Safe water enterprises have a multitude of options to deliver products and services. Important is to thoroughly reflect how the delivery shall look like and whether it is executed in-house, by outsourcing or pursuing a mixed approach. This factsheet provides different insights on what aspects to consider when developing and implementing a distribution strategy and discusses advantages and disadvantages that are coming along with the 3 approaches.
The case studies of TARA in India and Spouts of Water in Uganda provide distinct insights on how distribution processes can be designed and implemented.
In the business model canvas (see factsheet on business model development) the distribution process is understood as the channels and customer relationships where the value proposition is delivered to the specific customer segment. At the end of any distribution process - often-called 'last mile distribution' to reach the end-customer, a water business will have to make a decision whether to distribute the water product, service or HWTS product itself, to outsource this task or to pursue a mixed approach. Both options come with advantages as well as disadvantages INCLUSIVE BUSINESS ACTION NETWORK, 2016; HEIERLI, 2008). Based on the observed businesses cases under the Safe Water Program Phase II, every firm not only struggled with its last mile delivery, but also the consequences of initially outsourcing this process. This handout presents different options for the last mile delivery and how to overcome struggles to reach the end-customer.
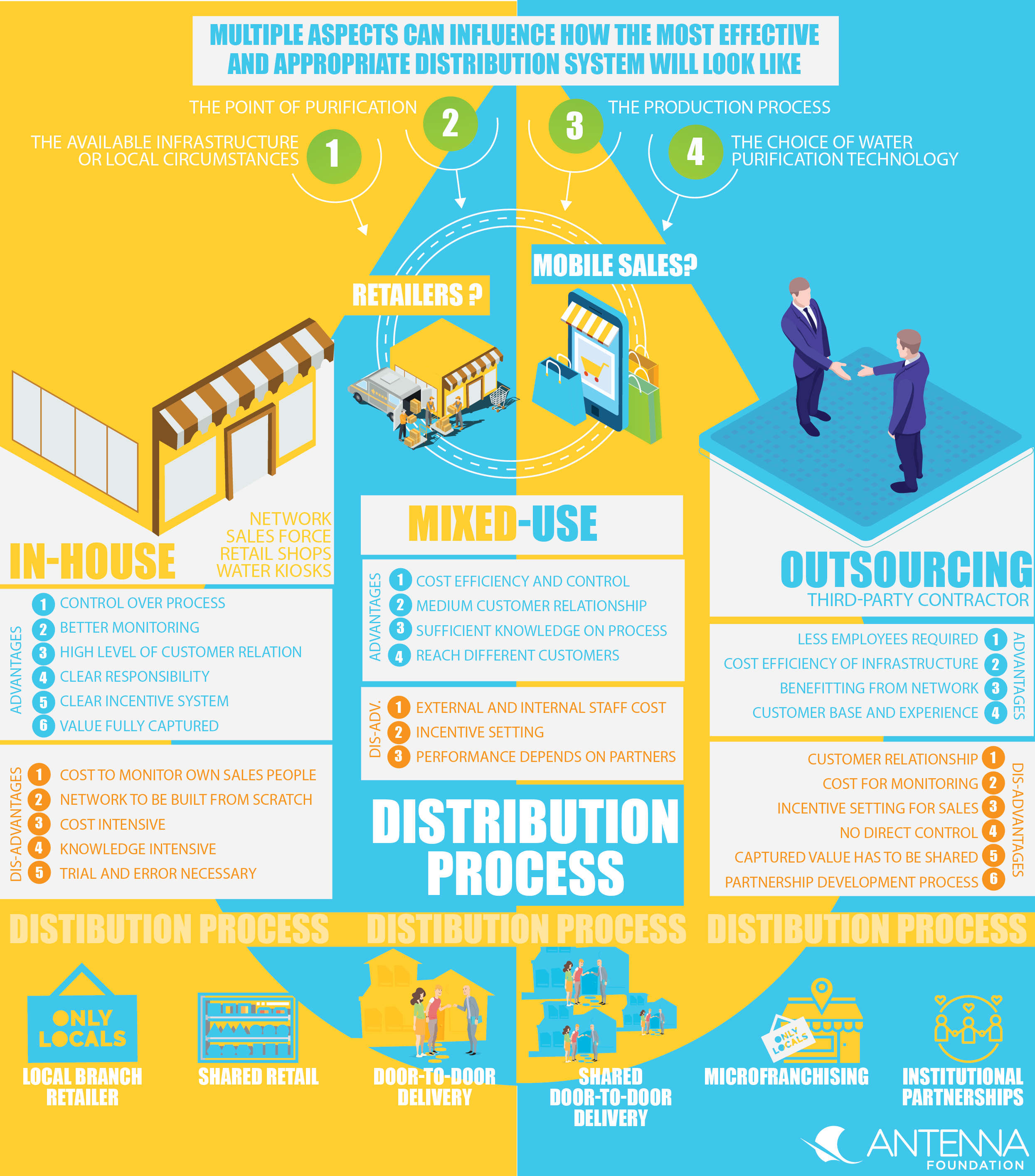
Safe water businesses can opt to provide safe water or household water treatment solution (HWTS) products through different distribution mechanisms. Multiple aspects can influence how the most effective and appropriate distribution system will look like:
1. the choice of water purification technology
2. the production process
3. the point of purification and
4. the available infrastructure or local circumstances
These aspects have to be considered in order to reliably and successfully cater safe water or HWTS to your BoP customers (ASHOKA, 2014).
The tool caters towards businesses that are about to launch their product or water service. It addresses also social enterprises experiencing difficulties with last mile delivery of their product or service.
Subscribe here to the new Sanitation and Water Entrepreneurship Pact (SWEP) newsletter. SWEP is a network of organizations joining hands to help entrepreneurs design and develop lasting water and sanitation businesses.
Businesses have to decide whether to distribute HWTS or safe water by in-house staff, by outsourcing it to a third party or by pursuing a mixed approach. The table below provides an overview of the 3 approaches and discusses their respective advantages and disadvantages. These insights will help a safe water enterprise to conceptualise or remodel its distribution process.
|
| Outsourcing | Mixed | In-house |
| Description | The distribution of HWTS products or safe water delivery services is sourced out to a third-party contractor. | The distribution is partly executed through a distribution system developed by the enterprise itself and through a third-party partnership. | The safe water enterprise is setting up an in-house distribution network, training sales force or setting up its own retail shops or water kiosks. |
| Example | The locally produced safe water product is sold through an existing retail company or pharmacies for example. | The safe water products are sold through an existing retail system and by door-to-door delivery executed by in-house trained staff. | Safe water kiosks are set up, water is treated and directly sold through a company’s own staff. |
| Advantages |
|
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
|
Overview of advantages and disadvantages of safe water distribution methods. Source: Antenna, 2018
In order to cater safe water products and services to the BoP there is a variety of last mile distribution methods that have been established and successfully executed over time. These methods can be used as single method or in combination and executed in-house, by a third party or mixed. An overview of last mile distribution methods can be found subsequently in Table 2:
| Delivery process | Description | Illustration |
| Door-to-door delivery | A network of door-to-door sales forces or microfranchisees promotes and sells one or multiple products from one company (e.g. health, energy, agriculture). For more information please see tool on social marketing. | |
| Shared door-to-door delivery | Door-to-door sales forces are selling products from different companies and brands in a certain area. | 
Antenna, 2014 |
| Local branch retailer | Products from a single brand or a single supplier are sold in a retail shop (e.g. franchise, branded kiosks, local branches). | Source: Antenna, 2015 |
| Shared retail | Products from multiple companies and brands are displayed and sold in fixed retail locations (e.g. retail chains or small shops). Here a variety of products for different use and purposes can be sold. | 
|
| Institutional partnerships | Collaboration with a partnering organization. Can facilitate market entry as distribution can be built on existing knowledge and relationships (case study on smart partnering). |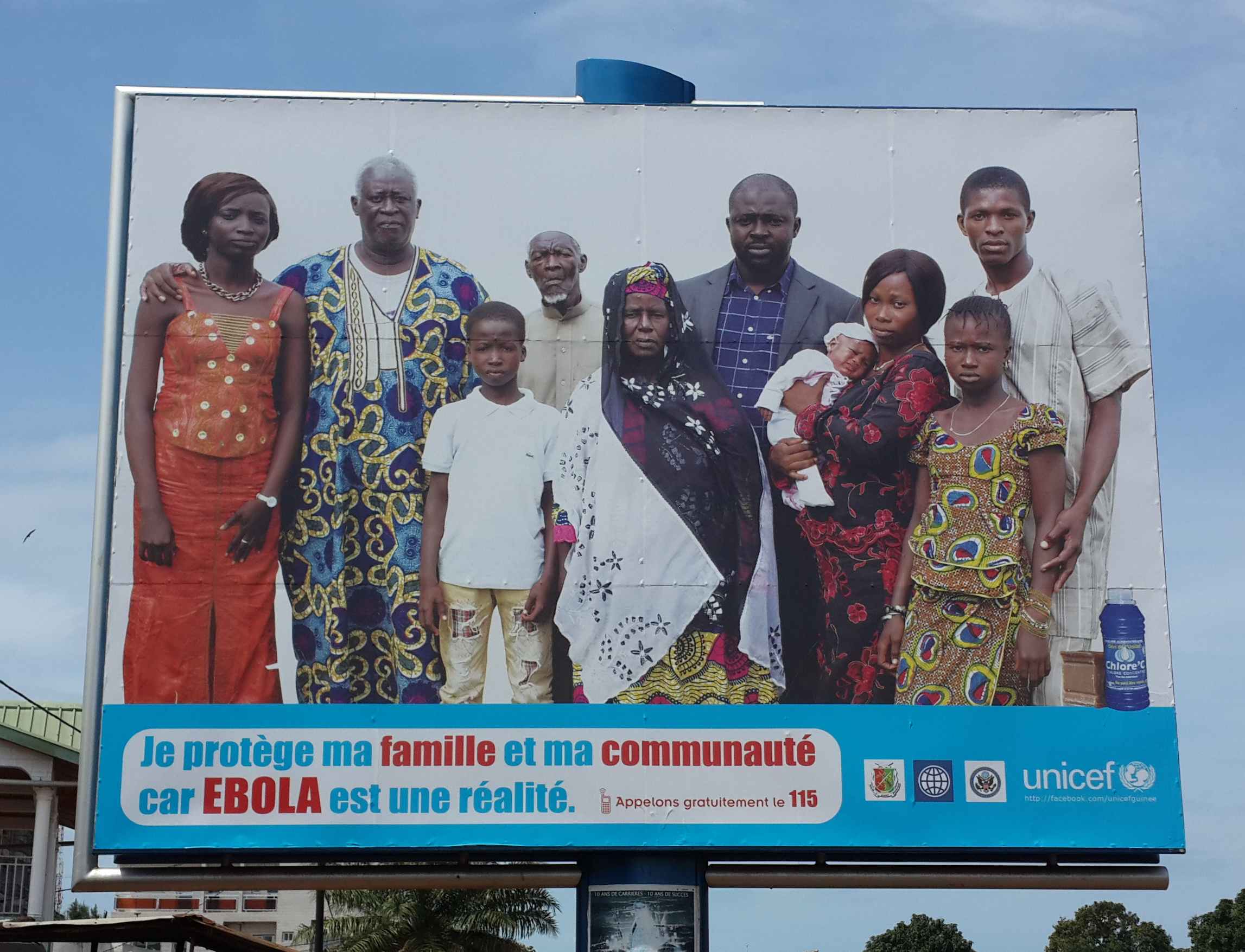 
Unicef in Guinea. Source: Antenna, 2016 |
| Collaboration with local micro-entrepreneurs (women, self-help-groups etc.) leveraging “the basic concept of traditional franchising, but it is especially focused on creating opportunities for the world’s poorest people to own and manage their own businesses” (LEHR, 2011) Mixed form of distribution as training, sales material and basic salary is provided. Additional salary is based on commission. (Case study on distribution process) | Source: Antenna, 2017 |
These insights can help your company develop and implement a distribution strategy. The accompanying case studies help you understand how other safe water business initiatives have been implementing their distribution process and what lessons learnt they acquired.
The case studies of TARA in India and Spouts of Water in Uganda provide distinct insights on how distribution processes can be designed and implemented.
Overcoming the Last Mile Challenge: Distributing Value to Billions
Water at the BoP
Marketing Safe Water Systems: Why it is so hard to get safe water to the poor – and so profitable to sell it to the rich
This book provides unique insights – from the varied perspectives of users, disseminators, producers and retailers – into the marketing challenges of point-of-use water treatment devices.
HEIERLI, U. (2008): Marketing Safe Water Systems: Why it is so hard to get safe water to the poor – and so profitable to sell it to the rich. Bern: Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) URL [Accessed: 18.05.2019]Access to Safe Water for the Base of the Pyramid – Lessons Learned from 15 Case Studies
The book provides insights on how innovative approaches led by social entrepreneurs, NGOs, and corporations have proven that sustainable solutions could provide safe water at the Base of the Pyramid. To illustrate these findings 15 case studies are provided of innovative social enterprises active in Africa and Asia.
HYSTRA (2011): Access to Safe Water for the Base of the Pyramid – Lessons Learned from 15 Case Studies. Hybrid Strategies Consulting URL [Accessed: 16.04.2018] PDFKNOW-HOW – Last mile distribution at the BoP
Microfranchising at the Base of the Pyramid
Evaluating the Sustainability of Ceramic Filters for Point-of-Use Drinking Water Treatment
This study evaluates the social, economic, and environmental sustainability of ceramic filters impregnated with silver nanoparticles for point-of-use (POU) drinking water treatment in developing countries.
REN, D. et al. (2013): Evaluating the Sustainability of Ceramic Filters for Point-of-Use Drinking Water Treatment. In: Environmental Science & Technology: Volume 47 Issue 19, 11206-11213. URL [Accessed: 16.04.2018]Business Linkages: Supporting Entrepreneurship at the Base of the Pyramid
This paper presents the interesting results of the Roundtable Dialogue in Brazil in 2008 that brought together approximately 40 corporate business linkage practitioners and selected operational partners from civil society and the international development community to discuss supply, distribution, and sales models that foster entrepreneurship and enterprise development among those currently living in conditions of poverty.
JENKINS, B. ET AL. (2008): Business Linkages: Supporting Entrepreneurship at the Base of the Pyramid. Report of a Roundtable Dialogue June 10-12, 2008, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Washington DC: International Finance Corporation, International Business Leaders Forum, and the CSR Initiative at the Harvard Kennedy School URL [Accessed: 16.04.2018]The last 500 feet
This essay discusses the question of the so-called last mile delivery and offers different insights and approaches to meet the basic needs of people in rural and remote areas through viable market-based approaches.
POLAK, P. (2013): The last 500 feet. URL [Accessed: 16.04.2018]
