELL) URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]Bringing pit emptying out of the darkness
This paper is one of a series that look sanitation partnerships in poor urban communities, that questions when and why partnership may be appropriate or inappropriate to the delivery of on-site sanitation services. It is a comparison of two manual emptying projects.
EALES, K. (2005): Bringing pit emptying out of the darkness. A comparison of approaches in Durban, South Africa, and Kibera, Kenya. United Kingdom: Building Partnerships for Development in Water and Sanitation URL [Accessed: 21.10.2013]The Gulper – a manual latrine/drain pit pump
This short document describes the functioning of the gulper technology to empty pit latrines or septic tanks.
IaW (2007): The Gulper – a manual latrine/drain pit pump. Phnom Penh/Casteren: Ideas at Work (IaW) URL [Accessed: 28.05.2019]Manual Desludging Hand Pump (MDHP)
This paper introduces manual desludging hand pump. The design, its use and maintenance is illustrated with many images.
OXFAM (n.y): Manual Desludging Hand Pump (MDHP). Various places: Oxfam International URL [Accessed: 09.12.2010]After the Pit Latrine is Full. What Then? Effective Options for Pit Latrine Management
In rural areas, the Ventilated Improved Pit Latrine (VIP) is often considered as the basic standard for sanitation. Large numbers of VIPs have even been constructed in urban areas where other sanitation options were not economically feasible. Pit filling times vary widely depending on factors such as numbers of users, soil type and pit lining methodology. Pits are also generally used for solid waste disposal, and this hastens the filling time.
STILL, D.A. (2002): After the Pit Latrine is Full. What Then? Effective Options for Pit Latrine Management. Pretoria: Water Research Commission URL [Accessed: 09.12.2010]Environmental Health. Presentation
This PowerPoint presentation contains information on environmental health aspects of water and sanitation. It contains a definition of environmental health, describes various water-related diseases and also hygiene approaches. There is also a related lecture to this document.
EAWAG ; SANDEC (2008): Environmental Health. Presentation. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 2 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation
A presentation about faecal sludge management in developing countries.
EAWAG ; SANDEC (2008): Faecal Sludge Management. Pdf Presentation. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 5 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (Eawag), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (Sandec) URL [Accessed: 23.05.2012]Pit Emptying Business in Temeke-Dsm. Tanzania Country Programme
A chapter of this presentation shows experiences with the latrine emptying technology ‘gulper’.
WATERAID (2010): Pit Emptying Business in Temeke-Dsm. Tanzania Country Programme. London: WaterAid URL [Accessed: 13.12.2010]http://desludging.org/
This website contains all important information about the manual desludging hand pump.
http://www.flickr.com/gtzecosan
Pictures about the reality of manual pit emptying in Kenya.

