Depending on the end-use of the effluent or national standards for discharge in water bodies, a post-treatment step may be required to remove pathogens, residual suspended solids and/or dissolved constituents. Tertiary filtration and disinfection processes are most commonly used to achieve this.
Post-treatment is not always necessary and a pragmatic approach is recommended. The effluent quality should match the intended end-use practice or the quality of the receiving water body. The WHO Guidelines for the Safe Use of Wastewater, Excreta and Greywater (see also Volume I, III and IV) provide useful information on the assessment and management of risks associated with microbial hazards and toxic chemicals.
Among a wide range of tertiary and advanced treatment technologies for effluent, the most widespread include tertiary filtration and disinfection processes.
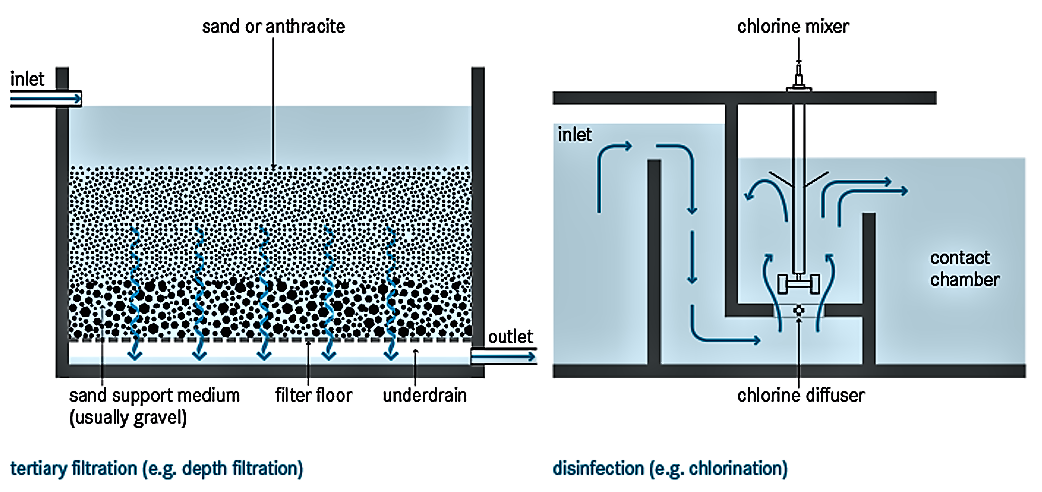
Filtration processes can be classified as either depth (or packed-bed) filtration or surface filtration processes. Depth filtration involves the removal of residual suspended solids by passing the liquid through a filter bed comprised of a granular filter medium (e.g., sand).
If activated carbon is used as a filter medium, the dominating process is adsorption. Activated carbon adsorbers not only remove a variety of organic and inorganic compounds, they also eliminate taste and odour. Surface filtration involves the removal of particulate material by mechanical sieving as the liquid passes through a thin septum (i.e., filter layer). Membranes are also surface filters. Low pressure membrane filtration processes (including gravity-driven membrane filters) are being developed. Depth filtration is successfully used to remove protozoan cysts and oocysts, while ultrafiltration membranes can also reliably eliminate bacteria and viruses.
The destruction, inactivation, or removal of pathogenic microorganisms can be achieved by chemical, physical, or biological means. Due to its low cost, high availability and easy operation, chlorine has historically been the disinfectant of choice for treating wastewater.
Chlorine oxidizes organic matter, including microorganisms and pathogens (see also drinking water chlorination). Concerns about harmful disinfection by-products (DBP) and chemical safety, however, have increasingly led to chlorination being replaced by alternative disinfection systems, such as (UV) radiation and ozonation (O3). UV radiation is found in sunlight and kills viruses and bacteria (see also drinking water UV disinfection or SODIS).Thus, disinfection naturally takes place in shallow ponds (see also waste stabilisation ponds). UV radiation can also be generated through special lamps, which can be installed in a channel or pipe.
Ozone is a powerful oxidant and is generated from oxygen in an energy-intensive process. It degrades both organic and inorganic pollutants, including odour-producing agents. Similar to chlorine, the formation of unwanted by-products is one of the problems associated with the use of ozone as a disinfectant.
With both chlorine and ozone disinfection, by-products may form and threaten environmental and human health. There are also safety concerns related to the handling and storage of liquid chlorine. Activated carbon adsorption and ozonation can remove unpleasant colours and odours, increasing the acceptance of reusing reclaimed water.
All post-treatment methods require continuous monitoring (influent and effluent quality, head loss of filters, dosage of disinfectants, etc.) to ensure a high performance.
Due to the accumulation of solids and microbial growth, the effectiveness of sand, membrane and activated carbon filters decreases over time. Frequent cleaning (backwashing) or replacement of the filter material is, therefore, required. For chlorination, trained personnel are required to determine the right dosage of chlorine and ensure proper mixing. Ozone must be generated onsite because it is chemically unstable and rapidly decomposes to oxygen. In UV disinfection, the UV lamp needs regular cleaning and annual replacement.
The decision to install a post-treatment technology depends mainly on the quality requirement for the desired end-use of the effluent and/or national standards. Other factors are the effluent characteristics, budget, availability of materials, and O&M capacity.
Pathogens tend to be masked by suspended solids in unfiltered secondary effluent. Therefore, a filtration step prior to disinfection brings about much better results with fewer chemicals.
Membrane filters are costly and require expert know-how for O&M, especially, to avoid damaging the membrane. In activated carbon adsorption the filter material is contaminated after usage and needs proper treatment/disposal. Chlorine should not be used if the water contains significant amounts of organic matter, as disinfection by-products can form. Ozonation costs are generally higher compared to other disinfection methods.
Ultraviolet Disinfection. Guidelines for Drinking Water and Water Reuse
This document describes in detail dose, design, operation & maintenance, field commissioning and monitoring of UV disinfection for drinking water and reuse water.
NWRI (2012): Ultraviolet Disinfection. Guidelines for Drinking Water and Water Reuse. Fountain Valley (US): National Water Research Institute (NWRI) and Water Research Foundation (WRF) URL [Accessed: 20.03.2014]How to Design Wastewater Systems for Local Conditions in Developing Countries
This manual provides guidance in the design of wastewater systems in developing country settings. It promotes a context-specific approach to technology selection by guiding the user to select the most suitable technologies for their area. It provides tools and field guides for source characterization and site evaluation, as well as technology identification and selection. This manual is primarily addressed to private and public sector service providers, regulators and engineers/development specialists in charge of implementing wastewater systems.
ROBBINS, D.M. LIGON, G.C. (2014): How to Design Wastewater Systems for Local Conditions in Developing Countries. London: International Water Association (IWA) URL [Accessed: 20.01.2015]SSWM Toolbox: Water Purification
Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Reuse
Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume II. Wastewater Use in Agriculture
Volume II of the Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and greywater provides information on the assessment and management of risks associated with microbial hazards and toxic chemicals. It explains requirements to promote the safe use of wastewater in agriculture, including minimum procedures and specific health-based targets, and how those requirements are intended to be used. It also describes the approaches used in deriving the guidelines, including health-based targets, and includes a substantive revision of approaches to ensuring microbial safety.
WHO (2006): Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater excreta and greywater. Volume II. Wastewater Use in Agriculture. Geneva: World Health Organisation URL [Accessed: 05.06.2019] PDF