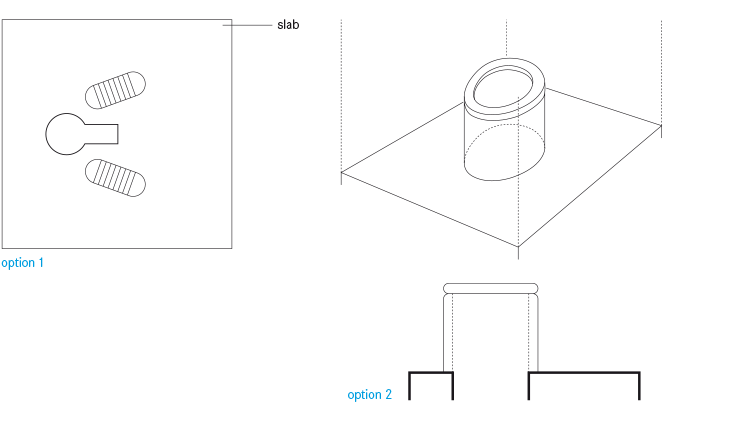
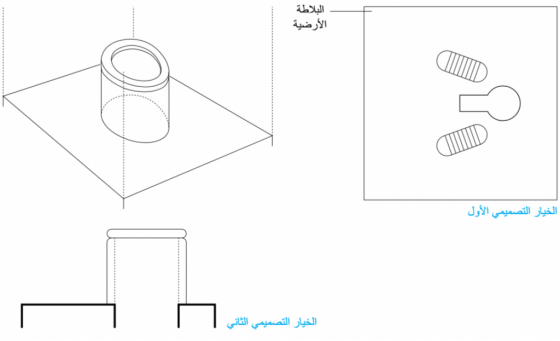
المِرحاض الجاف Dry Toilet هو مِرحاض يعمل بدون مياه الدفْق، وقد يكون المِرحاض الجاف عبارة عن قاعدة مِرحاض مرتفعة يستعملها المُستخدم بالجلوس عليها، أو قد يكون بلاطة أرضية يستعملها المُستخدم للجلوس فوقها بوضعية القُرفصاء دون ملامستها. وفي كلتا الحالتين تُجمع فضلات الجسم -كلٌّ من البول والبُراز- في فتحة التجميع.
يشير المِرحاض الجاف -في هذا الكتاب- تحديدًا إلى قاعدة المِرحاض التي يجلس عليها المُستخدم مباشرةً أو البلاطة الأرضية المُستخدمة للجلوس فوقها بوضعية القُرفصاء، وفي مصادر أخرى قد يُشير المِرحاض الجاف إلى أنواع مختلفة من التقنيات أو توليفات مُجمِّعة من بعض التقنيات (وخاصةً الحُفَر).
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
| البراز، البول، مياه تنظيف الشرج , مواد التطهير الجافة |
فضلات الجسم، مياه تنظيف الشرج, مواد التطهير الجافة |
التشغيل والصيانة
يجب الحفاظ على نظافة وجفاف السطح الذي يتم الجلوس أو الوقوف عليه للوقاية من انتقال الأمراض أو مُسببات الأمراض، وللحد من الروائح الكريهة. ولا يحتوي المِرحاض الجاف على أي أجزاء ميكانيكية؛ لذلك فإنه لا يحتاج لأي إصلاحات إلا في حالة تعرضه للتشقق.
يُوضع المِرحاض الجاف عادةً فوق حُفرة؛ إذا تم استخدام حفرتين فيجب أن تكون قاعدة المِرحاض Pedestal أو البلاطة الأرضية Slab مصممين بطريقة تُمكّن من رفعهما ونقلهما من حُفرة لأخرى. ويجب أن يكون حجم البلاطة الأرضية أو قاعدة المِرحاض مناسبًا تمامًا للحُفرة بحيث يكون آمنًا للمُستخدم، وفي نفس الوقت يمنع تسرب مياه الأمطار للحُفرة )والذي قد يتسبب في طفحها( ويُمكن أن تُغلَق الحُفرة بغطاء لمنع دخول أي حشرات أو قوارض غير مرغوب فيها. ومن الممكن أن يتم تصنيع قواعد المراحيض أو البلاطات الأرضية محليًّا باستخدام الخرسانة )بشرط توفر الرمل والأسمنت( وتتوفر أيضًا مُنتجات منها مصنوعة من الألياف الزجاجية )الفيبر جلاس( والخزف والفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ، ويمكن استخدام القوالب الخشبية والمعدنية لإنتاج عدة وحدات بسرعة وكفاءة.
تُعتبر المراحيض الجافة سهلة الاستعمال لأغلب المُستخدمين، إلا أن الأمر قد يتطلب عمل بعض التجهيزات الخاصة للمُستخدمين المُسنين وذوي الاحتياجات الخاصة الذين قد يجدون بعض المشقة. عندما تُصنع المراحيض الجافة محليًّا فإنه يمكن أن تُصمم بشكل خاص لتتلائم مع احتياجات الفئة المستهدفة من المُستخدمين )على سبيل المثال: المراحيض الصغيرة للأطفال(وحيث إنه لا حاجة لفصل البول عن البُراز في هذا النوع، فغالبًا ما يُعد الخيار الأسهل والأكثر راحة عمليًّا.
Read some of our most visited factsheets on sustainable sanitation such as the one on menstrual hygiene management!
الجلوس بوضعية القرفصاء هو وضع طبيعي للعديد من الناس؛ لذلك قد تكون البلاطة الأرضية ذات الحالة الجيدة والمخصصة للجلوس فوقها بوضعية القرفصاء هي الخيار الأكثر قبولًا. وقد تُشكِّل الروائح مشكلةً، حيث لا يوجد بالمراحيض الجافة حاجز مائي( Water Seal أو كوع الرائحة(، وذلك اعتمادًا على تقنية الجمع والتخزين/المُعالجة المتصلة بهم.
حلول تقنيات وممارسات افضل للصرف الصحى دليل الاحياء الهاشمية فى نواكشوط -موريتانيا
المياه ،الصرف الصحي النظافة الصحية وظروف الإقامة في السجون
نظرة شمولية لتقنية الإصحاح البيئي
بناء الحمامات وطرق تحسينها وصيانتها
الصرف الصحي الموقعي والمركزي - للمدن والتجمعات السكانية الصغيرة
Latrine Building
Introduction to Low Cost Sanitation Latrine Construction
This manual describes how to construct latrines.
CAWST (2011): Introduction to Low Cost Sanitation Latrine Construction. A CAWST Construction Manual. Calgary: CAWST URL [Accessed: 25.08.2014]Toilets That Make Compost
This book describes in an easy-to-understand and picture-based way how to construct three different low cost sanitation solutions, namely arborloos, fossa alterna and urine diversion toilets.
MORGAN, P. EcoSanRes (2007): Toilets That Make Compost . Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]Ecological Toilets
This book describes how to construct Arborloo toilets and how it can be upgraded to VIPs at a later stage.
MORGAN, P. EcoSanRes (2009): Ecological Toilets. (pdf presentation). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]An Engineer’s Guide to Latrine Slabs
Providing sanitation for all is a major global challenge involving many complex issues. The user of a latrine however, will have more local concerns such as the condition of the latrine slab. This is one of the key components of the most common type of sanitary facility. This booklet highlights the design, manufacture and maintenance features that help to improve the safety and comfort of users.
REED, B. (2012): An Engineer’s Guide to Latrine Slabs. Leicestershire: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) Loughborough University URL [Accessed: 08.10.2013]Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition
This compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) URL [Accessed: 28.07.2014] PDFCompendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic)
This is the Arabic version of the Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies. The Compendium gives a systematic overview on different sanitation systems and technologies and describes a wide range of available low-cost sanitation technologies.
TILLEY, E. ULRICH, L. LUETHI, C. REYMOND, P. SCHERTENLEIB, R. ZURBRUEGG, C. (2014): Compendium of Sanitation Systems and Technologies (Arabic). 2nd Revised Edition. Duebendorf, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (Eawag) PDFPathogens in Dry Sanitations Systems and Risk of Using Sludge Produced in Agriculture
A paper about the most common pathogens which exist in faecal sludge and how to control these.
JIMENEZ, B. NAVARRO, I. MAYA, C. (n.y): Pathogens in Dry Sanitations Systems and Risk of Using Sludge Produced in Agriculture. Mexico: University of Coyocan URL [Accessed: 06.10.2010]How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation
The purpose of this guide is to assist local contracting authorities and their partners in identifying those sanitation technologies best suited to the different contexts that exist within their town. The first part of the guide contains a planning process and a set of criteria to be completed; these assist you in characterizing each area of intervention so that you are then in a position to identify the most appropriate technical solutions. The second part of the guide consists of technical factsheets which give a practical overview of the technical and economic characteristics, the operating principle and the pros and cons of the 29 sanitation technology options most commonly used in sub-Saharan Africa.
MONVOIS, J. GABERT, J. FRENOUX, C. GUILLAUME, M. (2010): How to Select Appropriate Technical Solutions for Sanitation. (= Six Methodological Guides for a Water and Sanitation Services' Development Strategy , 4 ). Cotonou and Paris: Partenariat pour le Développement Municipal (PDM) and Programme Solidarité Eau (pS-Eau) URL [Accessed: 19.10.2011]Toilets That Make Compost
This book describes in an easy-to-understand and picture-based way how to construct three different low cost sanitation solutions, namely arborloos, fossa alterna and urine diversion toilets.
MORGAN, P. EcoSanRes (2007): Toilets That Make Compost . Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]Ecological Toilets
This book describes how to construct Arborloo toilets and how it can be upgraded to VIPs at a later stage.
MORGAN, P. EcoSanRes (2009): Ecological Toilets. (pdf presentation). Stockholm: Stockholm Environment Institute URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]Smart Sanitation Solutions
Smart Sanitation Solutions presents examples of low-cost household and community-based sanitation solutions that have proven effective and affordable. A wide range of innovative technologies for toilets, collection, transportation, treatment and use of sanitation products that have already helped thousands of poor families to improve their lives is illustrated.
NWP (2006): Smart Sanitation Solutions. Examples of innovative, low-cost technologies for toilets, collection, transportation, treatment and use of sanitation products. (= Smart water solutions ). Amsterdam: Netherlands Water Partnership (NWP) URL [Accessed: 09.05.2019]Ventilation of dry toilets
This thesis aims at showing possibilities to improve ventilation standards of dry toilet facilities. Therefore, numerous structures were monitored over a period of three months, from March to June, in the southwestern districts of Uganda. The considerations and recommendations of this paper should support further development and improve future toilet structures in view of ventilation practices and design purviews. It should therefore contribute to a higher quality and acceptance of the dry toilets in the long term.
GROTH, F. (2005): Ventilation of dry toilets. (= Master Thesis ). Pinkafeld: Fachhochschulstudiengänge Burgenland GmbH URL [Accessed: 11.08.2010]An Engineer’s Guide to Latrine Slabs
Providing sanitation for all is a major global challenge involving many complex issues. The user of a latrine however, will have more local concerns such as the condition of the latrine slab. This is one of the key components of the most common type of sanitary facility. This booklet highlights the design, manufacture and maintenance features that help to improve the safety and comfort of users.
REED, B. (2012): An Engineer’s Guide to Latrine Slabs. Leicestershire: Water, Engineering and Development Centre (WEDC) Loughborough University URL [Accessed: 08.10.2013]Introduction to Low Cost Sanitation Latrine Construction
This manual describes how to construct latrines.
CAWST (2011): Introduction to Low Cost Sanitation Latrine Construction. A CAWST Construction Manual. Calgary: CAWST URL [Accessed: 25.08.2014]Is it Time to kill off the Flush Toilet?
Critical article on the conventional flush-and-forget toilet systems on the occasion of the World Toilet Summit and Expo in Macau.
DUNCAN, D. (2008): Is it Time to kill off the Flush Toilet?. المُدخلات: TIME.com: URL [Accessed: 10.08.2008]http://www.drytoilet.org/
The Global Dry Toilet Association of Finland collects and distributes information on different types of dry toilet solutions, develops dry toilet technology (DT-technology) and culture, promotes the use of dry toilets, looks after the interests of dry toilet users, organises exhibitions, conferences and other events, participates in research and publish research results, finds ways to solve problems regarding dry toilets and makes statements to the press and public regarding dry toilets.


