مرشح الرمل الحيوي(البيولوجي) (BSF) هو جهاز بسيط لمعالجة المياه المنزلية ،وهو أكثر ابتكارا من المرشحات الرملية البطيئة التقليدية المصممة خصيصا للاستخدام المتقطع ( الغير منتظم ) . يتكون هذا المرشح من حاوية أسمنتية أو بلاستيكية مملوئة برمل وحصي تم اختيارها وتجهزها خصيصا لهذا الغرض. وكلما تدفق الماء من خلال المرشح ، فإن التصفية الفيزيائية تزيل مسببات الأمراض، والحديد، والعكارة , والمنجنيز من مياه الشرب. تمكث طبقة ضحلة سطحية من المياه فوق الرمال وتتكون طبقة حيوية (بيوفيلم). تساهم الطبقة الحيوية في إزالة مسببات الأمراض بسبب الافتراس والتنافس على الغذاء بين الكائنات الحية الدقيقة الغير ضارة الموجودة في الطبقة الحيوية والكائنات الضارة في المياه.
| المُدخلات | المُخرَجات |
|---|---|
المياة العذبة |
مياه الشرب |
مرشح الرمل الحيوي(البيولوجي) هو أكثر ابتكارا من مرشحات المياه الرملية البطيئة التقليدية (التي استخدمت لمعالجة المياه للمجتمع لمئات من السنين (تقرير مركز المياه الميسرة وتكنولوجيا الصرف الصحي لعام 2009)، والمصممة خصيصا للاستخدام المتقطع أو المنزلي. تم اختراع هذا المرشح (الفلتر) من قبل الدكتور ديفيد مانز في 1990 في جامعة كالجاري، كندا. المرشح سهل الاستخدام ويمكن أن ينتج محليا في أي مكان في العالم لأنه يتم بنائه بالمواد التي تتوافر بسهولة. تكاليف رأس مال المرشحات تعتمد على تكاليف المواد المحلية وتكاليف الأيدي العاملة . ومع ذلك، فإنها لا تتطلب مستهلكات ( مواد مستهلكة) وتكاليف التشغيل تكاد لا تذكر.
المرشح يتكون من وعاء بسيط مع غطاء، تضم طبقات من الرمل والحصى، والتي تحتجز فيزيائيا الرواسب ومسببات الأمراض وغيرها من الشوائب من الماء. والغشاء الحيوي (البيوفيلم)، الذي يتشكل كطبقة رقيقة فوق الرمل ، يمكث على قمة عمود الرمل ويسهم في ازالة مسببات الأمراض.
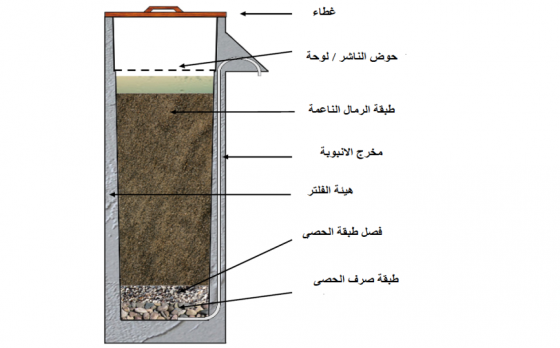
مكونات فلتر الرمل الحيوي(البيولوجى المصدر: CAWST 2009b
حاوية المرشح يمكن أن تكون مصنوعة من الخرسانة أو البلاستيك أو أي من المواد العازلة للمياه و المقاومة للصدأ غير السامة .ومع ذلك فإن النسخة الأكتر استخداما على نطاق واسع هي الوعاء الخرساني ، ما يقرب من 0.9 مترا طولا ومساحة سطح من 0.3متر مربع (LANTAGNE 2006). يتكون صندوق المرشح الخرساني من قالب صلب أو من انبوبة مصنعة مسبقا (CAWST 2009a). يتم تعبئة الحاوية بطبقات منفذة ومغسولة من الرمل والحصى، ويعرف أيضا بوسط ترشيح (CAWST 2009a). فوق طبقة الرمال تمكث طبقة راسية من المياه ارتفاعها 5 سم ، والتي يتم الحفاظ عليها بضبط ارتفاع أنبوبة المخرج (LANTAGNE 2006؛. CAWST 2009a). هذه هى ميزة التصميم التى تسمح بتشكيل الغشاء الحيوى البيوفيلم ( الطبقة الحيوية الثابتة) ويميز المرشح عن غيره من المرشحات الرملية البطيئة، مما يسمح بانشائه على نطاق صغير، والاستخدام المتقطع (http://www.cawst.org/en/resources/biosand-filter). هناك طبقة انتشار تجنب المياه من أن تصل إلى سطح الرمال بشكل سريع جدا، والتي يمكن أن تحدث خللا واضطرابا البيوفيلم.
عملية تشغيل المرشح بسيطة جدا. يسكب الماء على قمة المرشح حسب الحاجة. ثم ينتقل الماء ببطء من خلال طبقة الرمل والحصى.وفي قاعدة المرشح يتم جمع الماء في انبوبة وتفرغ عبر نظام الأنابيب البلاستيكية خارج المرشح ليتم جمعها وتخزينها في حاوية المياه النظيفة. مرشحات الخرسانة لديها مخرج انبوبي وهي كجزءا لا يتجزأ من الخرسانة، وتحميه من الكسر والتسريبات (CAWST 2009a).
المياه المعالجة ينبغي جمعها من قبل المستخدم في حاوية تخزين آمنة موضوعة على حامل أو قالب، بحيث يتم فتح الحاوية فقط تحت المخرج، للتقليل من خطر إعادة التلوث (CAWST 2009a).

أسرة في جابا، نيبال تستخدام فلتر بيوزند خرساني لمعالجة مياه الشرب. المصدر: منظمة البيئة والصحة العامة
يتم إزالة مسببات الأمراض والمواد الصلبة العالقة من خلال مجموعة من العمليات البيولوجية والفيزيائية التي تحدث في الطبقة الحيوية (البيوفيلم) وعبر طبقة الرمال. وتشمل هذه العمليات الاحتجاز الميكانيكي، الافتراس ، الادمصاص والموت الطبيعي
(NGAI et al. 2007; EAWAG/SANDEC 2008; CAWST 2009a).
* الإحتجاز الميكانيكي والغربلة : المواد الصلبة العالقة ومسببات الأمراض تحتجز فيزيائيا في الفراغات بين حبيبات الرمل.
* الإدمصاص والالتصاق:الكائنات المسببة للأمراض تلتصق ببعض (وبالتالي تتغربل بسهولة أكتر )،وبالمواد الصلبة العالقة في الماء، وبحبيبات الرمل.
* الافتراس: يتم استهلاك الكائنات المسببة للامرض عن طريق الكائنات الدقيقة الأخرى في الطبقة البيولوجية هذه الطبقة البيولوجية تتكون وتنضج في خلال أسبوع إلى ثلاثة أسابيع إعتمادا على حجم المياه الموضوع خلال المرشح وكمية المواد المغذية ( المغذيات) والكائنات الحية الدقيقة في الماء.
* الموت الطبيعي: مسببات الأمراض تنهي دورة حياتها أو تموت بسبب عدم وجود ما يكفي من الغذاء أو الأكسجين بالنسبة لها للبقاء على قيد الحياة.

نسخة بلاستيكية من فلتر الرمل الحيوي(البيولوجي) متصل الي خزان مياه تجاري (كناري). المصدر: اليسار: (مؤسسة الأخبار الدولية، نيويورك)
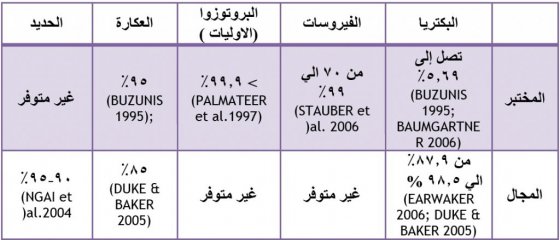
مرشح الرمل الحيوي (البيولوجي) هي تقنية أثبتت جدواها( مثبتة) ،حيث يزيل مسببات الأمراض مثل البكتيريا والبروتوزوا والديدان الطفيلية. المرشح هو أيضا فعال إلى حد ما لإزالة الفيروسات (CAWST 2009a). يتم إزالة العوامل( المحددات) الفيزيائية مثل العكارة والحديد أيضا من مياه الشرب. ومع ذلك، لا يتم إزالة المواد الكيميائية الذائبة (مثل المبيدات العضوية أو الزرنيخ). المياه المعالجة لديها عادة لون ، وطعم ورائحة مقبولة.
يبين الجدول بالأسفل كفاءة معالجة مرشح الرمل الحيوي(البيولوجي) في إزالة مسببات الأمراض، والعكارة والحديد ،مقتبس من (CAWST 2009a).
تقدر دراسات الأثر الصحي حوالي من 30-47٪ إنخفاض في الإسهال بين جميع الفئات العمرية، بما في ذلك الأطفال دون سن الخامسة، خصوصا مجموعة السكان الأكثر عرضة لذلك. المصدر: SOBSEY (2007)؛ STAUBERوآخرون. (2007)
معدل التدفق من خلال المرشح تصبح بطيئة بمرور الوقت مع انسداد فتحات المسام بين حبيبات الرمل. لمستويات العكارة الأكبر من 50 وحدة NTU(وحدة قياس العكارة)، يجب أولا أن تصفى المياه من خلال قطعة قماش أو مرسب قبل استخدام المرشح (CWAST 2009a).
عندما ينخفض معدل التدفق إلى مستوى غير كاف للإستخدام المنزلي فإن المرشح يحتاج إلى التنظيف. ويتم ذلك من قبل "الدوامة والتفريغ" وهو إجراء بسيط يتم تطبيقة على الجزء العلوي من الرمال، ولا يستغرق سوى بضع دقائق (CWAST 2009a). عملية الدوامة والتفريغ تتكون من إضطراب وتحريك الرمال السطحية، وبالتالي يحدث تعليق للمواد المحتجزة فوق طبقة المياه الراسية العلوية .الماء غير النظيف يتم بعد ذلك إزالته والتخلص منه بعيدا. ويمكن تكرار هذه العملية عدة مرات للحصول على معدل التدفق المطلوب (http://www.cawst.org/en/resources/biosand-filter). الحاجة إلى التنظيف تعتمد على كمية ونوعية المياه التي وضعت خلال المرشح. إذا كان الماء نظيفا نسبيا (العكارة أقل من 30 وحدة (NTU)، يمكن للمرشح المحتمل تشغيله لعدة أشهر أن يعمل دون إجراء هذه الصيانة (http://www.cawst.org/en/resources/biosand-filter).
عند استخدام المرشح لأول مرة، فإنه الطبقة البيولوجية (البيوفيلم) لم تتكون بعد. الطبقة البيولوجية عادة ما تستغرق 20-30 يوما ليكتمل تكوينها ونضجها في مرشح جديد اعتمادا على جودة المياه الداخلة للمرشح ونوع الاستخدام (تقرير مركز المياه الميسرة وتكنولوجيا الصرف الصحي لعام 2009؛ http://www.cawst.org/en/resources/biosand-filter). كفاءة الإزالة والفعالية للمرشح تزيد طوال هذه الفترة.بعد التنظيف، يحدث إعادة إنشاء وترتيب للطبقة البيولوجية ، وسرعان ما تعود كفاءة الإزالة إلى مستواها السابق.
المرشح مناسب لمعالجة المياه في المنزل أو المدرسة أو على مستوى المجتمع المحلي. يمكن للمرشح علاج المياه السطحية أو المياه الجوفية الملوثة بكفاءة وبشكل مباشر نظرا لأنه أيضا يزيل العكارة والحديد. ومع ذلك، فمن المستحسن عدم استخدام الماء مع عكارة أكثر من 50 وحدة NTUوعلاوة على ذلك،. لا تتم إزالة المواد الكيميائية الذائبة (مثل المبيدات العضوية أو الزرنيخ).
المياه الكلورة ( المعالجة بالكلور ) لا يتم تطبيقها في هذا المرشح لان الكلور يقتل الكائنات الحية الدقيقة الموجودة في الطبقة الحيوية ( البيوفيلم) مما يؤدي الي انخفاض كفاءة ازالة الكائنات المسببة للامراض ومع ذلك، فإن الماء يمكن معالجته بالكلور بعد الترشيح من أجل تحسين أمان ( سلامة ) الماء لمجموعات كبار السن أو الأطفال في الأسرة / المجتمع.
يجب أن يتم بناء المرشح فقط من قبل الفنيين المدربين.على الرغم من أن البناء والتركيب يبدو بسيطا للغاية،التصميم والانشاء غير الصحيح للمرشح يمكن ان يؤدي إلي ضعف أداء المرشح ومع ذلك، فإن المواد عادة ما تكون متوفرة محليا والبناء من قبل الموظفين المحليين المدربين قد يخلق فرص عمل محلية.
Intermittently Operated Slow Sand Filtration: A New Water Treatment Process
The Effect of User Behaviour on the Performance of Two Household Water Filtration Systems
BioSandWater Filter
Biosand Filter Manual, Design, Construction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance
This training manual provides overview on biosand filters including construction, installation, operation and maintenance of BSF.
CAWST (2009): Biosand Filter Manual, Design, Construction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST). [Accessed: 12.05.2012] PDFThe Use and Performance of the Biosand Filter in the Artibonite Valley of Haiti: A Field Study of 107 Households
A field study to evaluate the use and performance of Biosand filters at the Artibonite Valley of Haiti. They found it as an attractive option for supplying safe water in rural areas of poorly developed countries with producing water in safe range in 97% of the cases
DUKE, W. BAKER, D. (2005): The Use and Performance of the Biosand Filter in the Artibonite Valley of Haiti: A Field Study of 107 Households. Victoria: University of Victoria URLEvaluation of Household Biosand Filters in Ethiopia
Reductions of E. coli, Echovirus type 12 and Bacteriophages in an Intermittently Operated Household Scale Slow Sand Filter
Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Options in Developing Countries. Review of Current Implementation Practices
Summary and brief evaluation of the main household water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) options for developing countries. Treated options are: chlorination, biosand filtration, ceramic filtration, solar disinfection, filtration and chlorination, flocculation and chlorination.
LANTAGNE, D. S. ; QUICK, R. ; MINTZ, E.D. (2006): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Options in Developing Countries. Review of Current Implementation Practices. المُدخلات: Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars (2006): Water Stories: Expanding: Opportunities in small-scale Water and Sanitation Projects: , 17-38. URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]Kanchan Arsenic Filter (KAF) - Research and Implementation of an Appropriate Drinking Water Solution for Rural Nepal
This paper describes the World Bank DM2003 award, and the plan to implement the KAF (Kanchan Arsenic Filter) project throughout the Terai region in Nepal. The objectives of this project include the establishment of local entrepreneurs for a financially sustainable distribution mechanism, the capacity-building of local people towards long-term, user-participatory safe water provision, the dissemination of KAF information from a central technology centre, as well as networking with other water supply implementers.
NGAI, T. MURCOTT, S. SHRESTHA, R. (2004): Kanchan Arsenic Filter (KAF) - Research and Implementation of an Appropriate Drinking Water Solution for Rural Nepal. Cambridge, MA and Kathmandu: Massachusetts Institute of Technology and ENPHO, Nepal URL [Accessed: 07.04.2010]Design for Sustainable Development – Household Drinking Water Filter for Arsenic and Pathogen Treatment in Nepal
Toxicant and Parasite Challenge of Manz Intermittent Slow Sand Filter
Study on removal of parasitic cysts and toxicants as well as bacteria by biosand filter.
PALMATEER, G. MANZ, D. JURKOVIC, A. McINNIS, R. UNGER, S. KWAN, K. K. DUDKA, B. (1997): Toxicant and Parasite Challenge of Manz Intermittent Slow Sand Filter. (= Environmental Toxicology , 217 / 14 ). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]UNC Health Impact Study in Cambodia
The Microbiological and Health Impact of the Biosand Filter in the Dominican Republic
Characterization of the Biosand Filter for Microbial Reductions Under Controlled Laboratory and Field Use Conditions
The BioSand Water Filter
Biosand Filter Manual, Design, Construction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance
This training manual provides overview on biosand filters including construction, installation, operation and maintenance of BSF.
CAWST (2009): Biosand Filter Manual, Design, Construction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST). [Accessed: 12.05.2012] PDFHousehold Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on the technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation household-level drinking water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 3 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 08.04.2010]استخدام معدات الترشيح ( الفلترة ) في معالجة مياه الشرب. مؤسسة التدريب المهني.معهد التدريب المتخصص للصناعات الكيماوية.المملكة الأردنية الهاشمية.
Language: Arabic
ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.
يهدف هذا الدليل إلى تقديم الإرشاد العملي، لتسهيل تطوير خطة سلامة المياه، مع التركيز على إمدادات المياه المنظمة التي تديرها منشأة مياه أو ما شابه.
منظمة الصحة العالمية,الإتحاد الدولي للمياه (2009): ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﺧﻄﺔ ﺳﻼﻣﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ. ﺩﻟﻴﻞ ﻣﻔﺼﻞ ﻹﺩﺍﺭﺓ ﺍﻟﻤﺨﺎﻃﺮ ﻟﻤﻘﺪﻣﻲ ﻣﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺮﺏ.جينف:منظمة الصحة العالمية.. URL [Accessed: 26.08.2017]Language: Arabic
ﺩﻻﺌل ﺠﻭﺩﺓ ﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺸﺭﺏ.جينيف.سويسرا
ﺍﻟﻌﻜﻭﺭﺓ ﻭﻜﻔﺎﺀﺓ ﺇﺯﺍﻟﺘﻬﺎ ﻓﻲ ﻤﺤﻁﺎﺕ ﺘﺼﻔﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﺎﻩ ﺍﻟﺭﺌﻴﺴﺔ ﻓﻲ ﻤﺤﺎﻓﻅﺔ ﻨﻴﻨﻭﻯ ﻗﺴﻡ ﻋﻠﻭﻡ ﺍﻟﺤﻴﺎﺓ ﻜﻠﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻌﻠﻭﻡ , ﺠﺎﻤﻌﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻭﺼل. ﻤﺠﻠﺔ ﻋﻠﻭﻡ ﺍﻟﺭﺍﻓﺩﻴﻥ، ﺍﻟﻤﺠﻠﺩ (24)، ﺍﻟﻌﺩﺩ (3)، ﺹ(،53-39).العراق
Language: Arabic
ﺍﻟﻤﺤﻄﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﻤﺪﻣﺠﺔ ﻟﻤﻌﺎﻟﺠﺔ ﺍﻟﺼﺮﻑ ﺍﻟﺼﺤﻲ ﺑﻮﺍﺳﻄﺔ ﺃﻏﺸﻴﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻔﺎﻋﻼﺕ ﺍﻟﺤﻴﻮﻳﺔ.
Language: Arabic
Biosand Water Filter Technology Household Concrete Design
The purpose of this paper is to describe the development, knowledge and the present design of the concrete household biosand water filter in a manner easily understood by readers who may or may not have advanced training in water treatment engineering.
MANZ, D.H. (2004): Biosand Water Filter Technology Household Concrete Design. URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]Kanchan Arsenic Filter (KAF) - Research and Implementation of an Appropriate Drinking Water Solution for Rural Nepal
This paper describes the World Bank DM2003 award, and the plan to implement the KAF (Kanchan Arsenic Filter) project throughout the Terai region in Nepal. The objectives of this project include the establishment of local entrepreneurs for a financially sustainable distribution mechanism, the capacity-building of local people towards long-term, user-participatory safe water provision, the dissemination of KAF information from a central technology centre, as well as networking with other water supply implementers.
NGAI, T. MURCOTT, S. SHRESTHA, R. (2004): Kanchan Arsenic Filter (KAF) - Research and Implementation of an Appropriate Drinking Water Solution for Rural Nepal. Cambridge, MA and Kathmandu: Massachusetts Institute of Technology and ENPHO, Nepal URL [Accessed: 07.04.2010]Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Options in Developing Countries. Review of Current Implementation Practices
Summary and brief evaluation of main household water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) options for developing countries. Options described are: chlorination, biosand filtration, ceramic filtration, solar disinfection, filtration and chlorination, flocculation and chlorination.
LANTAGNE, D. S. QUICK, R. MINTZ, E.D. (2006): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Options in Developing Countries. Review of Current Implementation Practices. المُدخلات: ECSP (2006): Water Stories: Expanding Opportunities in small-scale Water and Sanitation Projects. Washington D.C.: 17-38. URL [Accessed: 20.05.2019]Comparative Analysis of the Filtron and Biosand Water Filters
BioSandWater Filter
Smart Disinfection Solutions
This booklet, part of the Smart Water Solutions series provides a wide range of methods and products for home water treatment in rural areas.
NWP (2010): Smart Disinfection Solutions. Examples of small-scale disinfection products for safe drinking water. (= Smart water solutions ). Amsterdam: KIT Publishers URL [Accessed: 17.05.2019]Toxicant and Parasite Challenge of Manz Intermittent Slow Sand Filter
Study on removal of parasitic cysts and toxicants as well as bacteria by biosand filter.
PALMATEER, G. MANZ, D. JURKOVIC, A. McINNIS, R. UNGER, S. KWAN, K. K. DUDKA, B. (1997): Toxicant and Parasite Challenge of Manz Intermittent Slow Sand Filter. (= Environmental Toxicology , 217 / 14 ). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]Biosand Filtration: Application in the Developing World
Investigation on current issues that affect the implementation of biosand filter in the developing world.
YUNG, K. (2003): Biosand Filtration: Application in the Developing World. Waterloo: University of Waterloo URL [Accessed: 14.05.2012]Source Book of Alternative Technologies for Freshwater Augmentation in Latin America and the Caribbean
The Latin American and Caribbean countries have seen growing pressure on water resources, with increasing demand and costs, for agricultural, domestic and industrial consumption. This has brought about the need to maximize and augment the use of existing or unexploited sources of freshwater. There are many modern and traditional alternative technologies for improving the utility and augmenting the supply of water being employed in various countries, but with limited application elsewhere due to the lack of information transfer among water resources managers and planners. This book was prepared to provide water resource managers and planners, especially in developing countries and in countries with economies in transition, with information on the range of technologies that have been developed and used in the various countries throughout the world.
UNEP (1998): Source Book of Alternative Technologies for Freshwater Augmentation in Latin America and the Caribbean. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) URL [Accessed: 17.10.2011]Conservation et Traitement de l Eau a Domicile
This practical guide provides a review of different processing techniques and adequate water conservation at home and is structured around 10 key questions that should be posed before choosing a suitable solution.
DESILLE, D. (2013): Conservation et Traitement de l Eau a Domicile. Paris: Programme Solidarite Eau (PSeau) URL [Accessed: 06.06.2013]Use of Biosand Filters in Cambodia
Well-illustrated case study on the use of biosand filters in Cambodia.
WSP (2010): Use of Biosand Filters in Cambodia. Improving Household Drinking Water Quality. Washington D.C.: Water and Sanitation Program (WSP) URL [Accessed: 20.02.2012]The Use and Performance of the Biosand Filter in the Artibonite Valley of Haiti: A Field Study of 107 Households
A field study to evaluate the use and performance of Biosand filters at the Artibonite Valley of Haiti. They found it as an attractive option for supplying safe water in rural areas of poorly developed countries with producing water in safe range in 97% of the cases
DUKE, W. BAKER, D. (2005): The Use and Performance of the Biosand Filter in the Artibonite Valley of Haiti: A Field Study of 107 Households. Victoria: University of Victoria URLBiosand Household Water Filter Projects in Nepal
Investigation on effectiveness and performance of biosand filters in Nepal.
LEE, T.L. (2001): Biosand Household Water Filter Projects in Nepal. (= (Master Thesis) ). Toronto: University of Toronto URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]Characterisation of the Biosand Filter for E. Coli Reductions from Household Drinking Water under Controlled Laboratory and Field Use Conditions
This study provides results of laboratory and field studies on removal of E. coli by biosand filter. Field analysis was conducted on 55 household filter near Bonao, Dominican Republic.
STAUBER, C.E. ELLIOTT, M.A. KOKSAL, F. ORTIZ, G.M. DIGIANO, F.A. SOBSEY, M.D. (2006): Characterisation of the Biosand Filter for E. Coli Reductions from Household Drinking Water under Controlled Laboratory and Field Use Conditions. (= Water and Science & Technology , 3 / 54 ). IWAA Randomized Controlled Trial of the Concrete Biosand Filter and Its Impact on Diarrhoeal Disease in Bonao, Dominican Republic
This research provide information on ability of Bio-sand filters to improve water quality and to reduce diarrhoeal disease in user compared with non-user households in a randomized controlled trial in Bonao, Dominican Republic, during 2005–2006.
STAUBER, C. ORTIZ, G. LOOMIS, D. SOBSEY, M. (2009): A Randomized Controlled Trial of the Concrete Biosand Filter and Its Impact on Diarrhoeal Disease in Bonao, Dominican Republic. The American Society of Tropical Medicine and HygieneBiosand Filter Manual, Design, Construction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance
This training manual provides overview on biosand filters including construction, installation, operation and maintenance of BSF.
CAWST (2009): Biosand Filter Manual, Design, Construction, Installation, Operation and Maintenance. Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST). [Accessed: 12.05.2012] PDFBiosand Filter. Factsheet
Extensive factsheet on the principles, construction, operation and maintenance of ceramic candle filters for drinking water treatment.
CAWST (2009): Biosand Filter. Factsheet. (= Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Fact Sheet - Academic ). Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes
Lecture notes on the technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation household-level drinking water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Lecture Notes. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 3 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 08.04.2010]Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Presentation
Presentation on the technical and non-technical aspects of sanitation household-level drinking water treatment and safe storage (HWTS) in developing countries.
EAWAG/SANDEC (2008): Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage (HWTS). Presentation. (= Sandec Training Tool 1.0, Module 3 ). Duebendorf: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science (EAWAG), Department of Water and Sanitation in Developing Countries (SANDEC) URL [Accessed: 18.02.2011]Biosand Filter. Factsheet
Extensive factsheet on the principles, construction, operation and maintenance of ceramic candle filters for drinking water treatment.
CAWST (2009): Biosand Filter. Factsheet. (= Household Water Treatment and Safe Storage Fact Sheet - Academic ). Alberta: Center for Affordable Water and Sanitation Technology (CAWST) URL [Accessed: 19.05.2019]Biosand Filters - A practitioner's knowledge base
Biosandfilters.info is a knowledge base: technical updates, case studies, evaluations, expert knowledge from over 10 years supporting hundreds of organisations implement biosand filter (BSF) projects. Biosandfilters.info was initiated to provide support to new and existing BSF implementers to succeed in their programs. Create a user login to enjoy full functionality of this website.
Biosand Filter
This website is a good starting point to get into the subject of biosand filter. It's easy to understand and includes many pictures.
The NEW Manz Water Information Web Site (BioSand Water Filter)
This is the website Dr. David Manz, who has developed of the small scale humanitarian models of biosand filters.
Introduction to the Bio-Sand Water Filter
This video provides an overview of biosand filter and its promotion in developing countries.
How the BioSand Water Filter works - Samaritan's Purse CANADA
This video shows an animation on how biosand filters work.
Using BioSand Water Filters in Cambodia
This is a video produced by WSP on the biosand filter programme in Cambodia.

