After-sales processes follow-up on customer deals, warranty issues and bring back customer feedback in order to improve product and services towards customer needs. After-sales services may also offer additional complementary services, spare parts and accessories.
This factsheet provides concrete steps of how to develop and implement an after-sales strategy to allow a safe water enterprise to have a satisfied and increasing customer base and further opportunities to generate income.
The case study of how Hydrologic designed and implemented its after-sales scheme provides practical insights and lessons learnt to inspire other safe water initiatives’ development of an after-sales process.
After-sales services are services that provide customers with benefits after the initial product or service is sold. It can contain technical advice for product use, maintenance and repair services, the provision of spare parts, a warranty scheme or additional complementary services, as shown below. The after-sales service is the last step of the sales process and follows-up on customers in order to keep them satisfied, gain more information about sales behaviour and increase repurchases.
Complaints about products or services, correct or not, can lead to monetary losses due to high costs and deteriorate the reputation of a company. Enterprises have to reflect on how to address these potential situations of post-sales. That’s where the concept of after-sales steps in. After-sales services are perceived as a competitive advantage of a company. If executed in a comprehensive manner it will help improve customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and brand-recognition and prolong the life-span of the specific product and generate additional income through complementary services offered.
Especially in the BoP market context and in rural areas, after-sales services are pertinent to allow people a continuous access and use of household water treatment solutions (HWTS). Experiences of Safe Water Program Phase II’s partners revealed that conviction of water treatment and product use will be significantly increased if continuous use of HWTS can be guaranteed through after-sales services. In reaching BoP consumers, after-sales services are crucial, as customers are reluctant to purchase a one-go product and will be re-ensured when they know that spare parts or information are available in a nearby location. This fact poses a challenge for companies to be reachable and be present with after-sales services even in the most remote areas and asks for innovative after-sales strategies.
After-sales processes are pertinent for safe water entrepreneurs and NGOs that are starting or have already started their sales process. This paper will help the person in charge of sales/marketing/product development to learn how to increase customer satisfaction and how to collect customer insights from the ground in order to improve the quality of products or services. Collected data can also reveal how to develop additional products or services dependent on customer needs. The case study provided will give you additional insights on how different methods have been applied and what lessons learnt were made.
Subsequently insights on what aspects are essential in setting up an after-sales strategy and how to accordingly implement it are provided.
To develop an after-sales strategy and integrate it in accordance with a company’s need it is pertinent to have a working supply chain in place, especially for spare parts of the respective technology to allow people to repair sold HWTS products if necessary (OJOMO, 2015) (for more information on supply see factsheet on distribution process).
Note: After-sales do have its costs (labour, transport, exchange of broken products during warranty), that shall be forecasted and included in the first cost estimation of your product.
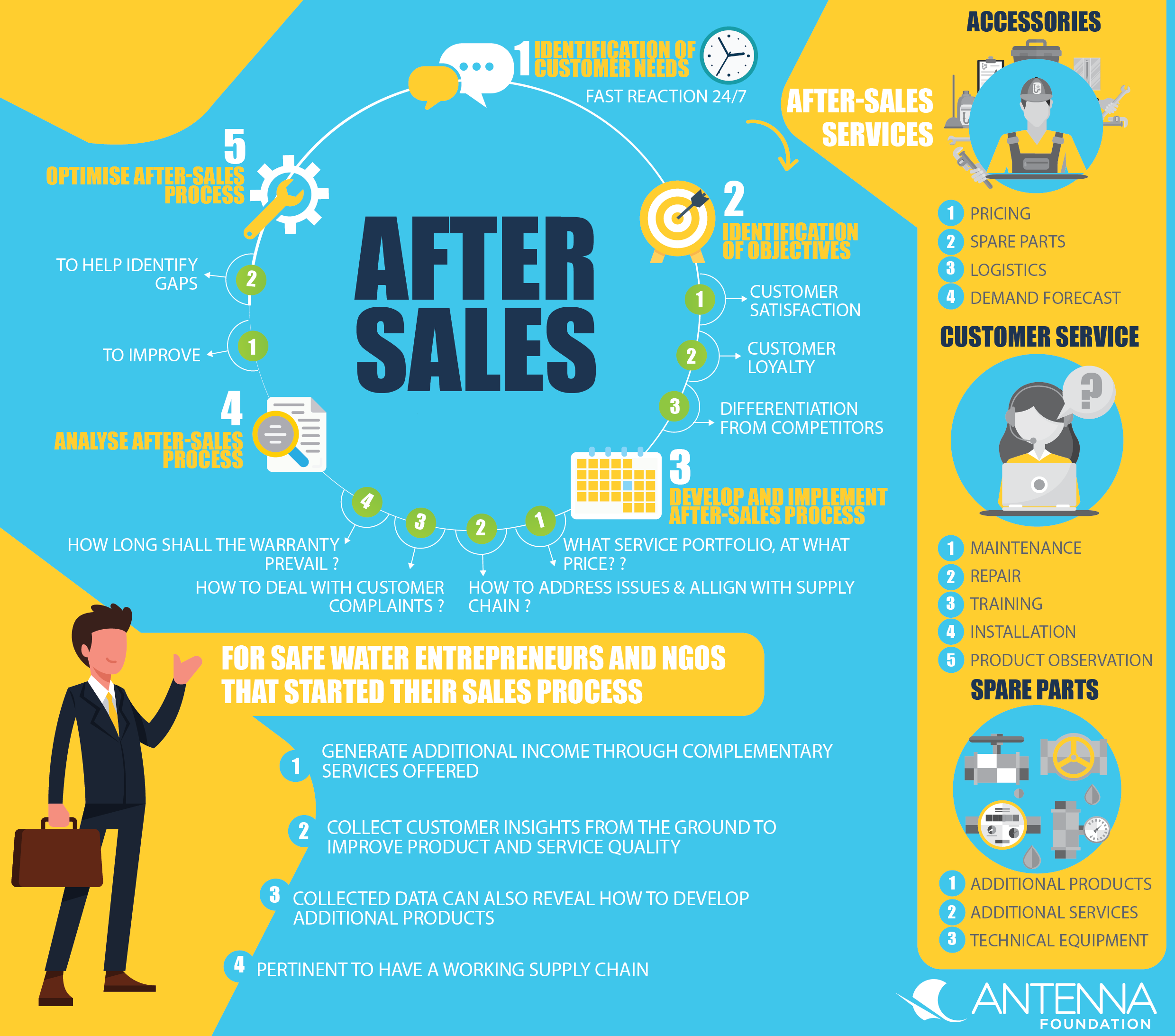
The figure below shows the most important steps to consider when defining a company’s after-sales strategy:
Source: Own illustration adapted from: Dombrowski & Malorny, 2016 and Jönke, 2012
These 5 steps are subsequently elaborated on in detail (JÖNKE, 2012; RIGOPOULOU ET AL., 2008):
1. Identification of customer needs: It is important to identify the customer needs and to define the objectives for your after-sales service accordingly. Examples of what customers are demanding can be 24-7 services, fast reaction time and spare parts delivery, a 24-7 call centre etc. Identifying these needs can be done via online customer surveys, focus groups, external experts etc.
2. Identification of objectives: Company’s objectives can include improvement of customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, differentiation from competitors etc. and need to be in line with a company’s overall strategy. For strategy implementation and identification of objectives see factsheet on managing your business – the balanced scorecard for more information.
3. Develop and implement after-sales process: According to your set objectives the after-sales service structure can be implemented consistently. Important during the development and implementation step is to consequently orient the processes towards the customer in accordance with the set goals. Specific questions to be addressed can include:
- What service portfolio shall be offered and at what price, respectively how shall costs be predicted? (ROLSTADAAS ET AL., 2008)
- There will be a broad range of customer questions and issues to be solved. Therefore, how shall the complexity be addressed best? Respectively, shall contact be possible online, on the phone or in person? (USERLIKE, 2016)
- How shall the after-sales deal best with customer complaints?
- How to align the spare parts distribution with the supply chain in place? (ROLSTADAAS ET AL., 2008)
- How long shall the warranty prevail?
- What shall be the price for services when warranty ends? (KOKEMULLER, 2018)
- Shall products be replaced during the reparation process?
4. Analyse after-sales process: To be able to improve the implemented after-sales services over time, the processes in place shall be analysed and monitored to see whether they comply with the set objectives. Based on these results, the after-sales process can be improved. A methods to analyse the implemented after-sales processes can be Service Blueprints or Value Stream Mapping. Service Blueprints map how services are delivered and where the interaction with the customer takes place. Executed consistently it will help identifying gaps in service delivery and customer orientation and improve the entire sales process. (see factsheet on value creation).
5. Optimise and adjust after-sales process: By adjusting the after-sales process according to the results of your process analyses a steady improvement and optimization of after-sales process is possible.
The case study about Hydrologic provides subsequently insights on how the after-sales process of the ceramic water filter manufacturer evolved over time.
Subscribe here to the new Sanitation and Water Entrepreneurship Pact (SWEP) newsletter. SWEP is a network of organizations joining hands to help entrepreneurs design and develop lasting water and sanitation businesses.
The case study of how Hydrologic designed and implemented its after-sales scheme provides practical insights and lessons learnt to inspire other safe water initiatives’ development of an after-sales process.
Managing After-Sales Services
Focus group research method
Sustainability and Scale-up of Household Water Treatment and safe Storage Practices: Enablers and Barriers to effective Implementation
This paper provides insights from the ground on scaling up sales of household water treatment products (HWTS). The data collected is based on interviews carried out in over 25 countries. 47 enabling factors as well as barriers were identified to sustaining and scaling up HWTS. The findings were clustered as: user guidance on HWTS products; resource availability; standards, certification and regulations; integration and collaboration; user preferences; and market strategies.
OJOMO, E. et al. (2015): Sustainability and Scale-up of Household Water Treatment and safe Storage Practices: Enablers and Barriers to effective Implementation. In: International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health: Volume 218 , 704–713. URL [Accessed: 23.07.2018] PDFAfter-sales service quality as an antecedent of customer satisfaction
Review of After-Sales Service Concepts
Global Value Chains in a Changing World
Sustainability and Scale-up of Household Water Treatment and safe Storage Practices: Enablers and Barriers to effective Implementation
This paper provides insights from the ground on scaling up sales of household water treatment products (HWTS). The data collected is based on interviews carried out in over 25 countries. 47 enabling factors as well as barriers were identified to sustaining and scaling up HWTS. The findings were clustered as: user guidance on HWTS products; resource availability; standards, certification and regulations; integration and collaboration; user preferences; and market strategies.
OJOMO, E. et al. (2015): Sustainability and Scale-up of Household Water Treatment and safe Storage Practices: Enablers and Barriers to effective Implementation. In: International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health: Volume 218 , 704–713. URL [Accessed: 23.07.2018] PDF

