About this perspective
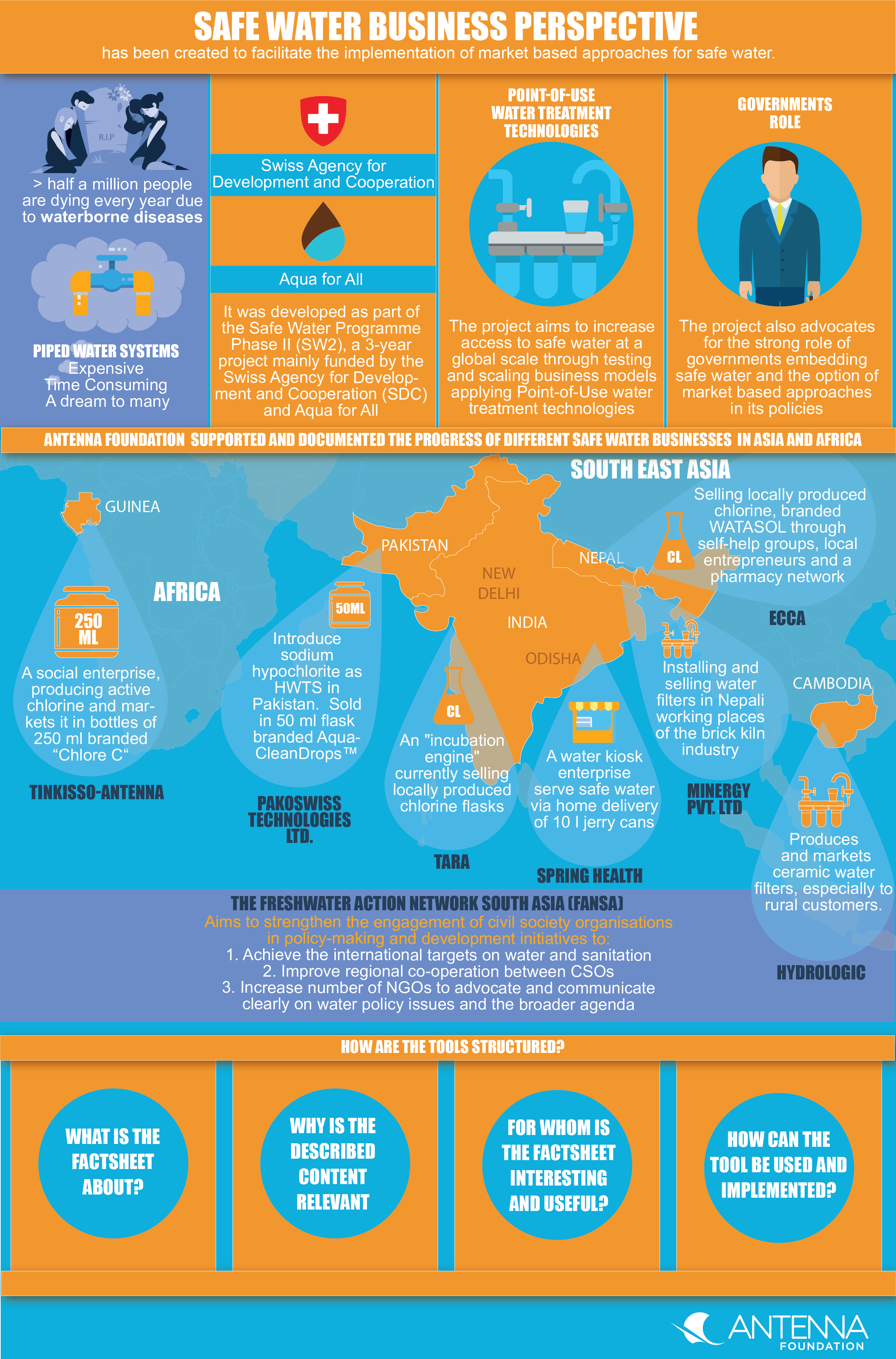
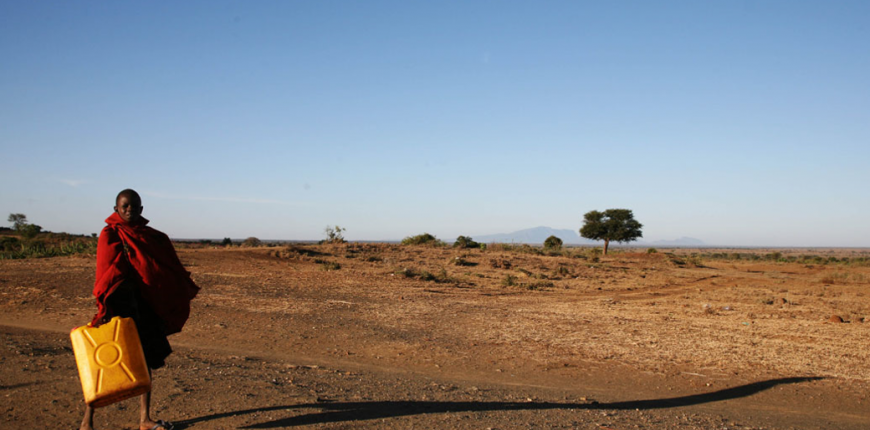
Still more than half a million people are dying every year due to waterborne diseases, as billions do drink water that is biologically and/or chemically contaminated. Having piped water systems delivering safe drinking water directly to people’s homes is still a dream for many. The construction of decent water and sewage infrastructure is expensive, time-consuming and not likely possible to achieve within a short period of time. Thinking out of the box and looking for diverse solutions that allow safe drinking water at the Point-of-Use could make it possible to reach everyone with safe water. Therefore this Safe Water Business Perspective has been created to facilitate the implementation of market based approaches for safe water.
The Safe Water Business Perspective project has been developed as part of the Safe Water Programme Phase II (SW2), a 3-year project mainly funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) and Aqua for All. The project aims to increase access to safe water at a global scale through testing and scaling business models applying Point-of-Use water treatment technologies. The project also advocates for a strong role and responsibility of governments embedding safe water and the option of market based approaches in its policies. Antenna Foundation coordinated this project and supported and documented the progress of different safe water businesses in Asia and Africa. The exhaustive list of business initiatives comprehends ECCA and MinErgy in Nepal, PakoSwiss in Pakistan, Spring Health and TARA in India, Tinkisso-Antenna in Guinea, and Hydrologic in Cambodia. The learnings and progress of these businesses are included in the Safe Water Business Perspective in form of case studies and lessons learnt.
Hydrologic is a social enterprise legally registered in Cambodia. The social enterprise evolved from an NGO project initiated by iDE in 2001. Hydrologic produces and markets two ceramic water filters (Tunsai and Super Tunsai) in Cambodia, especially to rural customers assuring them to have safe water. The innovative business model includes instruments such as instalment based payments, in-house after-sales services and sales of carbon credits for additional revenue generation.
Spring Health is a water kiosk enterprise active in rural Odisha, India since 2008. People are served with safe water at the doorstep via home delivery of 10 l jerry cans. The innovative business model reaches to over 200 rural villages and creates additional revenues by selling carbon credits.
The Society for Technology & Action for Rural Advancement (TARA) is a social enterprise set up in the year 1982 at New Delhi, India. It is an "incubation engine" of the Development Alternatives Group which has been providing development solutions in India and elsewhere. Currently micro-franchisees are selling locally produced chlorine flasks, branded Aqua+™ to rural BoP customers to assure safe drinking water at the household level.
MinErgy Pvt. Ltd. was registered in 2008 as a service-oriented company for the production and marketing of environmentally sound, cost effective technologies that would generate livelihoods. Today MinErgy is installing and selling water filters in Nepali working places of the brick kiln industry. The enterprise offers in addition a maintenance service to assure urban and rural water systems to continuously provide safe water.
Environmental Camps for Conservation Awareness (ECCA), established in 1987 in Kathmandu, Nepal, is an environmental organization that focuses on raising awareness through young people in schools, as pupils provide excellent communication channels with communities. ECCA aims to improve access to drinking water in schools and communities in central and eastern Nepal, through an entrepreneurial approach, selling locally produced chlorine, branded WATASOL through self-help groups, local entrepreneurs and a pharmacy network.
Tinkisso-Antenna established in 2007, is a Guinea-based social enterprise, producing active chlorine and markets it in bottles of 250 ml branded “Chlore C“. Tinkisso applies a diversified distribution strategy with direct sales to urban communities, through a reseller network in collaboration with pharmacies, NGOs, governmental institutions and multilateral organisations. Its sales are highly supported through its innovative social marketing campaigns.
Pakoswiss Technologies Ltd. is a social enterprise established in 2013 to take up the challenge of introducing sodium hypochlorite as HWTS in Pakistan. The locally produced chlorine is sold in 50 ml flask branded AquaCleanDrops™ to make disinfectants readily available and affordable for BoP customers in the cities of Islamabad and Rawalpindi, Pakistan.
Particularly for the implementation of the Human Right to Water and Sanitation SW2 has been collaborating with FANSA: The Freshwater Action Network South Asia (FANSA) aims to strengthen the engagement of civil society organisations in policy-making and development initiatives to achieve the international targets on water and sanitation, improve regional co-operation between CSOs of differing perspectives, priorities and skills and increase the number of NGOs to advocate and communicate clearly on water policy issues and the broader agenda. FANSA has been working in India, Pakistan and Nepal to engage CSOs and the government in discussing access to safe water and inclusion of it in national regulations.
How are the tools structured?
The factsheets are outlined applying the following structure:
What is the factsheet about?
The “what-section” provides a description of the scope and content the factsheet is emphasizing and explains the underlying concept and tools.
Why is the described content relevant?
Explains the purpose of the factsheet and elaborates on what problems and opportunities it addresses, and what the users’ benefits are from implementing the described tool(s).
For whom is the factsheet interesting and useful?
This part explains what audience the factsheet addresses and whom it is explicitly useful for.
How can the tool be used and implemented?
This part describes one or more methodologies of how the addressed topic can be used/ implemented in practice. It also provides an overview of helpful resources for implementation, such as checklists and templates among others.
Who are the funding partners?
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (70% of the total budget)
Aqua for All, Antenna Foundation, IRCWash and FANSA (30% of the total budget)
Created by
| Antenna Foundation is a Swiss Foundation that develops technological, health and commercial solutions in partnership with universities, non-profit organizations and private companies to meet the basic needs of marginalized populations in developing countries. Antenna coordinates the Safe Water Programme Phase II (SW2), a 3-year project funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) and Aqua for All. |  |
| Aqua for All is a non-profit organization established in 2002 by the Dutch water sector. Aqua for All is a well-known source of expertise on water, sanitation and hygiene-related challenges, offering a broad range of services to the public and private sector. With its business-like, efficient and result-oriented approach, the organization inspires and supports its stakeholders to help the world’s Base of the Pyramid gain sustainable access to safe water and adequate sanitation. |  |
| EAWAG is a world-wide leading institute for research, education, and expert consulting in aquatic science and technology. Parts of the social science department of EAWAG are researching business model developments around water and sewage and have been supprting the project with its wide range of expertise. |  |
| Freshwater Action Network South Asia (FANSA) aims to strengthen the engagement of civil society organisations in policy-making and development initiatives to achieve the international targets on water and sanitation. This goal is pursued by improving regional co-operation between civil society organisations (CSOs) of differing perspectives. Under SW2 FANSA has been working in India, Pakistan and Nepal to engage CSOs and the government in discussing access to safe water and including it in respective national regulations. |  |
| IRC is an NGO based in the Netherlands and active in countries in Africa, Latin America and Asia with the vision of a world where no child or adult dies of causes related to water or sanitation. A world where everyone has access to safe and reliable WASH services, forever. IRC is working with national and local governments, with NGOs and businesses, and with local communities to realize this ambitious vision. |  |
| The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) is the agency for international cooperation of the Swiss Federal Department of Foreign Affairs (FDFA). The SDC aims to contribute to a world without poverty and in peace, for sustainable development. It fosters economic self-reliance and state autonomy, contributes to the improvement of production conditions, helps address environmental problems, and ensures better access to education and basic healthcare services. |  |
Designed and implemented by: Seecon GmbH Reviewed, editing and coordination: Louise Carpentier Upload: Ruweida Al-Jabali, Franka Voss |  |










