التخلص السطحي Surface Disposal يشير إلى تشوين (الجمع في أكوام) الحمأة، أو البُراز، أو المواد الأخرى التي لا يتم استخدامها في أي مكان آخر؛ وبمجرد نقل المواد إلى موقع التخلص السطحي، لا يتم استخدامها لاحقًا. التخزين Storage يُشير إلى عملية التشوين المؤقتة، والتي يمكن عملها عندما لا توجد حاجة لاستخدام المواد في الوقت الحالي ومن المتوقع استخدامها في المستقبل، أو عند الرغبة في الحد من مسببات الأمراض بشكلٍ أكبر، أو تجفيف المواد قبل استعمالها.
تُستخدم هذه التقنية في المقام الأول للتعامل مع الحمأة، على الرغم من أنه يمكن استخدامها مع أي نوع من المواد الجافة غير المستخدمة. أحد استخدامات التخلص السطحي هي التخلص من مواد التنظيف الجافة مثل المناديل (ورق التواليت)، أكواز الذرة، الحجارة، أوراق الجرائد، و/أو أوراق الأشجار؛ هذه المواد لا يتم -دائمًا- التخلص منها مع المُنتجات السائلة في بعض التقنيات، ويلزم فصلها؛ حيث ينبغى توفير سلة مهملات بجانب واجهة المستخدم لتجميع مواد التنظيف الجافة ومواد النظافة أثناء الطمث. يمكن حرق المواد الجافة (مثل: أكواز الذرة) أو التخلص منها مع المخلفات المنزلية.
عندما لا توجد حاجة أو قبول للاستخدامات المفيدة للحمأة، يمكن وضعها في مدافن النفايات الأحادية Monofills (مدافن للحمأة فقط) أو يمكن تكويمها في أكوام دائمة. يساهم التخزين المؤقت في زيادة جفاف المُنتجات، والتخلص التام من مسببات الأمراض الموجودة بها قبل استخدامها.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
| الحمأة دبال الحفرة , السماد العضوي، البراز المجفف، مواد التنظيف الجافة، مخلفات المعالجة الاولية , |
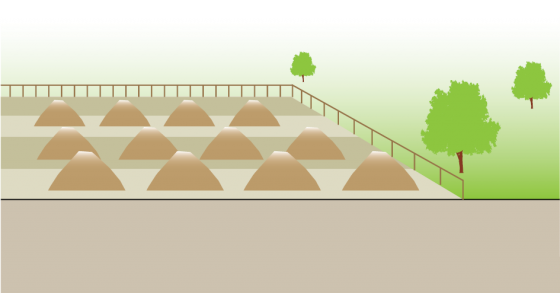
This technology is primarily used for sludge, although it is applicable for any type of dry, unusable material. One application of surface disposal is the disposal of dry cleansing materials, such as toilet paper, corn cobs, stones, newspaper and/or leaves. These materials cannot always be included along with other water-based products in some technologies and must be separated. A rubbish bin should be provided beside the user interface to collect the cleansing materials and menstrual hygiene materials. Dry materials can be burned (e.g., corn cobs) or disposed of along with the household waste. For simplicity, the remainder of this technology information sheet will be dedicated to sludge since standard solid waste practices are beyond the scope of the Compendium.When there is no demand for or acceptance of the beneficial use of sludge, it can be placed in monofills (sludge-only landfills) or heaped into permanent piles. Temporary storage contributes to further dehydration of the product and the die-off of pathogens before it is used.
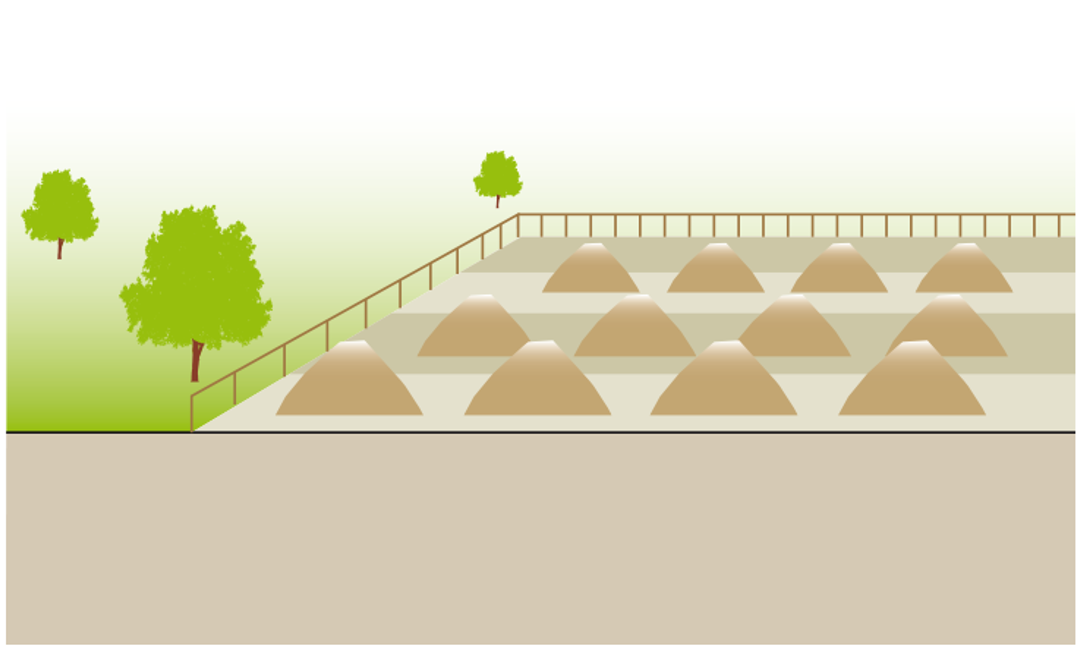
لا يُنصح بدفن )طمر( الحمأة مع المخلفات المنزلية الصلبة، لأن ذلك يقلل من عُمر المَدفن Landfill الذي صُمم خصيصًا لتجميع المواد الأكثر ضررًا. خلافًا لمدافن المخلفات المنزلية الصلبة الأكثر مركزية، يمكن لمواقع التخلص السطحي أن تقع بالقرب من أماكن مُعالجة الحمأة، لتقلل بذلك الاحتياج للنقل لمسافات طويلة.
الفارق الرئيسي بين التخلص السطحي والتطبيق في الأرض )استخدام الحمأة( هو معدل وسرعة التخلص؛ فلا توجد حدود لكميات الحمأة التي يمكن التخلص منها سطحيًا، حيث إن أحمال المُغذيات أو معدلات الزراعة ليست خاضعة للاهتمام هنا. بالرغم من ذلك، يجب الانتباه لتلوث المياه الجوفية والارتشاح. قد تتضمن الأنظمة الأكثر تقدمًا للتخلص السطحي البطانة الجيدة ونظام لجمع السوائل المرتشحة، وذلك لمنع المُغذيات والملوثات من التسرب إلى المياه الجوفية.
يجب تغطية مواقع التخزين المؤقت للمُنتجات، وذلك لتفادي بللها بمياه الأمطار أو توليد السوائل المرتشحة.
إذا كان موقع التخلص السطحي والتخزين محميًا )على سبيل المثال، بواسطة سياج( ويقع على مسافة بعيدة من العامة فينبغي ألا يكون هناك أي خطر من التعرض للمواد أو الإزعاج. ينبغي منع تلوث موارد المياه الجوفية بالسوائل المرتشحة عن طريق تحديد الموقع والتصميم الملائمين. ويجب توخي الحذر لحماية موقع التخلص أو التخزين من الحشرات، وتجميع المياه، فكلاهما قد يؤدي إلى تفاقم مشاكل الروائح وناقلات الأمراض.
يجب أن يتأكد العاملون أنه يتم التخلص من المواد المناسبة فقط في الموقع، ويجب المحافظة على التحكم في كثافة الحركة في الموقع وعدد ساعات التشغيل. كما يجب على العاملين ارتداء الملابس الواقية المناسبة.
تقييم كفاءة محطة معالجة مياه الصرف الصحي في النجف الأشرف
التلوث : المخاطر والحلول
Florida Commission Considers Sewage Sludge Rule Changes
Faecal Sludge Management
This is the first book to compile the current state of knowledge on faecal sludge management. It addresses the organization of the entire faecal sludge management service chain, from the collection and transport of sludge, to the current state of knowledge of treatment options, and the final end use or disposal of treated sludge. It presents an integrated approach that brings together technology, management, and planning, based on Sandec’s 20 years of experience in the field. It also discusses important factors to consider when evaluating and upscaling new treatment technology options. The book is designed for undergraduate and graduate students, engineers, and practitioners in the field who have some basic knowledge of environmental and/or wastewater engineering.
STRANDE, L. ; RONTELTAP, M. ; BRDJANOVIC, D. (2014): Faecal Sludge Management. Systems Approach for Implementation and Operation. London: IWA Publishing URL [Accessed: 16.07.2014]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFBiosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States
This report gives an overview on the use and disposal of biosolids/sewage sludge in the US between 1998 and 2010.
U.S. EPA (1999): Biosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States. Washington: United States Environmental Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]A Plain English Guide to the EPA Part 503 Biosolids Rule
Environmental Impacts Associated with Disposal of Saline Water Produced During Petroleum Production
Organic Wastes
Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFTechnology Review of Composting Toilets
This GIZ publication explains the design, use and operational requirements of composting toilets. Ample examples for composting toilets from around the world are included in the publication to show that these types of toilets have a wide range of applications under a variety of circumstances (for wealthy or poor people; for cold, hot, wet or dry climates; for urban or rural settings). The appendix contains a listing of suppliers.
BERGER, W. (2011): Technology Review of Composting Toilets. Eschborn: Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) URL [Accessed: 12.05.2019]Decentralised Composting for Cities of Low- and Middle-Income Countries – A User’s Manual
This book describes approaches and methods of composting on neighbourhood level in small-and middle-scale plants. It considers issues of waste collection, composting technologies, management systems, occupational health concerns, product quality, marketing and end-user demands.
DRESCHER, S. ZURBRUEGG, C. ENAYETULLAH, I. SINGHA, M.A.D. (2006): Decentralised Composting for Cities of Low- and Middle-Income Countries – A User’s Manual. Dhaka: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) and Waste Concern URL [Accessed: 16.08.2010]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFBiosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States
This report gives an overview on the use and disposal of biosolids/sewage sludge in the US between 1998 and 2010.
U.S. EPA (1999): Biosolids Generation, Use, and Disposal in the United States. Washington: United States Environmental Protection Agency URL [Accessed: 26.05.2019]Chapter 15. Case Studies
These three case studies illustrate a range of surface disposal activities being conducted throughout the United States. Activities covered include surface disposal of sewage sludge in a monofill, at a dedicated disposal site, and at a dedicated beneficial use site, in addition to sludge storage in lagoons prior to final disposal.
U.S. EPA (1995): Chapter 15. Case Studies. المُدخلات: U.S. EPA (1995): Surface Disposal of Sewage Sludge and Domestic septage. Process Design Manual. Washington: 251-265. URL [Accessed: 24.08.2010]

