Community contributions such as user fees, household investments, community-based savings and cost sharing are a major source for financing sustainable sanitation and water management products and services. These contributions are important, because sanitation and water systems will only be improved if community members are interested and willing to invest accordingly. This section will concentrate mainly on community-based savings. This is an effective method for saving a small amount of money by organising or joining a saving group of up to 25 people. These people might be colleagues, friends or neighbours coming from the same community. The method is very simple and easy to implement.
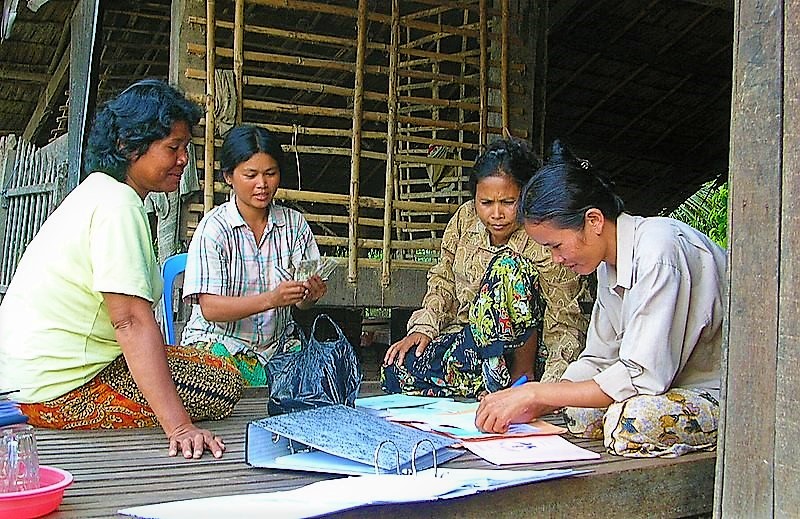

Community-based saving is a microfinance model that is considered to be an effective method for financing projects in sustainable sanitation and water management. Community-based saving is currently introduced in many developing countries to help particularly poor rural communities to save money by organising so-called community-based saving groups.
The basic objective of a community saving group is to encourage and create a saving culture in the community. Thereby, economic security is increased and financial services are brought closer to communities for promoting secure investment with savings (LUPP n.y.). The group can further decide to focus on savings or to also engage in giving loans to its members. In most cases, the group also engages in giving loans. Therefore, joining the saving group offers a unique opportunity for the household. It enables investments in water and sanitation services to ensure better healthcare (see water sanitation and health) for the whole family.
(Adapted from LUPP n.y.)
Community-based saving groups are either implemented by the group itself or with the support of local NGOs. The implementation of a community-based savings group consists of four phases. If the community members build up the group on their own, the first two steps are enough to consider. However, if there is support from an NGO, all four steps are important to follow through. The 4 phases are the following:
1. Introduction Phase:
The objective of the first step is to identify the participants or the members and facilitate the information of groups who become familiar with the basic characteristics of the community saving methodology and register within the group.
2. Intensive Phase:
In the second phase, the aim is to train and organise the group. In this phase the group establishes a management committee, sets up internal rules, and defines the objectives of the group.
- Establishing management committee: election of a leader, accountant, treasurer and assistant to the accountant.
- Setting up internal rules: How often a month does the group meet? Is the participation of members a must? What if somebody does not attend a meeting? What is the maximum fixed amount of money that can be invested? Where should money be kept to ensure safety? etc.
- Defining the objectives of the group: Does the group engage only in savings or also give small loans to members? If the group can engage in giving small loans, should an interest rate be charged for the loan? And if yes, how much should the interest rate be? What is the maximum loan period? etc.
After the group has appointed persons in charge of managing finances and the group, after it has set the objectives, developed rules and agreed on all conditions, the savings process can begin.
3. Development Phase:
The aim of the third phase is to help the group become autonomous. The support organisation should only intervene if the group needs any help or consultation.
4. Maturity Phase:
This phase is important to help the group to become independent of the project. In this phase, evaluation is conducted and based on evaluation it is decided whether the group can work independently or needs further assistance.
After the savings period ends, the members of the community saving groups can use the opportunity to invest in improving their water and sanitation conditions.
- For ensuring safety and to avoid trouble, the group must give thought to where the money should be saved. The money can either be kept in a cash box with a responsible person or deposited in the nearest bank.
- Assigning responsible people (with basic accounting skills) for managing the account is crucial.
- Members should all have membership books where investments are recorded to avoid any disputes.
Community-based saving groups are applicable almost everywhere, despite varying conditions in different communities. They are found both in rural as well as urban areas, where access to formal and affordable financial services is limited or lacking.
Community-based Microfinance: Community Savings and Loan Groups. Good practice in the musseques of Luanda
This document shows how community saving and loan groups work and provides examples of such groups in Luanda.
LUPP (n.y): Community-based Microfinance: Community Savings and Loan Groups. Good practice in the musseques of Luanda. Luanda Urban Poverty Programme (LUPP) URL [Accessed: 18.08.2011]Community-based savings bank in Cambodia
Local Financing Mechanisms for Water Supply. Background Report for WELL
This paper shows how local microfinance activities such as revolving funds, community rotating savings and credit associations (ROSCAS) work for improving water and sanitation in Ghana. In addition, other examples of local microfinance mechanisms for water and sanitation from Cambodia, Uganda, Cote d'Ivoire and India are provided.
AGBENORHERI, M. FONESKA, C. (2005): Local Financing Mechanisms for Water Supply. Background Report for WELL. URL [Accessed: 23.06.2019]Saving Groups: What are they? The SEEP Network Savings-Led Financial Services Working Group
This document describes the basic model of saving groups, its origin and variation in saving methodology. It also explains how these groups complement microfinance and provides lessons for the replication of the model.
ALLEN, H. PANETTA, D. (2010): Saving Groups: What are they? The SEEP Network Savings-Led Financial Services Working Group. The Small Enterprise Education and Promotion Network (SEEP) URL [Accessed: 21.06.2019]Community-based Microfinance: Community Savings and Loan Groups. Good practice in the musseques of Luanda
This document shows how community saving and loan groups work and provides examples of such groups in Luanda.
LUPP (n.y): Community-based Microfinance: Community Savings and Loan Groups. Good practice in the musseques of Luanda. Luanda Urban Poverty Programme (LUPP) URL [Accessed: 18.08.2011]Urban Community-based-Savings-and-Credit Systems in Cambodia, Lao People's Democratic Republic and Vietnam
This document provides information on saving mechanisms such as community-based saving and credit groups in Cambodia, savings and credit systems in Laos and the history of saving and credit programs in Vietnam
ESCAP UN (n.y): Urban Community-based-Savings-and-Credit Systems in Cambodia, Lao People's Democratic Republic and Vietnam. Economic and Social Commission for Asia and Pacific (ESCAP) URL [Accessed: 21.06.2019]Conservation Funds and Community Financing
This document is about community savings through Village Organisations (VOs) in Pakistan that are responsible for implementing different development projects.
HUSSAIN, A. (2003): Conservation Funds and Community Financing. World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), Pakistan URL [Accessed: 21.06.2019]A $ 0,14 toilet in a month: Financing Urban Eco-Sanitation through Group Savings in Malawi
This case shows how the members of Malawi Homeless People's Federation make monthly savings of at least 0,14 USD towards a pool fund called Mchenga fund. It finances their development needs according to the priorities of the members.
KHATAZA, R. (2008): A $ 0,14 toilet in a month: Financing Urban Eco-Sanitation through Group Savings in Malawi. Malawi: Centre for Community Organisation and Development (CCODE) URL [Accessed: 21.06.2019]What we do - WaterAid Malawi
This website provides information on savings for sanitation and other investments in Malawi.