Participatory planning requires the involvement of concerned stakeholders. This includes identifying public concerns and values and developing a broad consensus on planned initiatives. It is also about utilising the vast amount of information and knowledge that stakeholders hold to find workable, efficient and sustainable solutions (CAP-NET 2008). The stakeholder analysis is the process of identifying and analysing stakeholders, and plan for their participation (RIETBERGEN-McCRACKEN et al. 1998). There are a great number of methodologies concerning stakeholder analysis with a wide range of complexity (see e.g. RIETBERGEN-McCRACKEN et al. 1998; NETSSAF 2008; CAP-NET 2005). Here, we present a four-step methodology, that can be done fully or shortened according to one’s needs: (1) Stakeholder identification, (2) Stakeholders’ importance and influence (3) Stakeholder interests and (4) Stakeholder strategy plan. After identification, the next step is about analysing how important it is that certain stakeholders are involved, and about the degree of influence and power a stakeholder has to affect the outcome of an initiative.
Stakeholders must play a central role in setting up priorities and objectives of water and sanitation initiatives in order to ensure relevance and appropriateness. It is important that all stakeholders are involved in the development of projects and not just direct beneficiaries of an initiative.
When planning a strategy (see this category on Decision Making section) on which stakeholders to involve into the decision making (see PPT) process and how to communicate, cooperate and associate with them, it is worthwhile to find out more about the stakeholder characteristics.
This will later on help to attribute roles and responsibilities to different stakeholders so that the implementation is successful and so that no conflicts arise between the stakeholders.
Firstly, the degree of importance of the stakeholders is analysed, i.e., the degree how much somebody is concerned by an initiative.
Importance means the priority given to satisfying stakeholders’ needs and interests from being involved in the design of the project and in the project itself in order for it to be successful. In other words, this is about how important or essential is it that certain stakeholders are involved (WORLD AGROFORESTRY CENTER 2003).
Secondly, influence and power of a stakeholder can affect the success or failure of an initiative. Power refers to the ability of the stakeholder to affect the implementation of a project due to his or her strength or force (WINDBERG 2009). Power can be important in terms of supporting as well as in terms of constraining an initiative. For the success of an initiative, it is very important know whether (and how) a stakeholder can take action, how he/she can be involved, and how much capacity he/she has to contribute. Concerning failures, it is important know the possible (negative) influence a stakeholder has to constrain or even stop an initiative.
Subscribe here to the new Sanitation and Water Entrepreneurship Pact (SWEP) newsletter. SWEP is a network of organizations joining hands to help entrepreneurs design and develop lasting water and sanitation businesses.
There are different ways answer these questions (depending on the timeframe, e.g.). A short and effective way to categorise stakeholders for their importance and influence is the development of a “stakeholder importance and influence matrix”.
Draw the matrix below on a large flipchart. Write the name of each stakeholder included in the list made already on a separate card or ‘Post-it’ and stick the cards on the matrix according to the participants’ view of each stakeholder’s relative importance and influence (don’t use glue, or it will be difficult to move them around). Don’t worry about locating them exactly, since this is by nature a rather subjective exercise. Once all the cards are in place, stand back and have a look. If necessary, move some of the cards around until a consensus is reached. Then read the comments below about the relevance of each box.
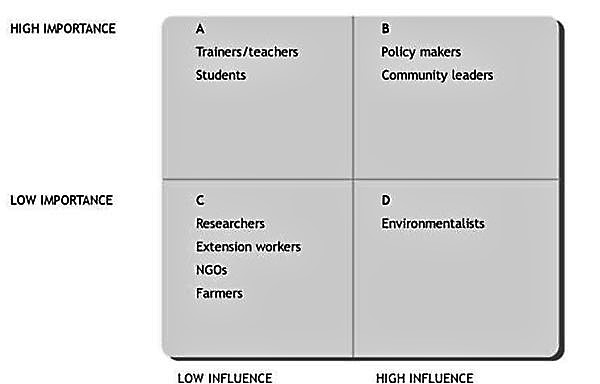
BOX A: This group will require special initiatives to protect their interests.
BOX B: A good working relationship must be created with this group.
BOX C: This group may be a source of risk, and will need careful monitoring and management.
BOX D: This group may have some limited involvement in evaluation but are, relatively, of low priority.
(WORLD AGROFORESTRY CENTER 2003)
Sometimes, it is worth also to further think about the reasons why stakeholders are important and have a certain influence and to keep this recorded. This helps planners not to forget important aspects of different stakeholders and to get a deeper insight of different stakeholder perspectives to better understand them. In particular in SSWM, where stakeholder interests and potential conflicts are often complex and many-sided, it can be worthwhile to take this time to understand stakeholder relations and importance and hence to avoid conflicts and implementation failures.
A simple possibility to develop qualitative information about stakeholder’s importance and influence is to list the main aspects why they are important and can influence the initiative and to add this information to the previously developed stakeholders list.
<----- Go back to Step 1: stakeholder identification
Continue with analysing -----> Step 3: stakeholder interests
Or see also:
-----> Step 4: stakeholder strategy plan
Knowing about the importance and influence of stakeholders is essential for the formulation of the stakeholder strategy plan (see next step) as well as for the future participatory decision-making. It contributes to gain an understanding how to associate with stakeholders in a certain way and how to avoid conflicts.
Integrated Water Resources Management Plans. Training Manual and Operational Guide
The Cap-Net manual is an introduction to essential parts of integrated water resource management (IWRM). Chapter 2 consists of management planning for IWRM, which provides good information about stakeholder process as well.
CAP-NET (2005): Integrated Water Resources Management Plans. Training Manual and Operational Guide. Pretoria: Cap-Net URL [Accessed: 30.06.2019]Integrated Water Resource Management for River Basin Organisations. Training Manual
Capacity Building for Ecological Sanitation
This publication deals with the educational aspects linked to ecologically sustainable sanitation, and contains extensive chapters on capacity building and knowledge management in the field of ecological sanitation.
UNESCO/IHP ; GTZ (2006): Capacity Building for Ecological Sanitation. Paris & Eschborn: German Agency for Technical Cooperation (GTZ) & International Hydrological Programme of UNESCO (UNESCO/IHP) URL [Accessed: 15.04.2019]NETSSAF Participatory Planning-Approach
This is the actual tutorial of the participative planning approach developed by NETSSAF, containing all the steps, sub-steps and case studies. It is freely available on the internet in French and English.
NETSSAF (2008): NETSSAF Participatory Planning-Approach. A tutorial for sustainable sanitation planning. Network for the Development of Sustainable Approaches for Large Scale Implementation of Sanitation in Africa (NETSSAF). [Accessed: 29.03.2010] PDFGuidance Note on how to do Stakeholder Analysis of Aid Projects and Programmes
This guidance note provides a step-by-step manual on how to do a stakeholder analysis. Effective strategies for stakeholder participation must be based on good analysis of individuals, groups, and institutions with an interest in a project.
ODA (1995): Guidance Note on how to do Stakeholder Analysis of Aid Projects and Programmes. London: Overseas Development Department (ODA) URL [Accessed: 30.06.2019]Strategy Development for Successful Implementation of Ecological Sanitation Approaches in Sri Lanka using Stakeholder Analysis. Report 3 of 3 from "Evaluation of the Appropriateness of Ecological Sanitation in Relation to the Social, Cultural and Economic
The presented stakeholder analysis provides the necessary information to develop strategies for the successful implementation of ecological sanitation approaches in Sri Lanka.
WINDBERG (2009): Strategy Development for Successful Implementation of Ecological Sanitation Approaches in Sri Lanka using Stakeholder Analysis. Report 3 of 3 from "Evaluation of the Appropriateness of Ecological Sanitation in Relation to the Social, Cultural and Economic. Paris: UNICEF URL [Accessed: 18.08.2010]Carrying Out a Stakeholder Analysis
Participation and Social Assessment: Tools and Techniques
This resource kit aims to share information and experiences on participatory methods in the context of development cooperation. The primary focus concentrates on providing practical guidance and case examples.
RIETBERGEN-McCRACKEN, J. NARAYAN, D. WORLD BANK (1998): Participation and Social Assessment: Tools and Techniques. Washington: World Bank URL [Accessed: 10.05.2010]Guidance Note on how to do Stakeholder Analysis of Aid Projects and Programmes
This guidance note provides a step-by-step manual on how to do a stakeholder analysis. Effective strategies for stakeholder participation must be based on good analysis of individuals, groups, and institutions with an interest in a project.
ODA (1995): Guidance Note on how to do Stakeholder Analysis of Aid Projects and Programmes. London: Overseas Development Department (ODA) URL [Accessed: 30.06.2019]Good Practices in Participatory Mapping
This report explores the power of participatory mapping. Covering a range of techniques, intermediaries, tools and impacts, it is shown how a systematic approach could contribute to addressing conflict-related issues and improving community ownership in sustainable environmental and natural resource management.
IFAD (2009): Good Practices in Participatory Mapping. Rome: International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) URL [Accessed: 04.05.2010]Integrated Water Resources Management Plans. Training Manual and Operational Guide
The Cap-Net manual is an introduction to essential parts of integrated water resource management (IWRM). Chapter 2 consists of management planning for IWRM, which provides good information about stakeholder process as well.
CAP-NET (2005): Integrated Water Resources Management Plans. Training Manual and Operational Guide. Pretoria: Cap-Net URL [Accessed: 30.06.2019]Capacity Building for Ecological Sanitation
This publication deals with the educational aspects linked to ecologically sustainable sanitation, and contains extensive chapters on capacity building and knowledge management in the field of ecological sanitation.
UNESCO/IHP ; GTZ (2006): Capacity Building for Ecological Sanitation. Paris & Eschborn: German Agency for Technical Cooperation (GTZ) & International Hydrological Programme of UNESCO (UNESCO/IHP) URL [Accessed: 15.04.2019]NETSSAF Participatory Planning-Approach
This is the actual tutorial of the participative planning approach developed by NETSSAF, containing all the steps, sub-steps and case studies. It is freely available on the internet in French and English.
NETSSAF (2008): NETSSAF Participatory Planning-Approach. A tutorial for sustainable sanitation planning. Network for the Development of Sustainable Approaches for Large Scale Implementation of Sanitation in Africa (NETSSAF). [Accessed: 29.03.2010] PDFParticipation and Social Assessment: Tools and Techniques
This resource kit aims to share information and experiences on participatory methods in the context of development cooperation. The primary focus concentrates on providing practical guidance and case examples.
RIETBERGEN-McCRACKEN, J. NARAYAN, D. WORLD BANK (1998): Participation and Social Assessment: Tools and Techniques. Washington: World Bank URL [Accessed: 10.05.2010]Getting communities engaged in water and sanitation projects: participatory design and consumer feedback
Community engagement in water and sanitation service delivery is key for ensuring project sustainability and accountability. This Topic Brief looks at community engagement approaches used by WSUP in three cities within the African Cities for the Future (ACF) programme: Antananarivo (Madagascar), Kumasi (Ghana) and Maputo (Mozambique). The Topic Brief highlights some of the key challenges, and ends with practical recommendations for programme managers about how to engage low-income communities in the design of water supply and sanitation projects.
WSUP (2013): Getting communities engaged in water and sanitation projects: participatory design and consumer feedback. London: Water & Sanitation for the Urban Poor (WSUP) URL [Accessed: 30.06.2019]Strategy Development for Successful Implementation of Ecological Sanitation Approaches in Sri Lanka using Stakeholder Analysis. Report 3 of 3 from "Evaluation of the Appropriateness of Ecological Sanitation in Relation to the Social, Cultural and Economic
The presented stakeholder analysis provides the necessary information to develop strategies for the successful implementation of ecological sanitation approaches in Sri Lanka.
WINDBERG (2009): Strategy Development for Successful Implementation of Ecological Sanitation Approaches in Sri Lanka using Stakeholder Analysis. Report 3 of 3 from "Evaluation of the Appropriateness of Ecological Sanitation in Relation to the Social, Cultural and Economic. Paris: UNICEF URL [Accessed: 18.08.2010]Stakeholder Analysis
This short PowerPoint presentation explains in a brief way how to do a stakeholder analysis and also contains empty tables that can be directly used for analysing stakeholders.
PUBLIC SECTOR IMPROVEMENT FACILITY (n.y): Stakeholder Analysis. URL [Accessed: 30.06.2019]10 Keys for Local and National Action
Ten key points that are prerequisite for successful municipal wastewater management. They cover policy issues, management approaches, technology selection and financing mechanisms.
UNEP ; WHO ; UN-HABITAT ; WSSCC (2003): 10 Keys for Local and National Action . The Hague: United Nations Environment Programme Global Programme of Action (UNEP/GPA), Coordination Office URL [Accessed: 30.06.2019]Carrying out a stakeholder analysis
This is a very practical, concise and easy to understand set of online guidelines for planning and running training courses. Although the training approaches and techniques described here are based soundly on the sciences of pedagogy and education, they also reflect the practical side of field work in the developing world.